AC Level 1 Chargers: A Reliable and Accessible Option for Electric Vehicle Charging
AC Level 1 chargers are the most basic and widely available type of charger for electric vehicles (EVs). They plug into a standard 120-volt household outlet, making them a convenient and accessible option for home charging.
While they offer slower charging speeds compared to higher-level chargers, they are a cost-effective and reliable solution for many EV owners.
Understanding the Basics of Level 1 Charging
A Level 1 charger is the simplest and most basic way to charge an electric vehicle (EV). It utilizes a standard household outlet (usually 120 volts AC) and the onboard charger within your EV to slowly replenish the battery.

- Electrical Outlet:
Level 1 charging utilizes a standard 120-volt AC electrical outlet, the same type you might find in your home for appliances like lamps or toasters. This makes Level 1 charging highly accessible since you can charge your EV wherever there’s a compatible outlet.
- Charging Speed:
Level 1 charging is the slowest of the three charging levels. It provides a low charging rate, usually delivering around 2-5 miles of range per hour of charging, depending on factors like the vehicle’s battery capacity and efficiency.
- Suitability:
Level 1 chargers are best suited for situations where the vehicle will be parked for an extended period, such as overnight charging at home or during the workday at the office. Since Level 1 charging is slow, it’s not ideal for quickly replenishing the battery, especially for long trips or daily commuting with significant driving distances.
- Convenience:
One of the primary advantages of Level 1 charging is its convenience. Since it uses standard household outlets, you don’t need any specialized charging equipment or infrastructure. You can simply plug your EV into any compatible outlet, whether it’s in your garage, driveway, or parking lot.
- Cost:
Level 1 charging is usually the most cost-effective option because it doesn’t require the installation of dedicated charging equipment. However, it may result in higher electricity bills over time due to the slower charging speed, especially if you rely on Level 1 charging for your daily charging needs.
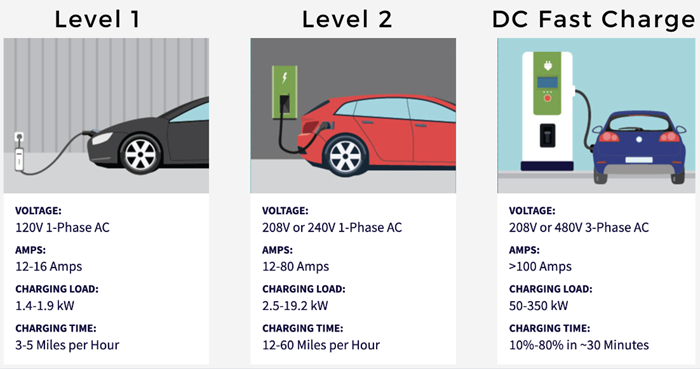
Additional factors to consider:
- Availability: Level 1 chargers are readily available at home, Level 2 chargers are becoming more common in homes and public places, and Level 3 chargers are primarily found at designated charging stations.
- Cost: Level 1 is the most economical, Level 2 has moderate installation costs, and Level 3 is the most expensive due to the high-power infrastructure required.
- Battery health: While infrequent use of DC Fast Charging is generally considered acceptable, some recommend Level 2 charging for regular use to minimize potential impacts on battery health with frequent high-power charging.
Benefits and Limitations of Level 1 Chargers for Electric Vehicle Owners
Level 1 chargers offer a convenient and readily available charging solution for electric vehicle owners.
- Benefits of Level 1 EV chargers:
Convenient Home Charging: Level 1 chargers offer the ultimate convenience for home charging. They utilize a standard 120-volt AC household outlet, eliminating the need for any special equipment installation. Simply plug your EV into a wall outlet, and you’re good to go. This is perfect for people who park their EVs in their garage or driveway overnight.
Cost-Effectiveness and Affordability: Level 1 charging is the most budget-friendly option for EV owners. It leverages your existing household electrical infrastructure, so there are no additional installation costs associated with the charger itself. You simply pay for the electricity used during charging.
Suitable for Daily Commutes: If your daily commutes are short, and you have access to overnight charging at home, a Level 1 charger might be sufficient. Even with a slow charging rate, you can likely replenish enough range overnight to cover your daily driving needs.
Easy to Use: There’s no complex setup or operation involved with Level 1 charging. Simply plug it in and let your EV’s onboard charger handle the conversion of AC power to DC power for the battery.

