Level 1 vs level 2 vs level 3 EV charger
The growing popularity of electric vehicles (EVs) has led to an increased demand for charging infrastructure. Understanding the different levels of EV chargers is crucial for EV owners and those considering making the switch.
This guide provides an overview of Level 1, Level 2, and Level 3 chargers, highlighting their key differences and suitability for various charging needs.
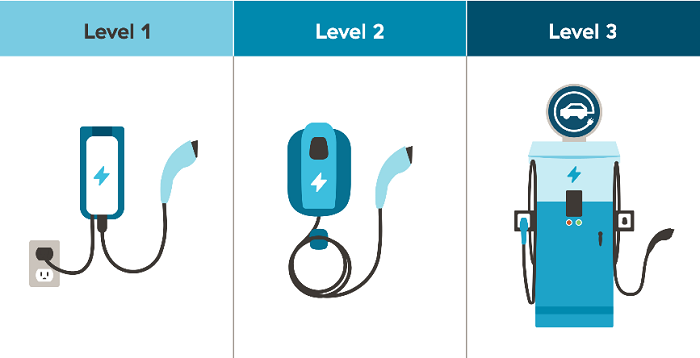
Detailed Analysis of Each Charger Level
A. Level 1 Chargers:
- Benefits of Level 1 Charging:
- Accessibility: Level 1 chargers are the most accessible, as they can be plugged into standard household outlets.
- Cost-Effectiveness: They are typically the most cost-effective option for EV owners, as no additional infrastructure or installation costs are required.
- Convenience: Level 1 chargers provide the convenience of charging at home, allowing EV owners to top up their vehicle’s battery overnight.
- Charging Convenience at Home:
Level 1 chargers offer the convenience of home charging, allowing EV owners to replenish their vehicle’s battery while parked at home overnight.
This ensures that the vehicle is fully charged and ready to go each morning without requiring a trip to a public charging station.
- Cost-Effectiveness of Level 1 Chargers:
Level 1 chargers are the most cost-effective option for EV owners, as they typically come included with the vehicle and require no additional investment in charging infrastructure.
They utilize existing electrical outlets, eliminating the need for the costly installation of dedicated charging equipment.
- Overview of Level 1 Charging:
Level 1 charging operates on standard household outlets with 120 volts AC power supply. It is the slowest charging option, providing approximately 2-5 miles of range per hour of charging.
- Advantages and Limitations of Level 1 Chargers:
- Advantages: accessibility, cost-effectiveness, and convenience for overnight charging at home.
- Limitations: slow charging speed, limited range added per hour, not suitable for rapid top-ups during the day.
B. Level 2 Chargers:
- Advantages of Level 2 Chargers for Electric Vehicles:
Enhanced Charging Speeds: Level 2 chargers offer significantly faster charging compared to Level 1 chargers, making them suitable for daily charging needs.
Compatibility: They are compatible with most electric cars and plug-in hybrids, providing versatility for EV owners.
- Enhanced Charging Speeds:
Level 2 chargers deliver faster charging speeds than Level 1 chargers, typically providing 10-60 miles of range per hour of charging.
This makes them suitable for both residential and commercial charging applications.
- Compatibility with Most Electric Cars:
Level 2 chargers are compatible with a wide range of electric cars and plug-in hybrids, offering versatility for EV owners regardless of their vehicle model.
- Level 2 Chargers – Features and Benefits:
- Features: require a 240-volt AC power source, typically installed with a dedicated circuit and charging unit.
- Benefits: faster charging speeds, compatibility with most electric vehicles, suitable for home, workplace, and public charging stations.
- Cost-Effectiveness for Daily Use:
While Level 2 chargers may require initial investment in installation, they offer cost-effective charging solutions for daily use, especially for EV owners with longer commutes or higher charging needs.
C. Level 3 Fast Chargers:
- Understanding Level 3 Fast Chargers:
Level 3 fast chargers, also known as DC fast chargers, are designed for rapid charging of electric vehicles.
They operate on high-power DC power and are typically installed at public charging stations and along highways.
- Rapid Charging Capabilities:
Level 3 chargers offer rapid charging capabilities, delivering up to 180 miles of range in just 30 minutes, depending on the vehicle and charger specifications.
This makes them ideal for long-distance travel and quick top-ups during road trips.
- Use Cases for Level 3 Charging Stations:
Level 3 charging stations are strategically located along highways and major routes to support long-distance travel for electric vehicles.
They are also suitable for quick top-ups for EVs with limited range or for drivers who require fast charging during the day.
