Unveiling the Secrets of Level 3 EV Charger Speed: A Comprehensive Guide
Electric vehicle (EV) charging technology has undergone significant advancements, especially with the advent of Level 3 charging, commonly referred to as DC fast charging. Mastering the nuances of Level 3 EV charger speed is essential for optimizing charging efficiency and widespread adoption. This detailed guide explores the specifics of Level 3 charging, its rapid charging capabilities, and how it has progressed alongside advancements in EV technology.

What Defines a Level 3 EV Charger?
Level 3 EV chargers, also referred to as DC fast chargers, are designed to provide high-powered, rapid charging for electric vehicles. Unlike Level 1 and Level 2 chargers, which use AC (alternating current) power and are commonly found in homes and public spaces, Level 3 chargers utilize DC (direct current) power to deliver a significantly faster charging experience.
The Basics of EV Charging Levels
Understanding the hierarchy of EV charging levels is essential for grasping the capabilities of Level 3 chargers:
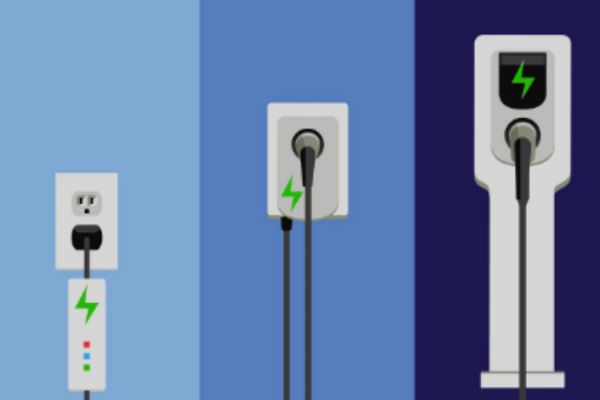
- Level 1 Charging: Utilizes standard household AC outlets (120 volts) and is suitable for overnight charging. Typically provides around 2 to 5 miles of range per hour of charging.
- Level 2 Charging: Requires dedicated charging equipment (240 volts) and is commonly found in homes, workplaces, and public charging stations. Delivers faster charging compared to Level 1, with speeds ranging from 10 to 60 miles of range per hour of charging.
- Level 3 Charging (DC Fast Charging): Employs DC power at high voltages (usually 200-600 volts) to provide rapid charging. This level is primarily used in public charging stations along highways and major routes, offering significantly faster charging rates compared to Level 1 and Level 2.

Key Characteristics of Level 3 Charging
Level 3 charging is distinguished by several key features:
- Speed: Offers charging rates ranging from 50 kW to over 350 kW, allowing EVs to recharge to 80% capacity in as little as 20-30 minutes.
- Compatibility: Designed for specific EV models equipped with DC fast charging capability. Not all EVs support Level 3 charging; compatibility varies by manufacturer.
- Infrastructure Requirements: Requires specialized charging equipment and infrastructure due to higher power demands, including substantial electrical connections and cooling systems.
- Application: Ideal for long-distance travel and quick top-ups, making it essential for enhancing the practicality and adoption of electric vehicles.
The Evolution of EV Charging Technologies
The development of Level 3 charging technology has been pivotal in advancing EV adoption:
- Early DC Fast Chargers: Initial Level 3 chargers provided charging rates around 50 kW, sufficient for basic rapid charging needs.
- Advancements in Power Output: Modern Level 3 chargers now exceed 100 kW and can reach upwards of 350 kW, significantly reducing charging times and improving convenience for EV drivers.
- Network Expansion: Increasing deployment of Level 3 charging networks along major highways and urban centers has expanded accessibility and convenience for electric vehicle owners.
- Standardization Efforts: Ongoing efforts to establish common charging protocols (such as CCS and CHAdeMO) aim to enhance interoperability and further accelerate the adoption of Level 3 charging infrastructure.
