Smart EV Charging: A Revolution in Energy Efficiency and User Convenience
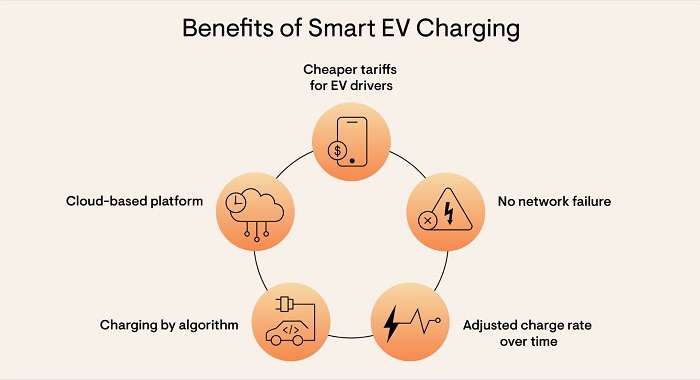
The electric vehicle (EV) landscape is undergoing a transformative shift, with smart charging systems emerging as a critical element in its evolution. These intelligent chargers go beyond simply replenishing battery power, offering a plethora of benefits that enhance the EV experience for both individuals and the grid.
Smart EV chargers are equipped with advanced features that allow them to optimize charging times, minimize grid impact, and even reduce electricity costs for users. Additionally, smart chargers offer remote monitoring and control, providing users with greater convenience and peace of mind.

Understanding Smart EV Charging
Smart EV charging refers to the integration of advanced technologies and intelligent systems into electric vehicle (EV) charging infrastructure. Unlike conventional charging systems, which simply supply power to charge the vehicle’s battery, smart EV chargers offer additional functionality and benefits that optimize the charging process.
Here’s an overview of the functionality and advantages of smart EV chargers over conventional systems:
- Remote Monitoring and Control: Smart EV chargers are equipped with connectivity features that allow users to remotely monitor and control the charging process. This means drivers can check the status of their vehicle’s charging session, start or stop charging, and adjust charging settings from their smartphones or other connected devices. Remote monitoring and control provide convenience and flexibility, allowing users to manage their charging needs more efficiently.
- Load Management: One of the key advantages of smart EV charging is load management. Smart chargers can communicate with utility providers and adjust charging rates based on grid demand and energy prices. This allows for more efficient use of electricity resources and helps reduce strain on the grid during peak demand periods. Load management features can also help users save money by charging when electricity rates are lower.
- Optimized Charging: Smart EV chargers often come with features that optimize the charging process for maximum efficiency. This includes capabilities such as scheduling charging sessions to take advantage of off-peak electricity rates, adjusting charging power based on vehicle battery capacity and state of charge, and prioritizing renewable energy sources when available. By optimizing charging, smart EV chargers can minimize energy waste and reduce charging times without compromising battery health.
- Data Analytics and Insights: Smart EV chargers collect and analyze data related to charging patterns, energy usage, and vehicle performance. This data can provide valuable insights to users, fleet operators, and utility companies, helping them make informed decisions about charging infrastructure planning, energy management, and fleet operations. Data analytics can also enable predictive maintenance and troubleshooting, improving overall system reliability and performance.
- Integration with Renewable Energy Sources: Many smart EV chargers support integration with renewable energy sources such as solar and wind power. By coordinating charging with renewable energy generation, users can reduce their carbon footprint and support the transition to a more sustainable energy system. Smart chargers can prioritize renewable energy sources when available and adjust charging schedules accordingly, maximizing the use of clean energy.

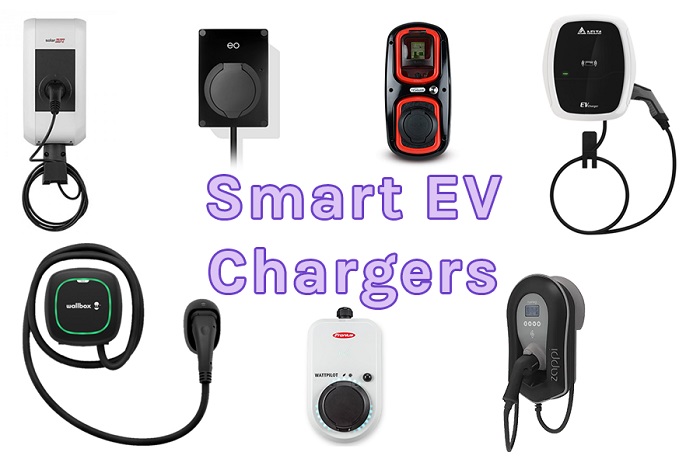
Key Features of Smart EV Chargers
1. Most Relevant Smart Charging Features
Among the array of smart charging features, power sharing, power boost, and dynamic power sharing stand out as particularly relevant for optimizing energy usage and accommodating multiple vehicles efficiently.