- Limitations of Level 1 Chargers:
Extremely Slow Charging: The biggest drawback of Level 1 chargers is their slow charging speed. Typically, they only add 3-5 miles of range per hour of charging. This can be impractical for situations where you need a quick charge before heading out.
Limited Range Gain: The slow charging rate makes Level 1 unsuitable for long trips. Unless you have access to charging overnight at your destination, a Level 1 charger wouldn’t be able to provide enough range for extended journeys.
Not Ideal for All EVs: While most modern EVs are compatible with Level 1 charging, some older models or those with very large battery packs might not be suitable for this slow charging method due to limitations in their onboard chargers.
- Common Misconceptions About Level 1 Charging
| Misconceptions | Fact |
| Level 1 charging is unsafe. | Level 1 chargers are designed for safe operation on standard household circuits. However, it’s always recommended to follow the manufacturer’s instructions and avoid using damaged cords or outlets. |
| You can use an extension cord for Level 1 charging. | Using a regular extension cord is not recommended due to safety concerns. The wiring in most extension cords might not be able to handle the sustained electrical load associated with EV charging. It’s best to plug directly into a wall outlet. |
| Level 1 charging only provides enough range for short trips. | Level 1 charging can still replenish a significant portion of the battery’s capacity overnight, providing ample range for daily commuting and errands. |
| It is inconvenient due to the longer charging times compared to higher-level chargers. | For many EV owners, the convenience of being able to charge at home outweighs the slower charging speed, especially when factoring in the cost savings and accessibility of Level 1 charging. |
Proper Usage and Safety Measures for Level 1 Charging
Level 1 charging, while convenient and affordable, requires proper usage and safety precautions to ensure a smooth and safe experience.
- Charging Speed with a Level 1 Charger:
Typical Range Gain: Expect 3-5 miles of range added per hour of charging.
Full Charge Times: Depending on your battery capacity, a full charge from empty can take anywhere from 10 to 40 hours.
- Installation and Usage Tips for Level 1 EV Chargers:
Use a Dedicated Circuit: Plug your Level 1 charger into a dedicated circuit to prevent overloading the electrical circuit and ensure safe charging.
Check Electrical System: Before installation, ensure your home’s electrical system can support Level 1 charging. Consider consulting an electrician if you’re unsure about your home’s electrical capacity.
Proper Outlet Placement: Install the charging cord where it won’t create tripping hazards or be exposed to water or other elements.
Inspect Charging Equipment: Regularly inspect the charging cable and outlet for signs of damage or wear. Replace any damaged components promptly.
Monitor Charging: Keep an eye on the charging progress and unplug the charger once the battery is sufficiently charged to prevent overcharging.

- Guidelines for Home Installation of a Level 1 Charger:
Level 1 chargers can typically be plugged into any standard 120-volt household outlet. Ensure the outlet is located in a convenient and accessible location, ideally near where you park your EV.
If the outlet is not located near your parking spot, consider using an extension cord rated for outdoor use and suitable for the charging load.
- Installation Requirements and Costs:
Installing a Level 1 charger is relatively straightforward and typically doesn’t require professional installation. However, if you need to install a dedicated outlet or circuit, you may need to hire an electrician, which can incur additional costs.
The primary cost associated with Level 1 charging is the purchase of the charging cable, which varies depending on the manufacturer and features.
- Factors Impacting Your Charging Station Decision:
Consider your daily driving habits and charging needs when choosing between Level 1, Level 2, or Level 3 charging options.
Evaluate the availability of charging infrastructure in your area, including public charging stations and workplace charging options.
Factor in the cost of installation, equipment, and electricity when deciding on the most suitable charging solution for your EV.
Cost Considerations for Level 1 and Level 3 Charging Stations
Here’s a breakdown of the cost considerations for Level 1 and Level 3 EV charging stations:
Level 1 Charger:
Level 1 charging is the most economical option. There’s no upfront charger cost, and it leverages your existing electrical infrastructure, eliminating installation charges. You simply pay for the electricity used during charging.
- Charger Cost: Very Low (In most cases, no additional charger cost is needed)
- Installation Cost: None (Utilizes a standard household outlet)
- Electricity Cost: You pay the standard electricity rate for your home. Depending on your electricity provider, off-peak charging rates might be available, potentially offering lower costs.