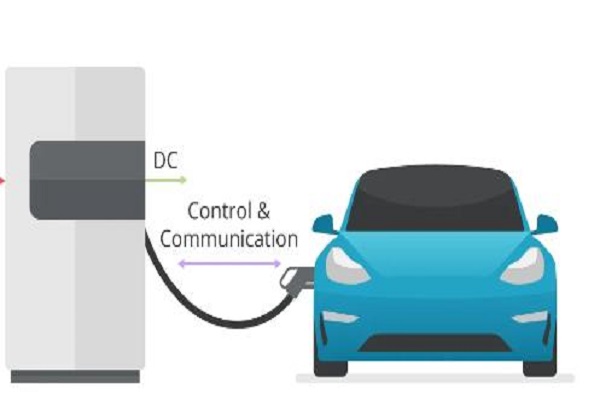
Why is Level 3 Charging Considered Fast Charging?
There are two main reasons why Level 3 charging is considered fast charging:
- Direct Current (DC) Delivery: Unlike Level 1 and Level 2 chargers that use Alternating Current (AC), Level 3 chargers utilize DC. This is a key difference. A car’s battery operates on DC, but AC charging requires the car’s onboard charger to convert it to DC for battery storage. Level 3 chargers bypass this conversion step, delivering power directly in the format the battery needs, significantly reducing charging time.
- High Power Output: Level 3 chargers pack a much bigger punch compared to other levels. We’re talking about power outputs ranging from 50 kW to a staggering 350 kW (or even more in some advanced stations). This high power translates to a much faster flow of electricity into the battery, enabling a substantial increase in range in a shorter amount of time.
Comparing Charging Speeds: Level 1, 2, and 3
To truly understand the “fast” in fast charging, let’s compare the charging speeds of the different levels:
- Level 1 (Slowest): Imagine topping off your phone with a low-wattage charger. That’s the equivalent of Level 1 charging for EVs. It adds a limited range per hour, making it suitable for overnight charging but not ideal for quick top-ups.
- Level 2 (Moderate): This is like using a regular phone charger. It’s faster than Level 1 and a good option for overnight or workplace charging, but still not the fastest option.
- Level 3 (Fastest): This is like plugging your phone into a fast charger. You see a significant jump in range added in a short time. Level 3 chargers can typically recharge an EV to 80% in just 15-45 minutes, making them perfect for long trips where you need a quick boost.
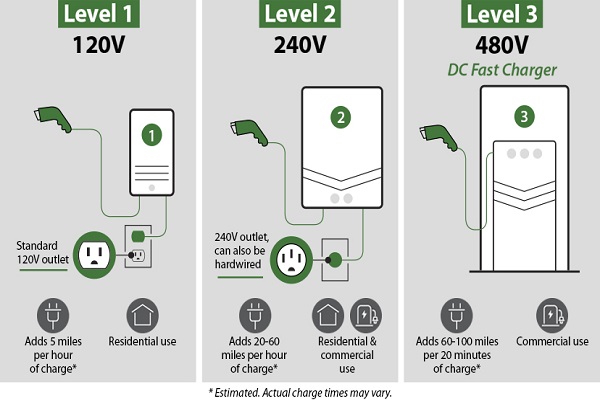
The Science Behind Fast Charging Technology
The science behind fast charging involves manipulating power (voltage and current) to deliver more energy to the battery quickly. Level 3 chargers achieve this by using high voltage (up to 480 volts) and strong current to push electrons into the battery at a much faster rate. However, there’s a trade-off. This rapid charging can generate more heat, which can slightly degrade battery health over time. That’s why Level 3 charging is best suited for occasional quick boosts, not for regular charging.
Impact of Level 3 Charging on EV Adoption
The existence of Level 3 charging stations is a significant factor driving the adoption of electric vehicles. Here’s how:
- Reduced Range Anxiety: Level 3 chargers offer peace of mind on long journeys. Drivers know they can find stations for quick top-ups, eliminating the fear of running out of power in the middle of nowhere.
- Increased Usable Range: With the ability to add a significant amount of range in a short time, Level 3 charging effectively increases the usable range of an EV for road trips or long commutes.
- Faster Travel Times: Compared to relying solely on slower Level 1 or 2 charging, Level 3 stations significantly reduce charging time during trips, making electric vehicles more practical for long distances.