Power Sharing: This allows multiple EVs to share a single charger, dynamically adjusting power distribution based on individual needs.
Power Boost: Provides a temporary increase in charging power, ideal for topping off batteries before a long trip.
Dynamic Power Sharing: Enables the charger to adjust power consumption based on real-time grid conditions, helping to balance demand and reduce costs.
Overall, these smart charging features work in tandem to optimize energy usage, minimize charging times, and accommodate the diverse charging needs of multiple vehicles. By intelligently managing power allocation and adjusting charging rates in response to changing conditions, smart charging systems maximize the efficiency and effectiveness of electric vehicle charging, contributing to the broader goal of sustainable and environmentally friendly transportation.
2.Technological Comparisons
While all aim to optimize the charging process for electric vehicles (EVs), smart charging, bidirectional charging, and fast charging operate on distinct technological principles.
Smart charging utilizes intelligent algorithms to schedule charging during periods of low electricity demand, reducing strain on the grid and potentially lowering costs for EV owners. This technology relies on communication between the EV, charging station, and grid operator to dynamically adjust charging rates.
Bidirectional charging, also known as vehicle-to-grid (V2G), enables EVs to not only receive electricity but also feed it back into the grid. This technology allows EVs to act as distributed energy storage, providing grid operators with additional flexibility and resilience. Bidirectional charging requires specific hardware and communication protocols to ensure safe and efficient power transfer.
Fast charging focuses on delivering a high amount of energy to the EV battery in a short time. This technology typically uses high-power charging stations and specialized connectors to significantly reduce charging times compared to standard chargers. However, fast charging can generate significant heat and stress on the battery, potentially impacting its life span.
In summary, these technologies offer distinct approaches to EV charging, each with its own advantages and limitations. Smart charging prioritize grid efficiency and cost optimization, bidirectional charging enables EVs to participate in the grid as energy storage, and fast charging focuses on minimizing charging time. The choice of technology depends on various factors, including grid infrastructure, EV battery capacity, and individual charging needs.
User interaction and connectivity
Smart chargers are increasingly incorporating user interfaces and connectivity features that enhance the charging experience. App integration allows users to remotely monitor and control charging sessions, while remote management capabilities enable service providers to diagnose and troubleshoot issues. These features offer several benefits, including:
- Enhanced control: Users can start, stop, and schedule charging sessions remotely, optimizing energy usage and cost savings.
- Real-time monitoring: Users can track charging progress, energy consumption, and charger status in real-time, providing valuable insights into their charging habits.
- Remote diagnostics: Service providers can remotely diagnose and troubleshoot charger issues, minimizing downtime and improving customer satisfaction.
- Over-the-air updates: Firmware updates can be delivered wirelessly, ensuring users always have access to the latest features and bug fixes.
- Integration with Smart Home Systems
Smart chargers are evolving beyond simply topping off your electric vehicle’s battery. They are increasingly becoming integral components of a broader smart home ecosystem, interacting with other devices and systems to optimize energy usage and enhance the overall home experience.
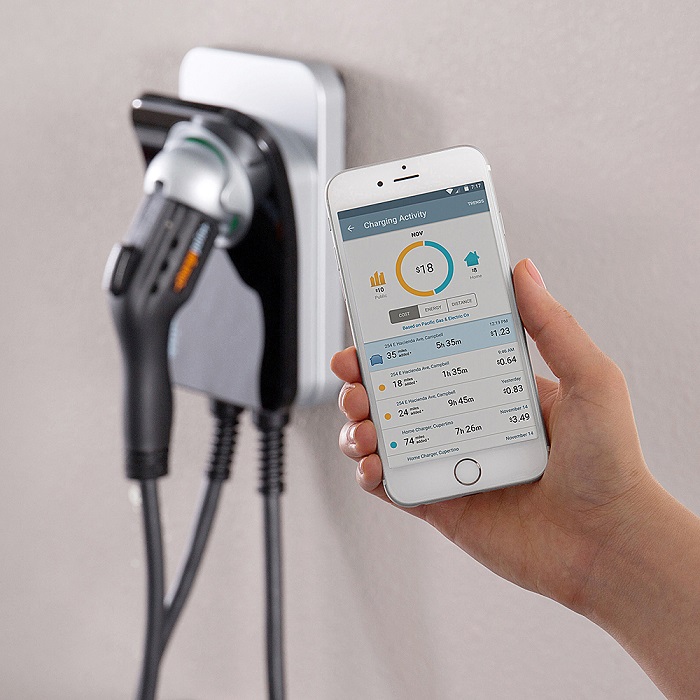

This integration allows for a more holistic approach to energy management, maximizing efficiency and cost savings.