- Superior Speed and Rapid Charging:
Level 3 chargers provide superior charging speeds compared to Level 1 and Level 2 chargers, making them the preferred option for drivers who need rapid charging solutions.
- High-Power Charging Stations:
Level 3 chargers operate on a high-power DC supply, typically ranging from 50 kW to 350 kW or more, enabling rapid charging of electric vehicles.
- Compatibility with Next-Generation EVs:
Level 3 chargers are designed to be compatible with next-generation electric vehicles that may have higher power requirements and larger battery capacities. They offer future-proof charging solutions for the evolving electric vehicle market.
- Benefits of Level 3 Fast Charging:
- Rapid charging capabilities for long-distance travel.
- High-power charging for quick top-ups.
- Compatibility with next-generation electric vehicles.
- Convenience for drivers needing fast charging solutions on the go.
Comparisons and Decision-Making Factors
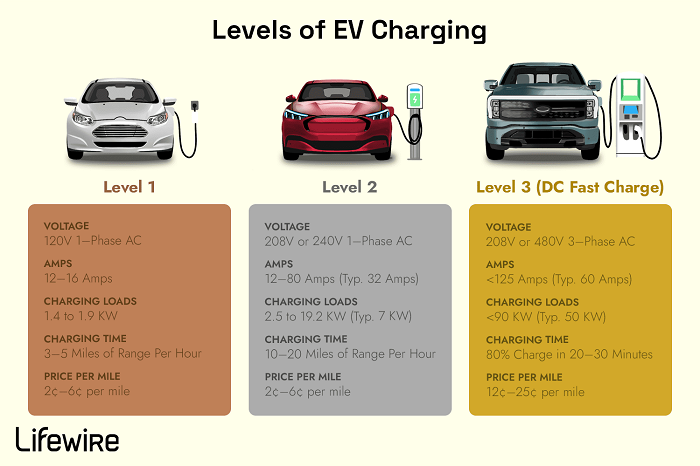
Level 1, Level 2, and Level 3 EV chargers differ significantly in their charging speed, power output, compatibility, and installation requirements. Here’s a breakdown of the key features of each:
| Compare | Level 1 Charger | Level 2 Charger | Level 3 Charger (DC Fast Charger) |
| Charging Speed | Slowest (adds 3-5 miles of range per hour) | Faster than Level 1 (adds 25-50 miles of range per hour) | Fastest (adds up to 200 miles of range within 30 minutes) |
| Power | Uses a standard 120v household outlet (similar to plugging in a toaster) | Uses 240v outlet (similar to a dryer outlet), requires dedicated circuit installation | Delivers DC (direct current) at high voltage (400v or higher), not suitable for home use |
| Convenience | Universally available, requires no installation | Readily available for home installation and public charging | Available at public charging stations along highways and in urban centers |
| Cost | Typically included with EV purchase, minimal operating cost | Moderate upfront cost for charger and installation, lower operating cost than Level 3 | The highest operating cost per kWh compared to Level 1 and 2, often charged by the minute |
| Best for | Overnight charging at home for regular commutes with short distances. | Everyday charging at home or public stations, suitable for most daily commutes. | Long-distance travel, quick top-ups on the go when time is limited. |
In essence:
- Charging Speed: Increases significantly from Level 1 to Level 2 to Level 3.
- Power: Levels 1 and 2 use AC (alternating current), while Level 3 utilizes high-voltage DC.
- Installation: Level 1 requires no installation, Level 2 might need a dedicated circuit, and Level 3 is for public stations only.
- Cost: Level 1 is the cheapest, Level 2 has moderate upfront costs, and Level 3 has the highest operating cost.
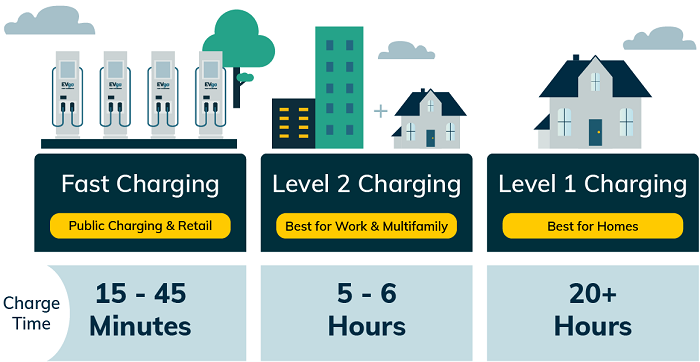
By understanding these key features, you can make an informed decision on the type of charger that best suits your electric vehicle’s needs and your driving habits.