Level 3 Charging Speeds
Level 3 charging, also known as DC fast charging, offers rapid charging speeds that significantly reduce the time required to recharge electric vehicle (EV) batteries compared to Level 1 and Level 2 chargers. These charging speeds can vary depending on the specific charger and the EV model being charged.
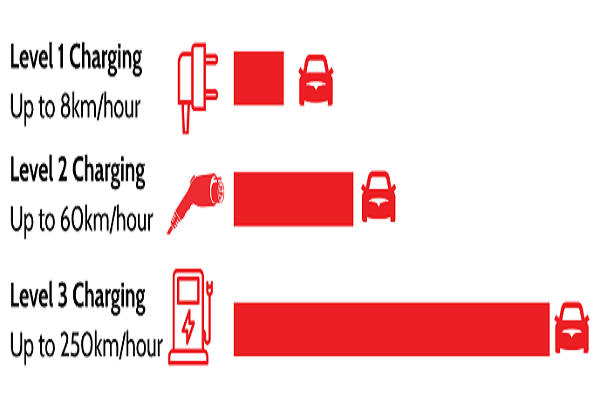
Average Charging Times
The average charging times for Level 3 charging can vary depending on factors such as the battery capacity of the EV, the power output of the charger, and the state of charge of the battery when charging begins. However, Level 3 chargers typically provide an 80% charge in 20-30 minutes for most EV models equipped with DC fast charging capability.
Factors Affecting Charging Speed
Several factors can influence the charging speed of Level 3 chargers:
- Charger Power Output: Higher-powered Level 3 chargers can deliver faster charging speeds compared to lower-powered ones. Chargers with power outputs ranging from 50 kW to over 350 kW are available, with higher power levels generally resulting in shorter charging times.
- Battery Capacity and State of Charge: The size and state of charge of the EV battery can affect charging speed. Charging a battery from a lower state of charge (e.g., 20%) to 80% typically takes less time than charging from 80% to 100% due to tapering charging rates as the battery approaches full capacity.
- Battery Temperature: Extreme temperatures, both hot and cold, can affect battery performance and charging efficiency. Charging speeds may be reduced in very cold temperatures to protect the battery, while overheating can also limit charging rates.
- Charging Infrastructure and Network Congestion: The availability of charging infrastructure and network congestion at charging stations can impact charging speeds. Busy charging stations may experience slower charging rates during peak times, while well-maintained infrastructure with adequate power supply can support faster charging speeds.
Comparison of Charging Speeds Among Top EV Models
Charging speeds can vary among different EV models, depending on factors such as battery size, onboard charging capabilities, and compatibility with Level 3 chargers. Some EV models are equipped with faster onboard chargers or support higher charging power levels, resulting in shorter charging times.
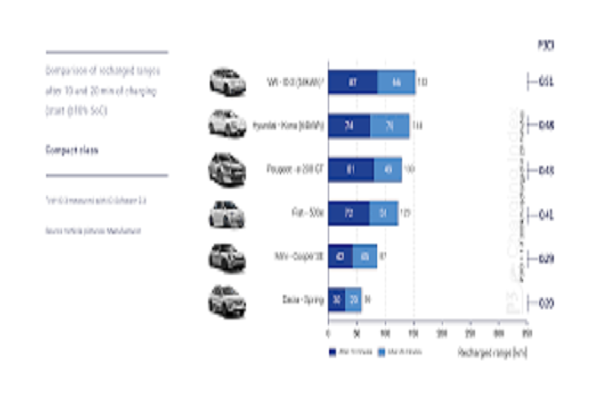
Future Developments in Charging Speed
Advancements in charging technology and infrastructure are expected to further improve charging speeds and efficiency in the future:
- Higher Power Output: Continued development of Level 3 charging technology may result in chargers with even higher power outputs, further reducing charging times for EVs.
- Battery Technology: Advances in battery technology, such as higher energy density and faster charging capabilities, could enable faster charging speeds and increased range for electric vehicles.
- Charging Network Expansion: Expansion of charging networks and deployment of additional Level 3 charging stations will improve accessibility and reduce wait times for charging, enhancing the overall charging experience for EV drivers.
Maximizing Charging Efficiency
To maximize charging efficiency and reduce charging times, EV drivers can take several steps:
- Plan Charging Stops: Use online tools or smartphone apps to plan charging stops along your route, taking into account the locations of Level 3 charging stations and their availability.