- Energy Management Systems: Smart chargers can communicate with energy management systems within a smart home to optimize energy usage and coordinate charging schedules based on overall household energy needs. This integration enables smart chargers to adjust charging rates dynamically, taking into account factors such as solar generation, grid demand, and energy storage levels.
- Renewable Energy Integration: Smart chargers often support integration with renewable energy sources such as solar panels. By coordinating charging with solar generation patterns, smart chargers maximize the use of clean energy and reduce reliance on the grid. Integration with renewable energy systems allows homeowners to charge their electric vehicles using solar power generated on-site, further enhancing sustainability and reducing electricity costs.
- Home Automation Platforms: Smart chargers can be integrated into popular home automation platforms such as Amazon Alexa, Google Assistant, and Apple HomeKit. This integration enables users to control charging sessions using voice commands or mobile apps, providing convenient access to charging status and scheduling functionalities from anywhere within the home.
- Smart Grid Interaction: Smart chargers can communicate with utility companies and grid operators to participate in demand response programs and grid balancing initiatives. By adjusting charging rates based on grid conditions and energy prices, smart chargers help to alleviate strain on the grid during peak demand periods and support the integration of renewable energy resources.
- Electric Vehicle Integration: Smart chargers can interact with electric vehicles themselves to exchange data and optimize charging parameters based on vehicle specifications and battery health. This integration allows smart chargers to adjust charging rates dynamically, monitor vehicle charging status, and provide insights into energy consumption and charging history.
- Energy Monitoring and Analytics: Smart chargers often include built-in energy monitoring capabilities that provide real-time data on energy usage, charging efficiency, and costs. This data can be integrated into broader home energy management systems to provide insights into overall household energy consumption and optimize energy-saving strategies.
Market Options and Consumer Guidance
- Selecting the Right Smart EV Charger
By carefully considering your vehicle type, desired charging speed, user lifestyle, and preferred features, you can select the ideal smart EV charger that seamlessly integrates into your daily routine and maximizes the benefits of electric vehicle ownership. Remember to research and compare different models to find the best fit for your specific needs and budget.

Vehicle Compatibility: The first step is identifying chargers compatible with your EV’s charging port and power requirements. Different models offer varying levels of compatibility, so double-check the specifications to avoid any mismatches. For instance, Tesla vehicles require specific chargers, while most other EVs utilize the J1772 standard connector.
Charging Speed: Consider your desired charging speed. Level 1 chargers, typically included with EVs, provide a slow charge, making them ideal for overnight top-ups. Level 2 chargers offer significantly faster charging, perfect for daily commutes or longer trips. Level 3 chargers, also known as DC fast chargers, are the quickest option, but they are primarily found in public charging stations.
User Lifestyle: Your daily driving habits and access to charging facilities play a significant role in selecting the right charger. If you primarily drive short distances and have access to home charging, a Level 2 charger might suffice. However, frequent long-distance travel or limited home charging options might necessitate a Level 3 charger for faster charging on the go.
Additional Features: Modern smart chargers offer a plethora of additional features that enhance functionality and convenience. Wi-Fi or Bluetooth connectivity allows for remote monitoring and control of charging sessions through smartphone apps. Smart scheduling enables charging during off-peak hours for cost savings, while load balancing ensures efficient power distribution when multiple devices are connected.
