Are level 1 chargers bad for my EV battery?
Level 1 EV chargers, also known as standard household outlets, offer a convenient and accessible way to charge your electric vehicle. However, concerns have been raised about their potential negative impact on battery health.
While Level 1 chargers deliver a slow and steady charge, minimizing stress on the battery, their extended charging times can lead to higher temperatures, potentially accelerating battery degradation.
Additionally, the repeated plugging and unplugging associated with Level 1 charging can increase wear and tear on the charging port.

Understanding Level 1 Chargers and Battery Health
Level 1 chargers are basic electric vehicle (EV) charging devices designed to operate on standard household electrical outlets with a 120-volt AC power supply.
These chargers typically consist of a power cord with a plug that can be inserted into a standard electrical outlet, and a connector on the other end that plugs into the EV’s charging port.
When connected, the Level 1 charger draws power from the electrical outlet and delivers it to the vehicle’s onboard charger. The onboard charger then converts the AC power into the DC power required to charge the EV’s battery.
Drawbacks of Level 1 Chargers for EV Battery Health:
Level 1 chargers are generally safe for battery health when used properly. However, there’s one potential drawback to consider.
Stress at Low Charge: If you constantly leave your EV plugged into a Level 1 charger at a low charge level (e.g., below 20%), it might increase stress on the battery over time. This is because batteries experience more stress when constantly maintaining a low charge or a full charge.
For optimal battery health, it’s recommended to:
- Avoid constantly leaving your EV plugged in, especially at low charge.
- Unplug your car once it reaches the desired charge level.
- If possible, utilize timer-controlled charging to top off the battery shortly before you need to depart.
Following these practices can help maintain optimal battery health and extend the lifespan of your electric vehicle.