- Preconditioning: Precondition the battery before charging by setting the cabin temperature or using a smartphone app to warm or cool the battery to its optimal operating temperature, which can improve charging efficiency.
- Avoid Deep Discharges: Minimize deep discharges of the battery whenever possible, as charging from a lower state of charge typically results in faster charging speeds compared to charging from a deeply depleted battery.
- Monitor Charging Progress: Keep track of the charging progress using the EV’s onboard display or smartphone app to ensure that the battery is charging at the expected rate, and adjust charging plans if necessary.
Level 3 Charging: Unveiling the Technological Marvel
Level 3 charging delivers impressive speed, but the magic lies in the underlying technology. Let’s peel back the layers and explore the key components:

Direct Current Fast Charging (DCFC) Technology
The heart of Level 3 charging lies in DCFC technology. Unlike Level 1 and 2 chargers that utilize Alternating Current (AC), Level 3 chargers are DC beasts. Here’s why it matters:
- AC vs. DC: A car’s battery operates on DC. AC charging requires the car’s onboard charger to convert it to DC for storage. Level 3 chargers bypass this conversion step, delivering power directly in the format the battery needs, saving time.
Software Improvements for Charging Speed
It’s not just about brute force. Software plays a crucial role in optimizing charging speed and safety:
- Communication Protocols: Advanced communication protocols allow chargers and vehicles to “talk” to each other. This enables real-time monitoring of battery health and temperature, ensuring safe and efficient charging at the optimal rate.
- Dynamic Power Management: Sophisticated software can dynamically adjust the charging power based on battery parameters, maximizing charging speed while safeguarding battery health.
Hardware Innovations in EV Charging
The muscle behind the magic comes from innovative hardware:
- High-Power Converters: Level 3 chargers house powerful AC-to-DC converters that efficiently transform incoming AC grid power into high-voltage DC for delivery to the battery.
- Heavy-Duty Cables: To handle the high currents involved, Level 3 stations use thick, specially designed cables to ensure safe and efficient power transfer between the charger and the vehicle.
Battery Management During Fast Charging
Fast charging is great for speed, but it’s important to manage battery health:
- Battery Management Systems (BMS): The car’s BMS plays a critical role. It monitors battery temperature, voltage, and current, regulating the charging process to prevent overheating and ensure safety.
- Cell Balancing: During charging, some battery cells may reach full capacity before others. The BMS employs cell balancing to ensure all cells are evenly charged, maximizing battery life.
Thermal Management Systems
Heat is a byproduct of fast charging. To prevent damage, thermal management systems are crucial:
- Liquid Cooling Systems: Many Level 3 chargers incorporate liquid cooling systems to regulate the temperature of power electronics and the battery pack during charging.
- Air Cooling Systems: Some chargers use air cooling systems for heat dissipation, though they may be less efficient than liquid cooling for very high-power applications.
How Fast Can Level 3 Chargers Power Up an EV?
Level 3 chargers, also known as DC fast chargers, are capable of delivering rapid charging speeds to electric vehicles (EVs), significantly reducing charging times compared to Level 1 and Level 2 chargers. The charging speed of Level 3 chargers can vary depending on several factors, including the charger’s power output, the EV’s battery capacity and state of charge, and external conditions such as temperature and network congestion.

Understanding Charging Times and Variables
The charging speed of a Level 3 charger is typically measured in kilowatts (kW) and represents the rate at which energy is transferred from the charger to the EV’s battery. Higher-powered Level 3 chargers can deliver faster charging speeds, allowing EVs to replenish their batteries more quickly.
Several variables can influence charging times when using Level 3 chargers:
- Charger Power Output: Higher-powered chargers can deliver more energy to the EV’s battery per unit of time, resulting in faster charging speeds. Level 3 chargers typically range from 50 kW to over 350 kW in power output.
- Battery Capacity: The size of the EV’s battery determines the amount of energy it can store and the time required to recharge it fully. EVs with larger battery capacities may take longer to charge than those with smaller batteries, even when using Level 3 chargers.