- Comprehensive reviews of the top Smart Chargers
Here’s an overview of some of the top smart chargers on the market, along with their features, user feedback, and suitability for different environments:
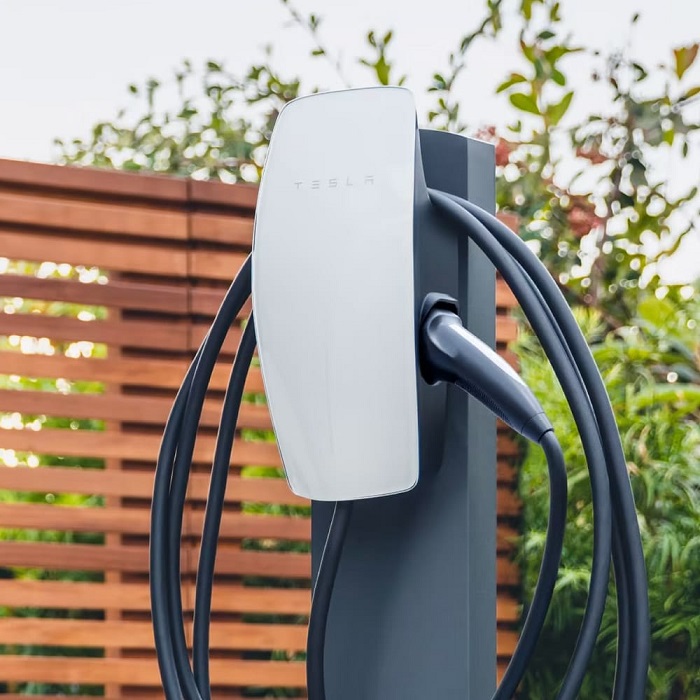
Tesla Wall Connector Gen 3:
- Features: Tesla’s Wall Connector Gen 3 offers up to 48 amps of power, enabling faster charging for Tesla vehicles. It has Wi-Fi connectivity for over-the-air updates and remote monitoring. It’s also compatible with Tesla’s energy management system for optimized charging.
- User Feedback: Users praise its sleek design and ease of use. The ability to monitor charging remotely is highly appreciated.
- Suitability: Ideal for residential settings, especially for Tesla owners who want faster charging at home.

JuiceBox Pro 40:
- Features: The JuiceBox Pro 40 supports up to 40 amps of charging power and offers smart grid features for energy optimization. It’s compatible with various electric vehicles and can be controlled remotely via a mobile app. It also supports Alexa voice control.
- User Feedback: Users appreciate its compatibility with different EVs and its energy-saving features. The mobile app receives positive feedback for its user-friendly interface.
- Suitability: Suitable for both residential and commercial settings, especially for users looking for energy-efficient charging solutions.
- Features: ChargePoint Home Flex is adjustable, allowing users to set the power output from 16 to 50 amps, catering to different EV charging needs. It offers smart scheduling, remote control, and real-time charging status updates via the mobile app.
- User Feedback: Users praise its flexibility in adjusting power output and scheduling charging sessions. The app interface is intuitive and easy to use.
- Suitability: Versatile for both residential and commercial settings, especially for users with varying charging needs or multiple EVs.
ClipperCreek HCS-40:
- Features: The ClipperCreek HCS-40 offers reliable charging at 32 amps and is compatible with all SAE J1772-compliant vehicles. It’s ruggedly built for outdoor use and features a durable, weatherproof enclosure.
- User Feedback: Users appreciate its durability and reliability. It’s often praised for its simple and straightforward operation.
- Suitability: Primarily
Technical Specifications and Safety
- Safety Features of Smart EV Chargers
Smart EV chargers are equipped with a range of safety features to ensure the protection of users and property. These include overcurrent and overvoltage protection, which prevent damage to the charger and vehicle in the event of electrical surges.
Additionally, smart chargers typically have built-in temperature monitoring and automatic shut-off mechanisms to prevent overheating. They also comply with stringent safety standards, such as UL and CE, which guarantee their reliability and performance.
Furthermore, smart chargers often integrate with home energy management systems, allowing users to optimize charging times and minimize the risks associated with overloading the electrical grid. These safety features make smart EV chargers a reliable and secure solution for charging electric vehicles.
- Regulatory Compliance and Industry Standards
Ensuring compliance with local and international regulations is paramount for the safe and reliable operation of charging solutions. This includes adherence to standards for electrical safety, electromagnetic compatibility, and communication protocols. Certified and compliant charging solutions provide assurance that they meet these requirements, minimizing risks and ensuring a positive user experience.
By prioritizing compliance, we can foster a robust and trustworthy ecosystem for electric vehicle charging, ultimately accelerating the transition to a sustainable future.
Economic and Environmental Impact
- Cost-Effectiveness and Savings
Smart chargers offer a compelling solution for optimizing energy consumption and reducing electricity bills. By strategically managing charging times based on grid demand and electricity pricing, they can significantly lower energy costs. Additionally, many utilities offer incentives for adopting smart charging technology, further enhancing their cost-effectiveness. This combination of reduced energy consumption and potential financial rewards makes smart chargers an attractive investment for both individuals and businesses.
