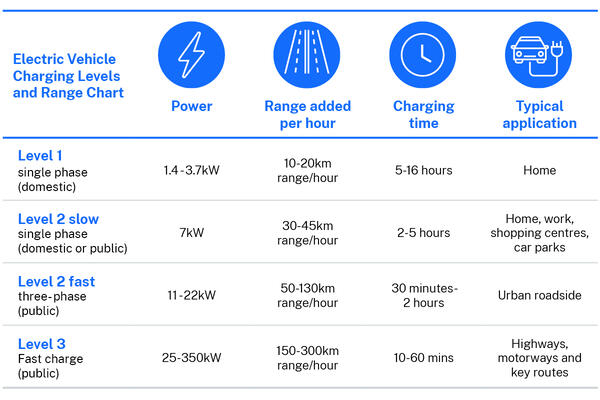
Level 3 Electric Car Charging Stations Overview
Level 3 Electric Car Charging Stations, also known as DC fast chargers, are the kingpins of rapid electric vehicle (EV) charging. Let’s delve into what they are, why they matter, and how they stack up against other charging options.
Definition of Level 3 Charging
Level 3 charging utilizes direct current (DC) to deliver high power outputs, typically ranging from 50 kW to 350 kW. This bypasses the on-board charger in your EV, significantly accelerating the charging process.
The Importance of Level 3 Charging for EV Adoption
Fast charging is a game-changer for EV adoption. It tackles what’s often called range anxiety, the fear of running out of power before reaching a charging station. Widespread Level 3 infrastructure makes long-distance travel in EVs more feasible, boosting consumer confidence.

Comparison with Level 1 and Level 2 Charging
- Level 1 charging is the slowest, typically using a standard household outlet.
- Level 2 charging, commonly found in homes and public stations, delivers faster charging than Level 1 but pales in comparison to Level 3.
Typical Locations for Level 3 Charging Stations
- Highways and major roads for convenient charging during long journeys.
- Urban centers where rapid charging is needed for taxis, ride-sharing services, and frequent commutes.
- Shopping malls and grocery stores to enable charging while running errands.
Challenges and Opportunities in Level 3 Charging Infrastructure Development
- Cost: Setting up Level 3 stations is expensive due to the high-power equipment required.
- Grid Integration: Upgrading the power grid to support widespread Level 3 adoption might be necessary.
- Standardization: Ensuring compatibility between different charging station manufacturers and EVs is crucial.
However, the opportunities are vast. Government incentives, technological advancements, and public-private partnerships can overcome these challenges. As Level 3 charging infrastructure expands, electric vehicles become a more practical and appealing option for everyone.
Technical Specifications of Level 3 Charging
Power Output Range and Charging Speed
Level 3 charging stations typically provide a power output range of 50 kW to 350 kW or more, depending on the specific charger model and manufacturer. Charging speeds vary accordingly, with higher-powered chargers capable of delivering faster charging rates. Charging times can range from approximately 20 minutes to 1 hour for a full charge, depending on factors such as the EV’s battery capacity and state of charge.
Connector Types (e.g., CHAdeMO, CCS, Tesla Supercharger)
Several connector types are used for Level 3 charging, each associated with different charging standards and supported by various EV manufacturers:
- CHAdeMO (Charge de Move): Developed by Japanese companies, CHAdeMO is a DC fast charging standard used primarily by Japanese automakers like Nissan and Mitsubishi.
- Combined Charging System (CCS): Adopted by European and North American automakers, CCS combines AC and DC charging capabilities in a single connector. It’s becoming increasingly common in the global EV market.
- Tesla Supercharger: Proprietary to Tesla vehicles, the Supercharger network consists of high-powered DC fast chargers specifically designed for Tesla EVs.
Impact on Electric Vehicle Battery Life
Fast charging, including Level 3 charging, can impact the overall lifespan of an electric vehicle battery. Rapid charging generates more heat within the battery cells, which can accelerate degradation over time. However, modern EVs are equipped with sophisticated battery management systems that optimize charging protocols to mitigate potential damage and prolong battery life. Additionally, advancements in battery technology, such as improved thermal management systems and higher-quality battery chemistries, help minimize the negative effects of fast charging on battery longevity.
Software Integration for Smart Charging
Smart charging software and systems enable advanced functionality and optimization of Level 3 charging infrastructure, including:
- Dynamic load management: Allocating charging power based on grid demand and available capacity to prevent strain on the electrical grid.
- Demand response integration: Adjusting charging rates and schedules in response to grid conditions, energy prices, or utility signals to optimize charging efficiency and cost.
- Billing and payment processing: Facilitating seamless payment transactions, user authentication, and billing management for charging services.
- Remote monitoring and diagnostics: Monitoring charging station performance, conducting remote diagnostics, and implementing predictive maintenance to ensure uptime and reliability.
Safety Standards and Protocols
Level 3 charging stations adhere to rigorous safety standards and protocols to ensure the protection of users, vehicles, and infrastructure. Common safety features and practices include:
- Ground fault protection: Detecting and mitigating electrical faults to prevent electric shock hazards.
- Overcurrent protection: Safeguarding against excessive current flow to prevent overheating and damage to electrical components.
- Temperature monitoring: Monitoring charging equipment and battery temperatures to prevent overheating and thermal runaway.
- Authentication and authorization: Implementing secure access controls and authentication mechanisms to prevent unauthorized use and tampering.
Compliance with industry standards: Adhering to relevant standards and regulations, such as SAE J1772 (for CCS), CHAdeMO, and regional electrical codes, to ensure interoperability and safety.
Cost Analysis of Level 3 Charging
Level 3 charging offers undeniable advantages, but it comes at a cost. Let’s delve into the financial aspects from various perspectives.

