Discover the Best Level 3 EV Charger Amperage for Rapid Charging
When selecting a Level 3 EV charger, understanding the importance of charger amperage is crucial for optimizing your electric vehicle’s charging time and efficiency. The amperage of a Level 3 EV charger directly influences how quickly your EV’s battery can be charged, making it an essential factor to consider for those looking to minimize downtime. With the right level 3 EV charger amperage, you can significantly enhance your charging experience by ensuring that your vehicle is ready to go when you are. This guide will explore the key aspects of choosing the appropriate amperage to meet your charging needs effectively.

Overview of Level 3 EV Charging
Electric vehicles are revolutionizing transportation, but their “refueling” needs can seem complex. Level 3 EV charging, also known as DC fast charging, stands out as the ultimate time-saver for busy drivers.
This guide unlocks the secrets of Level 3 charging. We’ll explore its definition and basic principles, delve into the critical role of amperage, and compare it to Levels 1 and 2 charging. Finally, we’ll shed light on the current standards and protocols that ensure safe and efficient high-speed charging. So, buckle up and get ready to learn how Level 3 charging can keep your electric adventures rolling!
Definition and Basics of Level 3 Charging
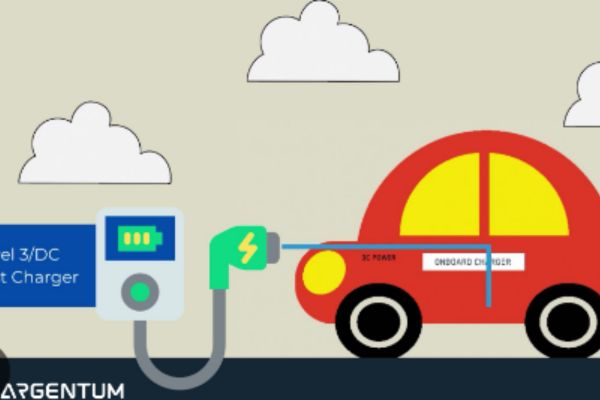
Imagine topping off your electric vehicle’s battery in just minutes, not hours. That’s the magic of Level 3 charging, also known as DC fast charging. Unlike Level 1 and 2 chargers that use household-style current, Level 3 utilizes a different approach:
- Direct Current (DC) Power: Level 3 chargers deliver DC power directly to the battery, bypassing the car’s onboard converter. This eliminates a conversion step, significantly speeding up the charging process.
- High Amperage: These chargers pack a serious punch in terms of amperage (current). Think of it like water pressure – the higher the amperage, the faster the electrons flow into your battery.
In essence, Level 3 charging provides a high-powered, direct line to your battery, resulting in dramatically faster charging times compared to other levels. Let’s delve deeper into the world of Level 3 charging and explore its advantages and considerations.

The Importance of Amperage in EV Charging
Amperage plays a pivotal role in electric vehicle (EV) charging, significantly influencing the speed and efficiency of the charging process. In essence, amperage represents the rate at which electric current flows from the charging station to the EV’s battery.
The higher the amperage, the faster the charging speed, enabling EV owners to replenish their battery power more quickly. Therefore, selecting the appropriate amperage for an EV charger is crucial to meet specific charging needs and optimize the charging experience.
Whether it’s a Level 1, Level 2, or Level 3 charger, understanding and considering amperage requirements ensure that EV drivers can efficiently charge their vehicles, minimizing downtime and maximizing convenience.
Distinction Between Level 1, Level 2, and Level 3 Charging
Not all EV chargers are created equal! Understanding the distinctions between Level 1, Level 2, and Level 3 chargers is crucial for making informed decisions about your charging needs. Here’s a breakdown:
- Level 1 Charging: The slowest option, often referred to as “trickle charging.” It utilizes a standard household outlet (120 volts) and delivers minimal amperage, making it suitable for overnight charging at home but impractical for on-the-go situations.
- Level 2 Charging: The happy medium, offering a significant step up in speed compared to Level 1. It uses a 240-volt circuit (similar to a dryer outlet) and provides higher amperage, allowing for a full charge in several hours. Level 2 chargers are commonly found at homes, workplaces, and public charging stations.
- Level 3 Charging (DC Fast Charging): The reigning champion of speed. It utilizes DC power directly compatible with your battery and boasts high amperage, enabling a full charge or a substantial top-up in just minutes. However, Level 3 chargers are typically found at public charging stations along highways and major urban areas due to their specialized infrastructure requirements.
Here’s a table summarizing the key differences:
| Feature | Level 1 Charging | Level 2 Charging | Level 3 Charging (DC Fast Charging) |
| Voltage | 120 volts AC | 240 volts AC | High-voltage DC |
| Amperage | Low | Moderate | High |
| Charging Speed | Slowest | Faster | Fastest |
| Typical Use Case | Overnight charging at home | Home, workplace, public stations | Public stations for on-the-go top-ups |
| Availability | Widespread (standard outlets) | Common (requires installation) | Limited (public stations) |
Choosing the right charger depends on your driving habits and charging needs. Level 2 is a versatile option for most daily commutes, while Level 3 is ideal for long trips or quick top-ups during road trips.
Current Standards and Protocols for Level 3 Charging
Level 3 charging’s high power capabilities necessitate robust safety measures and clear communication protocols to ensure a smooth and reliable charging experience. Here’s a look at the key standards and protocols governing this fast-charging technology:
Connector Standards: Several connector standards exist for Level 3 charging, with the most common being:
- CCS Combo Charging System (CCS): A prevalent standard in North America and Europe, combining AC and DC charging capabilities in one connector.
- CHAdeMO: Primarily used in Japan and some Asian countries, offering high-power DC charging.
- Tesla Supercharger: Proprietary to Tesla vehicles, offering some of the fastest charging speeds currently available.
Communication Protocols: Protocols like Open Charge Point Protocol (OCPP) ensure seamless communication between the charging station and your vehicle. This allows for functionalities like:
- Secure identification and authorization for charging sessions
- Real-time monitoring of charging progress and battery health
- Dynamic power allocation for efficient use of available electricity
Safety Standards: Stringent safety regulations are in place to minimize risks associated with high-voltage DC charging. These include:
- IEC 61851 (International Electrotechnical Commission): Defines safety requirements for AC and DC charging systems.
- SAE J1772 (Society of Automotive Engineers): Sets safety standards for electric vehicle connectors and charging systems in North America.
These standards and protocols work together to create a safe, efficient, and interoperable Level 3 charging ecosystem. By adhering to these guidelines, manufacturers and network providers ensure a reliable and positive experience for EV drivers on the go.