- Environmental Advantages
Smart charging plays a crucial role in fostering environmental sustainability by seamlessly integrating with renewable energy sources and minimizing greenhouse gas emissions. By strategically aligning charging periods with peak renewable energy generation, smart charging optimizes energy consumption and reduces reliance on fossil fuels. This integration not only mitigates environmental impacts but also enhances grid stability by balancing energy demand and supply.
Additionally, smart charging promotes efficient energy utilization by minimizing charging during peak demand periods, thereby reducing the strain on power grids and further lowering emissions. Consequently, smart charging emerges as a pivotal tool in the transition towards a sustainable and decarbonized energy future.

Advanced Technologies and Future Directions
- Underlying Technologies and Future Innovations
Smart chargers utilize a sophisticated blend of technologies to optimize the charging process. Machine learning algorithms analyze data like battery health, grid conditions, and user preferences to determine the most efficient charging schedule. Additionally, communication protocols like OCPP (Open Charge Point Protocol) enable seamless integration with charging networks and energy management systems.
Looking ahead, artificial intelligence (AI) and predictive analytics are poised to revolutionize smart charging. AI can analyze vast datasets to predict energy demand and optimize charging strategies for individual users and entire networAI-powered predictive maintenance can foresee potential problems and reduce charger downtime.ime. These advancements promise to enhance efficiency, grid stability, and user convenience, paving the way for a smarter and more sustainable future of electric vehicle charging.
- Case Studies and Real-World Applications
Smart EV chargers are revolutionizing the electric vehicle landscape, offering numerous benefits for both users and the grid. Let’s explore some real-world examples:
- Apartment Buildings: In Amsterdam, a smart charging system was installed in an apartment complex, enabling residents to charge their EVs without overloading the grid. The system dynamically adjusts charging rates based on individual needs and grid capacity, ensuring efficient and equitable access to charging.
- Office Buildings: Many companies are adopting smart charging solutions for their employee parking lots. This allows them to manage energy consumption, reduce costs, and promote sustainability. For example, a tech company in California implemented a smart charging system that prioritizes charging during off-peak hours, significantly lowering their electricity bills.
- Public Charging Stations: Smart charging is becoming increasingly common in public charging stations. This allows for dynamic pricing based on demand and time of day, encouraging off-peak charging and optimizing grid utilization. Additionally, features like remote monitoring and reservation systems enhance user convenience and accessibility.

Smart EV chargers are not just a convenience, but a crucial element in optimizing the electric vehicle charging experience. They offer a plethora of benefits, including dynamic load balancing, remote monitoring, and integration with renewable energy sources. By choosing a smart charger, consumers can not only ensure a seamless charging experience but also contribute to a more sustainable future. With advancements in technology constantly evolving, it’s essential to look beyond immediate needs and invest in a charger that will adapt and grow with the future of electric mobility.
Additional Resources
1. Whitepapers:
- “Smart Charging: Accelerating the Adoption of Electric Vehicles” by Rocky Mountain Institute – This whitepaper provides insights into the benefits and challenges of smart charging and explores strategies for accelerating the adoption of electric vehicles through smart charging solutions.
2. Industry Reports:
- “Global Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure Market Report” by Market Research Future – This comprehensive report offers an in-depth analysis of the global electric vehicle charging infrastructure market, including market trends, growth drivers, challenges, and key players.
- “Smart Charging Infrastructure for Electric Vehicles: Market Analysis and Forecasts” by Navigant Research – This report examines the market dynamics and growth prospects of smart charging infrastructure for electric vehicles, covering technological innovations, regulatory developments, and market forecasts.
3. Webinars and Conferences:
- EVS (Electric Vehicle Symposium) – EVS is a biennial international conference and exhibition focused on electric vehicles and related technologies. It brings together industry experts, policymakers, researchers, and stakeholders to discuss the latest advancements and challenges in the field of electric mobility.
- Webinars hosted by industry organizations such as the Electric Power Research Institute (EPRI), the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), and the Smart Electric Power Alliance (SEPA) often cover topics related to smart EV charging, including technical innovations, policy developments, and market trends.

Henry Michael is a leading expert in EV charging station research, specializing in innovative solutions for electric vehicle infrastructure. With a passion for sustainability and technological advancement, he is dedicated to advancing the accessibility and efficiency of EV charging worldwide.