Comparison of Installation Costs: Level 3 vs. Level 2
- Level 3: Significantly more expensive. The high-power equipment and potential grid upgrades can push the cost per station to $20,000 – $150,000+.
- Level 2: Comparatively cheaper. Installation typically ranges from $500 to $2,000, making them more accessible for wider deployment.
Pricing Strategies for Charging Service Providers
Charging service providers employ various pricing models:
- Pay-per-kWh: Consumers pay based on the kilowatt-hours (kWh) of electricity delivered, similar to how we pay for traditional electricity.
- Subscription Model: A monthly fee grants access to a network of chargers, potentially with discounted charging rates.
- Free Charging (Promotional): Some businesses might offer free charging to attract customers, especially during initial deployment phases.
Government Incentives and Subsidies
Governments around the world are promoting EV adoption through incentives like:
- Grants: Financial assistance to offset the cost of installing Level 3 charging stations.
- Tax credits: Rebates or tax reductions for businesses and individuals investing in EV charging infrastructure.
- Favorable electricity rates: Discounted electricity rates for charging stations to encourage their use.
ROI for Businesses Installing Level 3 Charging Stations

The return on investment (ROI) for businesses depends on factors like:
- Location: Stations in high-traffic areas with frequent EV use will see higher returns.
- Pricing Model: Effective pricing strategies are crucial for profitability.
- Customer Base: Businesses catering to EVs or attracting customers who value fast charging will benefit more.
While the initial investment is high, factors like government incentives and increased EV adoption can lead to a positive ROI in the long run.
Consumer Costs: Pay-per-use vs. Subscription Models
The cost for consumers varies based on the pricing model:
- Pay-per-kWh: Can be more expensive for occasional users but cost-effective for frequent long-distance travel.
- Subscription Model: Ideal for frequent EV users who travel long distances regularly. May not be economical for occasional users.
EV Charging Network Expansion: Bridging the Gap
Expanding the Level 3 charging network is crucial for widespread EV adoption. Let’s explore the current state, future plans, and the forces driving this growth.
Current Coverage and Density of Level 3 Chargers
Despite significant growth, the current Level 3 charging network has limitations. While coverage is expanding in major corridors and urban centers, rural areas and some highways still lack sufficient density.

Federal and State Infrastructure Plans
Many governments are investing heavily in EV infrastructure. The US Bipartisan Infrastructure Law allocates $7.5 billion for building a national network of 500,000 chargers by 2030. Similar initiatives are underway globally.
Role of Private Investment and Public-Private Partnerships
Private companies are crucial players. Leading car manufacturers, utility companies, and charging network operators are investing billions in expanding the network. Public-private partnerships combine government funding with private sector expertise to accelerate deployment.
International Expansion and Standardization Efforts
The need for a globally standardized approach is recognized. Efforts are underway to harmonize connector types and communication protocols to ensure seamless cross-border EV travel.
Future Projections for Network Growth
The future of EV charging networks is bright. Here are some projections:
- Rapid Expansion: Analyst predictions suggest millions of Level 3 chargers globally by 2030, significantly improving accessibility.
- Strategic Placement: Focus on filling gaps in underserved areas and highways for long-distance travel.
- Technological Advancements: Faster charging times, innovative station designs, and grid integration solutions are on the horizon.
The Bottom Line
Expanding the Level 3 charging network is a collaborative effort. With continued government support, private sector investment, and technological advancements, we can create a robust infrastructure that fuels the future of electric mobility.
User Experience at Level 3 Charging Stations