Level 3 Charger (DC Fast Charger):
Level 3 chargers are not suitable for personal home use due to the extremely high cost of purchasing and installing the equipment. Typically, businesses or government agencies deploy these chargers, and EV users can access them at designated charging stations.
- Charger Cost: Very High (These chargers require specialized equipment and are not sold for personal home use)
- Installation Cost: Very High (Requires a high-power grid connection and specialized installation by professionals)
- Electricity Cost: Charging costs at DC Fast Charging stations can be higher than the electricity rates you pay at home. The pricing models can vary depending on the charging network operator.
Here’s a table summarizing the key cost considerations:
| Factor | Level 1 Charger | Level 3 Charger (DC Fast Charger) |
| Charger Cost | Very Low | Very High (Not for personal use) |
| Installation Cost | None | Very High |
| Electricity Cost | Standard home electricity rate (potentially lower off-peak rates) | Higher than home electricity rates (varies by network) |
Additional factors to consider:
- Frequency of Use: If you only plan to use DC Fast Charging occasionally on long trips, the occasional higher charging costs might be acceptable. However, for frequent use, Level 2 charging or home charging with Level 1 might be more cost-effective in the long run.
- Public Charging Network Fees: Some public charging networks might have membership fees or additional service charges on top of the electricity costs for using their charging stations, including DC Fast Chargers.
By considering these cost factors and your individual driving habits, you can make an informed decision about the most economical charging solution for your electric vehicle.
Maximizing the Efficiency of Level 1 Charging for Electric Vehicle Owners
Level 1 charging, while slow, can be a viable option for some EV owners. Here are some tips to optimize its usage and efficiency:
- Tips for Optimal Usage and Charging Speed:
Schedule Charging Strategically: If your electricity provider offers time-based rates, schedule charging sessions during off-peak hours when electricity costs are typically lower. This can significantly improve the overall cost-effectiveness of Level 1 charging.
Minimize Charging Losses: Avoid extreme temperatures (very hot or cold) during charging, as this can impact efficiency. Ideally, charge in a climate-controlled garage or shaded area whenever possible.

Park Close to the Outlet: Park your EV as close as possible to the outlet to avoid using an extension cord. Extension cords can introduce resistance and reduce charging efficiency.
Maintain Proper Tire Pressure: Keeping your tires properly inflated reduces rolling resistance, which can indirectly improve overall range and efficiency, even with slower Level 1 charging.
Reduce Cabin Conditioning: While plugged in, limit pre-conditioning or climate control usage in your EV. These features can consume additional battery power and slow down charging.
- Regular Inspections and Cleaning Procedures:
Inspect the Charger: Regularly check the Level 1 charging cable for any signs of damage or fraying. Damaged cords can pose safety hazards and reduce efficiency.
Outlet Maintenance: Ensure the outlet you’re using is in good condition and free of dust or debris. Loose connections can also impact charging efficiency.
Clean Charging Contacts: Occasionally clean the charging contacts on both the EV and the charger with a dry cloth to remove any dirt or buildup that might hinder proper connection.
- Optimizing Charging Efficiency and Battery Performance:
Don’t Fully Deplete the Battery: It’s generally recommended to avoid letting your EV’s battery completely drain before charging. Regularly topping up the battery with Level 1 charging during off-peak hours can help maintain battery health and potentially improve efficiency over time.
Consult the Manual: Always refer to your EV’s owner’s manual for specific recommendations on charging practices and battery care. Different EVs might have slight variations in optimal charging strategies.
Considerations for Home and Public Charging
While Level 1 charging offers a convenient and budget-friendly option, deciding between a home charger or using public stations depends on your individual needs and driving habits. Here’s a breakdown of the key factors to consider:

- Home Level 1 Charger Installation:
Electrical Capacity: Ensure your home’s electrical system can handle the additional load of EV charging. Consulting a qualified electrician is recommended if you are unsure about your system’s capacity.
Outlet Requirements: A dedicated 120-volt AC outlet in good condition is ideal. Avoid outlets with loose wiring or signs of overheating. Using extension cords is not recommended.
EV Model Compatibility: Most modern EVs are compatible with Level 1 charging. However, consult your owner’s manual to confirm compatibility, especially for older models.
Charging Time and Battery Health: Level 1 charging is slow. Expect long charging times (10–40 hours for a full charge). Frequent use might not be ideal for battery health in some EVs. Consult your manual for recommendations.