Impact of Charging Habits
1. Understanding Battery Degradation with Level 1 Chargers:
While Level 1 chargers provide a slower charging rate, the bigger impact on battery health often comes from your charging habits, not the charger type itself. Level 1 chargers themselves do not inherently degrade batteries more than other charging methods.
Consistently charging an EV to high or low states of charge, as well as leaving it plugged in at low charge levels for extended periods, can contribute to accelerated battery degradation. Here’s why:
- Battery Stress and Charge Levels: Electric vehicle batteries experience more stress when constantly maintained at extreme charge levels, either too high (above 80%) or too low (below 20%) for extended periods.
- Level 1 Charging and Daily Use: If you use Level 1 charging for your daily top-ups and keep your battery within a healthy range (20% to 80%), it won’t significantly accelerate battery degradation.
2. Managing Charging Cycles to Preserve EV Battery Life:
To preserve your EV battery’s health and maximize its lifespan, focus on these practices:
- Avoid Extreme Charge Levels: Whenever possible, avoid keeping your battery fully charged for long durations (overnight charging at 100% every night). Likewise, try not to let it deplete to very low levels before plugging in.
- Avoiding deep discharges: Aim for shallower charging cycles. Instead of letting the battery completely drain and then charging to 100%, focus on more frequent top-ups within the recommended 20% to 80% range.
- Minimizing exposure to high temperatures: High temperatures can accelerate battery degradation, so avoid charging in extreme heat and minimize exposure to prolonged periods of high temperatures.
3. Utilizing Level 1 Chargers as a Backup Charging Solution:
Level 1 chargers can serve as a convenient backup charging solution, particularly for occasional charging or topping off the battery. Using Level 1 chargers sparingly and for short durations can help minimize the negative impacts of constant low-level charging on battery health.
- Minimizing Constant Low-Level Charging: If you only use Level 1 for topping off the battery before short trips, it minimizes the time spent at low charge levels, reducing potential stress on the battery.
- Complementing Level 2 Charging: If you have a Level 2 charger installed at home for everyday charging, using Level 1 occasionally for short top-ups can be a good strategy to manage battery health.
Comparing Level 1 and Level 2 Chargers
Choosing between a Level 1 and Level 2 charger depends on your charging needs and priorities.
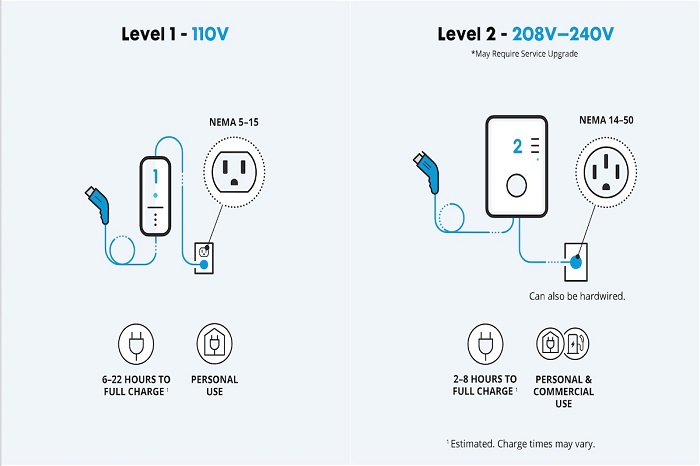
1. Comparison Between Level 1 and Level 2 Chargers:
- Charging Speed: The biggest difference lies in charging speed. Level 1 chargers are significantly slower, typically adding only 3-5 miles of range per hour. Level 2 chargers, on the other hand, offer a much faster charging rate, providing 25–50 miles of range per hour.
- Efficiency: Both Level 1 and Level 2 chargers are efficient in terms of energy transfer. However, due to the lower power delivery, Level 1 chargers might experience slightly higher energy loss during charging compared to Level 2.
2. Cost Variations between Level 1 and Level 2 Chargers:
- Level 1 Charger Cost: Level 1 chargers are generally more cost-effective. In most cases, they come included with the purchase of your EV, or have a very low upfront cost if purchased separately. There are minimal operational expenses as they use standard household outlets.
- Level 2 Charger Cost: Level 2 chargers require a dedicated 240v outlet installation, which can incur additional costs. However, the operational expense per charge might be comparable to Level 1 depending on your electricity rates.
In essence, Level 1 chargers are ideal for situations where slow charging over longer periods is acceptable, while Level 2 chargers are better suited for those who need faster charging for daily commutes or frequent top-ups. The upfront cost consideration for Level 2 charger installation needs to be weighed against the convenience and time saved with faster charging speeds.
Optimizing Level 1 Charging for Battery Health
Level 1 chargers are a convenient and affordable option for EV charging, but some practices can maximize battery health during use.
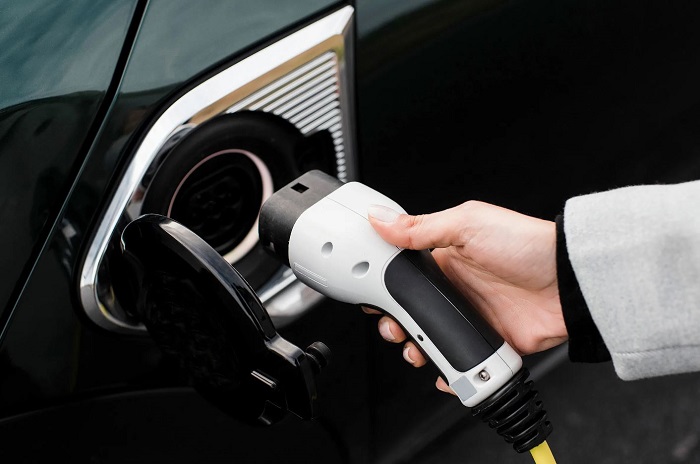

- Unplug After Reaching Desired Charge Level: To optimize battery health, it’s advisable to unplug the Level 1 charger once the desired charge level is reached. Leaving the vehicle constantly plugged in at full charge can contribute to battery degradation over time.
- Avoid Extreme Temperatures: Charging in extreme temperatures, whether too hot or too cold, can impact battery health. Try to charge the vehicle in moderate temperature conditions whenever possible to minimize stress on the battery cells.
- Regularly Monitor Charging Sessions: Keep an eye on charging sessions and battery levels to ensure they are within optimal ranges. This helps prevent overcharging or discharging to excessively low levels, which can affect battery longevity.
- Inspect Charger and Outlet: Regularly inspect the Level 1 charger and the electrical outlet for any signs of damage or malfunction. Damaged equipment should be repaired or replaced promptly to prevent safety hazards and ensure proper charging operation.
- Follow Manufacturer Recommendations: Adhere to the manufacturer’s recommendations and guidelines for charging your specific electric vehicle model. These instructions may include specific charging practices or precautions to optimize battery health and performance.
While Level 1 chargers are not inherently bad for EV batteries, their slow charging times can lead to unhealthy charging habits. Leaving your car plugged in for extended periods at a low charge level can stress the battery.
To maximize battery life, prioritize Level 2 or 3 charging whenever possible and avoid fully depleting the battery. By adopting healthy charging practices, you can ensure your EV battery enjoys a long and healthy lifespan regardless of the charger type used.

Henry Michael is a leading expert in EV charging station research, specializing in innovative solutions for electric vehicle infrastructure. With a passion for sustainability and technological advancement, he is dedicated to advancing the accessibility and efficiency of EV charging worldwide.