- State of Charge: Charging from a lower state of charge (SOC) to 80% typically occurs more rapidly than charging from 80% to 100%. This is because charging speed often tapers off as the battery approaches full capacity to protect the battery and prolong its lifespan.
- Temperature: Extreme temperatures, both hot and cold, can affect battery performance and charging efficiency. Charging speeds may be reduced in very cold temperatures to protect the battery, while overheating can also limit charging rates.
- Network Congestion: The availability of charging infrastructure and network congestion at charging stations can impact charging speeds. Busy charging stations may experience slower charging rates during peak times, while well-maintained infrastructure with adequate power supply can support faster charging speeds.
Case Studies: Real-World Charging Speeds
Real-world charging speeds achieved with Level 3 chargers can vary depending on the specific EV model, charger type, and environmental conditions. Here are some examples of typical charging times for popular EV models using Level 3 chargers:
- Tesla Model 3: With Tesla’s proprietary Supercharger network, the Model 3 can achieve charging rates of up to 250 kW, allowing it to replenish its battery from 10% to 80% in approximately 30 minutes.
- Chevrolet Bolt EV: The Bolt EV, equipped with CCS (Combined Charging System) fast charging capability, can charge at rates of up to 50 kW on compatible Level 3 chargers, providing approximately 90 miles of range in 30 minutes.
- Nissan LEAF: The Nissan LEAF, which supports CHAdeMO fast charging, can charge at rates of up to 50 kW on compatible Level 3 chargers, providing approximately 80% charge in 40-60 minutes, depending on the battery size and state of charge.
These case studies highlight the variability in charging speeds among different EV models and charging networks. While Level 3 chargers offer significantly faster charging compared to Level 1 and Level 2 chargers, actual charging times may vary based on several factors, emphasizing the importance of understanding charging variables and selecting compatible charging infrastructure to optimize the EV charging experience.
Frequently Asked Questions About Level 3 EV Charging: Unveiling the Mysteries
Level 3 charging offers a world of speed and convenience, but it also comes with some unique considerations. Let’s explore some frequently asked questions to shed light on these aspects.
Costs Associated with Level 3 Charging
Level 3 charging stations typically cost more per kWh compared to Level 2 stations. The exact cost can vary depending on factors like location, electricity prices, and the charging network provider. Here are some ways to manage the cost:
- Charging Network Memberships: Some charging networks offer memberships with discounted rates for Level 3 charging.
- Planning Your Route: Look for stations with competitive pricing along your travel route. Apps and websites can help you compare prices.
- Charge Only When Needed: Level 3 charging is ideal for quick top-ups on long trips. Utilize Level 2 charging for overnight or workplace charging whenever possible, as it’s usually more cost-effective.
Safety Tips for Level 3 Charging
Level 3 charging is a safe and well-established technology. However, as with any electrical application, it’s wise to follow these safety tips:
- Use the Correct Connector: Ensure your car’s DC fast-charging port is compatible with the charger’s connector (usually CCS or CHAdeMO).
- Park Safely: Follow the designated parking instructions at the charging station.
- Never Tamper with Equipment: Leave the equipment operation to the professionals. Report any malfunctions to the station operator.
- Keep an Eye on Your Car: While charging is generally automated, it’s good practice to monitor your car for any unusual signs.

Impact of Fast Charging
Electric vehicles are inherently eco-friendly, but the source of the electricity used for charging plays a role. Here’s how to consider the environmental impact of Level 3 charging:
- Grid Mix Matters: The environmental impact depends on the electricity mix in your region. If the grid relies heavily on fossil fuels, Level 3 charging might have a higher carbon footprint.
- The Future is Greener: As the world transitions towards renewable energy sources like solar and wind, the environmental impact of Level 3 charging will continue to diminish.
- Overall Benefit: Even with some considerations, Level 3 charging still offers a significant environmental benefit compared to gasoline-powered vehicles, especially as the grid gets cleaner.

Henry Michael is a leading expert in EV charging station research, specializing in innovative solutions for electric vehicle infrastructure. With a passion for sustainability and technological advancement, he is dedicated to advancing the accessibility and efficiency of EV charging worldwide.