Average Charging Time and Waiting Times
The average charging time at Level 3 charging stations varies depending on factors such as the EV’s battery capacity, the charging station’s power output, and the state of charge when the vehicle is plugged in. Typically, Level 3 chargers can provide an 80% charge in around 20-30 minutes, significantly faster than Level 2 chargers. However, waiting times may occur during peak usage periods, especially at popular charging locations along major travel routes or in urban areas. Users may experience longer wait times if all charging stalls are occupied, necessitating the implementation of queue management systems or the expansion of charging infrastructure to meet growing demand.
Accessibility and Ease of Use
Level 3 charging stations are designed to be user-friendly and accessible to all EV drivers. Features that enhance accessibility and ease of use include clear signage, intuitive user interfaces, ergonomic charging connectors, and ADA-compliant design elements for users with disabilities. Charging stations are often equipped with instructions for initiating charging sessions, making payments, and accessing additional services, ensuring a seamless experience for both novice and experienced EV owners.
Additional Amenities and Services at Charging Locations
Many Level 3 charging locations offer additional amenities and services to enhance the user experience and provide added convenience during charging sessions. These amenities may include:
- Restrooms
- Food and beverage options
- Wi-Fi access
- Seating areas
- EV-specific parking spaces
- EV charging loyalty programs or rewards
- Retail outlets or shopping centers
- Outdoor recreational areas
Providing these amenities encourages EV drivers to spend time at charging locations, increasing the likelihood of return visits and fostering positive associations with the charging provider or location.
Mobile App Integration for Charger Availability and Payment
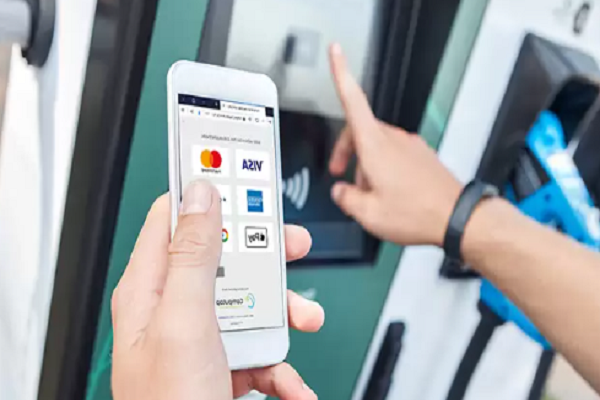

Mobile apps play a critical role in enhancing the user experience at Level 3 charging stations by providing real-time information on charger availability, status updates, and payment options. Charging network operators and service providers offer mobile apps that enable users to:
- Locate nearby charging stations
- Check charger availability and occupancy
- Initiate and monitor charging sessions remotely
- Make payments and view charging transaction history
- Receive notifications and alerts
Integration with mobile apps streamlines the charging process, improves user convenience, and enables EV drivers to plan their routes and charging stops more efficiently.
Community Feedback and Reviews
Community feedback and reviews play an essential role in shaping the user experience at Level 3 charging stations and informing future improvements. Charging network operators and service providers actively solicit feedback from users through online surveys, customer support channels, and social media platforms to identify areas for improvement and address user concerns promptly. Positive reviews and testimonials from satisfied users can also enhance the reputation and credibility of charging providers, attracting new customers and fostering loyalty within the EV community. Conversely, negative feedback can highlight areas for improvement and prompt corrective action to enhance the overall user experience.
Environmental Impact of Level 3 Charging: A Balancing Act
Level 3 charging stations offer a double-edged sword when it comes to the environment. While they promote electric vehicles (EVs) which can significantly reduce emissions, their impact depends on several factors.
Reduction of Carbon Footprint Through Fast Charging
- EV Adoption and Reduced Emissions: By making long-distance travel in EVs more feasible, Level 3 charging stations encourage a shift away from gasoline-powered vehicles, leading to a potential reduction in overall carbon footprint.
Energy Source Considerations: Renewable vs. Non-Renewable
- Clean Energy Makes a Difference: The environmental benefit hinges on the electricity source powering the stations. If the grid relies heavily on fossil fuels, the carbon footprint might not be significantly lower than gasoline vehicles.
- Renewable Integration: The potential is immense if the grid transitions towards renewable sources like solar and wind power. This would significantly enhance the environmental benefits of Level 3 charging.
Battery Disposal and Recycling Practices
- Responsible Recycling: EV batteries contain critical materials. Proper disposal and recycling practices are crucial to minimize environmental damage and resource depletion.

Role in Supporting Green City Initiatives
- Reduced Urban Pollution: Widespread adoption of EVs and Level 3 charging can significantly improve air quality in cities by reducing tailpipe emissions.
- Smart Grid Integration: Smart charging technologies can optimize energy use and minimize strain on the grid during peak hours, further enhancing sustainability.
Future Technologies to Enhance Environmental Benefits
- Second-Life Battery Applications: Utilizing used EV batteries for stationary energy storage can improve grid stability and reduce reliance on fossil fuels.
- Bidirectional Charging: Future advancements might enable EVs to feed excess power back to the grid, contributing to a more sustainable energy ecosystem.
In Conclusion
Level 3 charging stations have the potential to be a powerful tool for environmental progress. By promoting EV adoption, integrating renewable energy sources, and implementing responsible battery practices, we can unlock their full potential in creating a cleaner future.

Henry Michael is a leading expert in EV charging station research, specializing in innovative solutions for electric vehicle infrastructure. With a passion for sustainability and technological advancement, he is dedicated to advancing the accessibility and efficiency of EV charging worldwide.