Technical Specifications of Level 3 Chargers
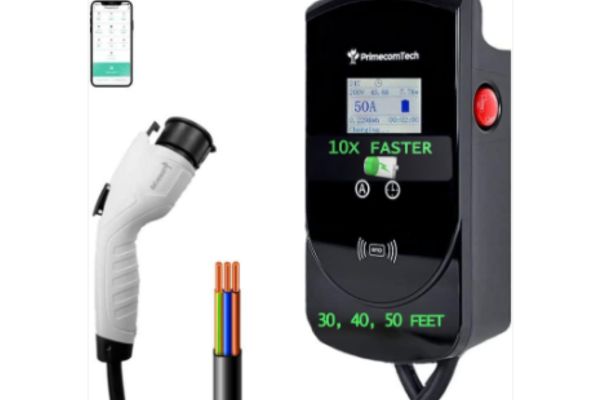
Level 3 chargers, also known as DC fast chargers, feature distinct technical specifications that enable rapid charging of electric vehicles (EVs) while on the road.
Typical Amperage and Voltage Ranges
Level 3 chargers operate at high voltage and current levels, usually ranging from 200 to 1000 volts DC and 100 to 500 amperes. These high levels of voltage and amperage allow for fast charging times, making Level 3 chargers ideal for quick pit stops during long journeys.
Connector Types and Compatibility
There are several connector types used for Level 3 charging, including CCS (Combined Charging System), CHAdeMO, and Tesla Supercharger connectors. CCS is becoming increasingly common due to its ability to accommodate both AC and DC charging, making it compatible with a wide range of EVs. CHAdeMO connectors are prevalent in Asian markets and are primarily used by Japanese automakers. Tesla Superchargers are proprietary to Tesla vehicles but offer extremely fast charging speeds for Tesla owners.
Charging Speeds and How Amperage Affects Them
The charging speed of a Level 3 charger is influenced by several factors, including the charger’s amperage, the EV’s battery capacity, and the state of charge. Higher amperage levels generally result in faster charging speeds, allowing EVs to replenish their battery capacity more quickly. However, it’s essential to note that charging speed typically decreases as the battery approaches full capacity, a phenomenon known as tapering.
Power Delivery Mechanism
Level 3 chargers deliver power directly to the EV’s battery in the form of direct current (DC). Unlike Level 1 and Level 2 chargers, which convert AC power from the grid to DC power using an onboard charger in the EV, Level 3 chargers bypass the onboard charger and deliver DC power directly to the battery. This direct power delivery mechanism minimizes energy losses and allows for faster charging times.
Overall, Level 3 chargers offer a convenient and efficient charging solution for EV owners, especially during long-distance travel, thanks to their high charging speeds and compatibility with a wide range of EV models.

Future of Level 3 Charging Technology
Level 3 charging has revolutionized how we “refuel” electric vehicles, offering a glimpse into the future of fast and convenient EV charging. But the journey doesn’t end here. Let’s explore the exciting advancements and research brewing in the world of Level 3 charging technology.
Technological Advancements and R&D
The race is on to push the boundaries of Level 3 charging even further. Here are some promising areas of research and development:
- Improved Battery Technology: Advancements in battery materials and thermal management systems could enable faster charging and potentially even higher capacities for future EVs. This would further enhance the effectiveness of Level 3 charging.
- Bidirectional Charging: Imagine using your EV’s battery to power your home or even feed electricity back into the grid during peak demand periods. Bidirectional charging technology holds immense potential for increased grid stability and energy efficiency, with Level 3 chargers potentially playing a key role in this future.
- Wireless Charging: While still in its early stages, wireless charging technology could eliminate the need for physical connections altogether. Imagine pulling into a designated parking spot and your EV automatically starts charging – a future convenience facilitated by advancements in wireless charging for Level 3 applications.
Higher Amperage and Faster Charging Solutions
One of the most anticipated advancements involves even higher amperage capabilities for Level 3 chargers. Here’s what this could mean:
- Ultra-Fast Charging: Imagine topping off your EV battery in a matter of minutes, not tens of minutes. Pushing the amperage limits of Level 3 chargers could potentially achieve ultra-fast charging speeds, significantly reducing charging times and making long-distance travel even more seamless for EV drivers.
- Infrastructure Upgrades: Reaching these ultra-fast charging capabilities will likely necessitate upgrades to the underlying electrical grid infrastructure to handle the increased power demands. Collaboration between energy providers, charging network operators, and government initiatives will be crucial for realizing this future.
The future of Level 3 charging is brimming with exciting possibilities. By investing in R&D and exploring innovative technologies, we can unlock even faster charging times, greater convenience, and a more sustainable EV charging ecosystem.

Henry Michael is a leading expert in EV charging station research, specializing in innovative solutions for electric vehicle infrastructure. With a passion for sustainability and technological advancement, he is dedicated to advancing the accessibility and efficiency of EV charging worldwide.