- Public Level 1 Charging Stations:
Accessibility and Availability: Public Level 1 stations are less common than Level 2 or DC Fast Charging stations. Availability might be limited, depending on your location.
Cost Comparison: Public charging stations might have usage fees, which can add up over time compared to charging at home with your own Level 1 charger.
Convenience and Flexibility: Public stations offer the flexibility to charge on the go, but you might need to wait for availability, especially if demand is high.
Here’s a table summarizing the key considerations:
| Factor | Home Level 1 Charge | Public Level 1 Charging Station |
| Installation | Requires minimal setup (outlet check) | No installation is required |
| Cost | Low (electricity cost) | Usage fees may apply |
| Convenience | Highly convenient (charge overnight) | Less convenient (availability, wait times) |
| Accessibility | Guaranteed access at home | Subject to station availability |
| Charging Speed | Slow (10–40 hours for a full charge) | Slow (10–40 hours for a full charge) |
| Battery Health | Frequent use might impact some EVs | May not be ideal for frequent top-ups |
In essence:
- Home Level 1: Ideal for those with short commutes, access to overnight charging at home, and compatible EVs. It’s the most economical option in the long run.
- Public Level 1: A suitable option for occasional top-ups on the go, especially if you have access to a free public station near you. However, relying heavily on public Level 1 stations might not be practical due to limitations in availability and charging speed.
Choosing the Right Charging Station for Your Electric Car: Factors to Consider
Choosing the right charging station for your electric car involves several factors to consider. Here’s a comprehensive guide:
- Charging Speed and Power Output: Determine the charging speed you need based on your driving habits and charging requirements. Level 1 chargers provide the slowest charging speed, while Level 2 and Level 3 chargers offer faster charging options. Consider the power output of the charging station, measured in kilowatts (kW), which impacts charging speed. Higher power output results in faster charging times.
- Compatibility with Your Electric Car: Ensure compatibility between the charging station and your electric car. Check the plug type, connector, and communication protocol (e.g., J1772 for Level 1 and Level 2 chargers, CCS or CHAdeMO for Level 3 chargers) to ensure they match your vehicle’s specifications.
- Home or Public Charging: Decide whether you need a charging station for home use, public charging, or both. Home charging stations, such as Level 1 or Level 2 chargers, offer convenience and accessibility, while public charging stations provide flexibility for charging on-the-go. Consider installing a Level 2 charger at home for faster charging or accessing public charging stations for longer trips or emergency charging needs.
- Installation and Electrical Requirements: Assess your home’s electrical capacity and infrastructure to determine the feasibility of installing a charging station. Consider factors such as available electrical outlets, circuit capacity, distance to parking spots, and any necessary electrical upgrades. Level 1 chargers typically use standard 120-volt household outlets, while Level 2 and Level 3 chargers may require dedicated circuits and professional installation.
- Cost and Budget: Evaluate the cost of purchasing and installing the charging station, including equipment, installation fees, and any additional electrical work. Consider long-term savings on fuel costs, potential incentives or rebates, and the overall return on investment (ROI) of the charging station. Balance your budget with desired features and charging speed to find the right charging solution for your needs.
- Network and Accessibility: Research the availability and accessibility of charging networks in your area. Consider factors such as the number of charging stations, network coverage, reliability, and user experience. Choose a charging station compatible with popular charging networks or with wide network coverage to ensure accessibility and convenience.
- Features and Connectivity: Look for additional features and connectivity options that enhance the user experience and convenience. This may include smartphone apps for monitoring and controlling charging sessions, Wi-Fi connectivity, RFID authentication, and integration with smart home systems or energy management platforms.
By considering these factors, you can choose the right charging station for your electric car that meets your charging needs, budget, and lifestyle preferences. Be sure to research and compare different charging stations, consult with electricians or experts if needed, and plan for future scalability as electric vehicle technology continues to evolve.
AC Level 1 chargers offer a reliable and accessible entry point into EV charging. While their slow charging speed might not be suitable for everyone, they remain a valuable option for many EV owners, particularly those with limited driving needs or who prioritize affordability and convenience.
As EV adoption continues to grow, Level 1 chargers will likely remain a popular choice for home charging due to their widespread availability and ease of use.

Henry Michael is a leading expert in EV charging station research, specializing in innovative solutions for electric vehicle infrastructure. With a passion for sustainability and technological advancement, he is dedicated to advancing the accessibility and efficiency of EV charging worldwide.