Factors Influencing Charger Selection
Selecting the right charger for your electric vehicle (EV) is crucial. When it comes to selecting the right charger for your electric vehicle (EV), several factors come into play:
1. Charging Time vs. Convenience
- Level 1 Charger (120v outlet): slowest charging option, typically adds 3-5 miles of range per hour.Ideal for overnight charging at home for regular commutes.
- Level 2 Charger (240v outlet): provides a faster charge, adding 25–50 miles of range per hour. Suitable for home installations and public charging stations for everyday top-ups.
- Level 3 Charger (DC Fast Charger): offers the fastest charging, capable of adding up to 200 miles of range within 30 minutes. Best suited for long-distance trips on public charging networks.
2. Cost and Installation Considerations
- Level 1 chargers are typically included with the EV purchase.
- Level 2 charger installation costs vary depending on your electrical system and amperage requirements.
- Level 3 chargers are readily available at public charging stations but incur higher charging costs per kWh.
3. Charging Station Availability
- Level 1 charging is universally available at any standard household outlet.
- Level 2 chargers are becoming increasingly common at homes and public places like workplaces, shopping malls, and dedicated charging stations.
- Level 3 charger availability is still expanding, primarily concentrated along major highways and urban centers.
4. Usage Frequency and Charging Needs
- If you have a regular daily commute with access to charging at home or work, a Level 1 or 2 charger might suffice.
- For frequent long-distance travel, access to a Level 3 DC fast charging network becomes more important.
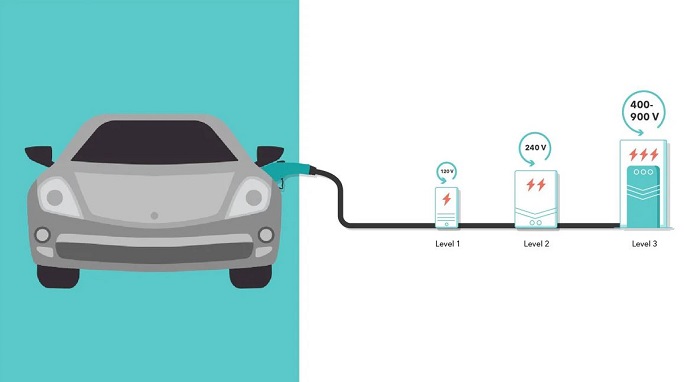
5. Home Charging vs. Public Charging
- Home charging with a Level 2 charger is generally the most cost-effective option.
- Public charging stations offer convenience, especially for those who live in apartments or lack home charging facilities.
6. Long-Distance Travel Considerations
- Plan your route beforehand to locate Level 3 charging stations along the way.
- Factor in charging times when estimating travel duration.
- Some EVs offer extended ranges that can reduce reliance on frequent charging stops.
7. Choosing the Right Charger for Your EV
By considering these factors, you can make an informed decision about the charger that best suits your driving habits and needs.
8. Additional Considerations:
- Cost Analysis of Level 1, Level 2, and Level 3 Chargers: The initial cost of Level 1 chargers is minimal, while Level 2 charger installation can range from $200 to $1000. Level 3 chargers are not available for home installation due to their high-voltage requirements. Public charging station fees can vary depending on location and charging level.
- Impact of Charging Level on Electric Cars’ Battery Life: Frequent use of Level 3 chargers can slightly degrade battery health over time compared to slower Level 1 or 2 charging. However, proper charging practices and advancements in battery technology can mitigate this effect.
Choosing the right EV charger for your needs depends on several factors, including your driving habits, budget, and access to charging infrastructure. Level 1 chargers are the most affordable option but offer the slowest charging speeds. Level 2 chargers are a good compromise, providing faster charging times at a moderate price point. Level 3 chargers are the fastest option but are also the most expensive and require access to a high-powered charging station.
Level 2 chargers are the most common choice for home charging, as they offer a good balance of speed and affordability. They typically require a 240-volt circuit and are installable by a qualified electrician. Level 3 chargers are typically installed in public places, such as shopping malls and gas stations. They require a high-powered connection and are more expensive to install.
Ultimately, the best EV charger for you will depend on your individual needs and circumstances. Consider your driving habits, budget, and access to charging infrastructure when making your decision.

Henry Michael is a leading expert in EV charging station research, specializing in innovative solutions for electric vehicle infrastructure. With a passion for sustainability and technological advancement, he is dedicated to advancing the accessibility and efficiency of EV charging worldwide.







