Explore the implications of Level 1 EV charging kW/h.
Level 1 EV charging, while slower than its higher-powered counterparts, offers a multitude of benefits for both drivers and the environment. Utilizing standard household outlets, Level 1 charging provides a convenient and accessible way to power your electric vehicle, particularly for short commutes or overnight charging.

What is Level 1 EV Charging?
Understanding the Basics of Level 1 Charging
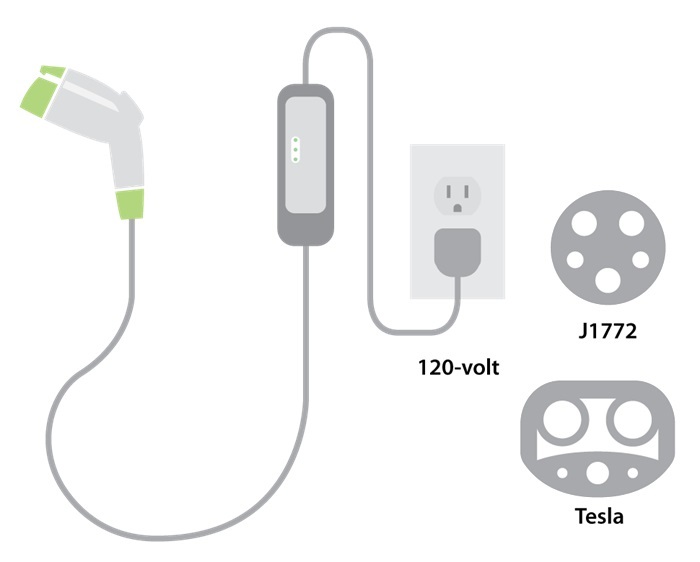
Level 1 charging is the slowest but most basic method for charging an electric vehicle (EV). It uses the same type of outlet you’d find in your home, typically a 120-volt (V) outlet. The charger that comes with most EVs is a Level 1 charger, making it a convenient option for topping off your battery at home overnight or when you have access to an outlet.
Here’s a breakdown of Level 1 charging:
- Standard Outlet Usage: Level 1 charging utilizes a standard 120-volt AC household outlet, making it widely accessible.
- Charging Speed: It is the slowest form of EV charging, typically providing around 2-5 miles of range per hour of charging, depending on the vehicle.
- Charging Equipment: Level 1 charging doesn’t require any special equipment other than the EV’s charging cable, which usually comes with the vehicle.
- Convenience: Since it uses standard outlets, Level 1 charging can be done almost anywhere there’s an available outlet, including home garages, workplaces, or public parking spaces.
Benefits of Level 1 Charging for EV Owners
Despite its slow speed, Level 1 charging offers some advantages:
- Accessibility: Level 1 charging is accessible to almost all EV owners since it only requires a standard household outlet, eliminating the need for specialized charging infrastructure.
- Cost-Effectiveness: It is the least expensive charging option since it doesn’t require the installation of dedicated charging stations.
- Convenience: Level 1 charging provides the flexibility to charge your EV wherever there’s a standard outlet, offering convenience for daily charging needs.
However, it’s important to remember that Level 1 charging is best suited for situations where you have ample time to charge, such as overnight.
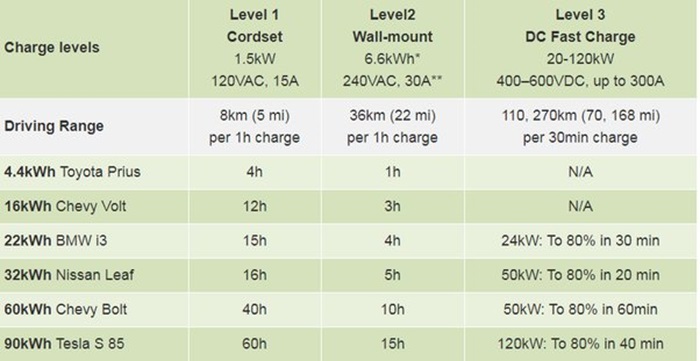
Level 1 vs. Level 2 Charging: A Comparison
Here’s a table summarizing the key differences between Level 1 and Level 2 charging:
| Feature | Level 1 Charging | Level 2 Charging |
| Voltage | 120V | 240V |
| Power | 1.2-2.4 kW | 6.2-19.2 kW |
| Charging Speed | Slow (3-5 miles per hour) | Faster (20-30 miles per hour) |
| Installation | No | May require installation |
| Cost | Lower (no installation cost) | Higher (installation cost) |
| Ideal Use | Overnight charging | Daily charging |
In summary, Level 1 charging provides a basic, accessible, and cost-effective way to charge EVs, especially for those with shorter daily driving distances or who have access to charging at home or work. However, for faster charging speeds and increased convenience, Level 2 charging may be a more suitable option for some EV owners, depending on their specific needs and usage patterns.
How Many kWh Does Level 1 EV Charging Consume?
The amount of kWh (kilowatt-hours) consumed during Level 1 EV charging depends on several factors, including the battery size of the EV, the charging efficiency, and the duration of charging. Here’s how you can calculate kWh usage for Level 1 charging and some tips to optimize kWh consumption:
Calculating kWh Usage for Level 1 Charging
- Battery Size: Determine the total capacity of your EV’s battery in kWh. Usually, the manufacturer will provide this information or it will be in the vehicle’s specifications.
- Charging Efficiency: Consider the charging efficiency of your EV, which is typically around 85-90%. This accounts for energy losses during the charging process.
- Charging Duration: Measure the duration for which you are charging your EV using Level 1 charging.
The formula to calculate kWh usage for Level 1 charging:
Energy Consumed (kWh) = Battery Capacity (kWh) x Charging Efficiency x Charging Duration (hours)
For example, if your EV has a battery capacity of 60 kWh, and you charge it for 8 hours with a charging efficiency of 90%, the calculation would be:
Energy Consumed = 60{kWh} x 0.90 x 8{hours} = 432 {kWh}
Tips to Optimize kWh Consumption During Level 1 Charging
- Charge During Off-Peak Hours: Electricity rates may vary depending on the time of day. Charging during off-peak hours when electricity demand is lower, can help reduce kWh costs.
- Manage Charging Times: Adjust your charging schedule based on your daily driving needs. Charging for longer periods at a slower rate (e.g., overnight) can maximize kWh usage efficiency.
- Limit Auxiliary Loads: Minimize the use of auxiliary loads such as heating, air conditioning, and entertainment systems while charging to optimize kWh consumption for charging the battery.
- Monitor Charging Progress: Many EVs provide charging progress indicators, allowing you to track kWh consumption during charging sessions. Monitoring this information can help you optimize your charging habits over time.
By understanding how to calculate kWh usage for Level 1 charging and implementing optimization tips, EV owners can efficiently manage their charging routines while minimizing electricity costs and environmental impact.
Is Level 1 Charging Sufficient for Your EV?
Determining if Level 1 charging is sufficient for your EV depends on various factors related to your lifestyle, driving habits, and charging needs. Here are some key considerations to help you decide if Level 1 charging fits your EV lifestyle:

Factors to Consider Before Opting for Level 1 Charging:
- Daily Driving Distance: Evaluate your typical daily driving distance. If you have a shorter commute or drive fewer miles each day, Level 1 charging may be sufficient to meet your daily charging needs, especially if you have enough time to charge overnight.
- Battery Capacity: Consider the size of your EV’s battery. If your EV has a smaller battery capacity and you drive relatively short distances, Level 1 charging may provide adequate range for your daily needs with overnight charging.
- Charging Time: Assess your daily schedule and charging patterns. Level 1 charging is slower compared to Level 2 or DC fast charging, so if you have long gaps between daily driving or can leave your EV plugged in for extended periods, Level 1 charging may be suitable.
- Access to Charging Outlets: Determine the availability of standard 120-volt outlets in your home, workplace, or other locations where you park your EV. If you have easy access to outlets and can charge your EV overnight or during extended periods of parking, Level 1 charging may be convenient.
- Driving Patterns: Analyze your driving patterns, including any occasional long-distance trips. While Level 1 charging may be sufficient for daily driving, if you frequently take longer trips or need to recharge quickly while on the road, you may need access to faster charging options.
- Time Flexibility: Consider your flexibility in charging times. Level 1 charging is slower but can be effective if you have the flexibility to charge your EV overnight or during periods of extended downtime.
- Cost Considerations: Evaluate the cost of installing Level 2 charging infrastructure versus using Level 1 charging. While Level 1 charging is more accessible and cost-effective, investing in Level 2 charging may provide faster charging speeds and added convenience if it fits within your budget.
By carefully considering these factors, you can determine if Level 1 charging aligns with your EV lifestyle and meets your daily charging requirements. Keep in mind that Level 1 charging may be suitable for some EV owners, particularly those with shorter daily driving distances and access to convenient charging outlets, while others may benefit from faster charging options such as Level 2 or DC fast charging, depending on their specific needs and preferences.
Impacts of Level 1 Charging on Energy Bills
Level 1 charging can definitely impact your energy bill, but the effect is generally considered less significant compared to Level 2 charging. Here’s a breakdown of the key points:

- Lower overall energy consumption: Level 1 chargers use less power (1.2–2.4 kW) compared to Level 2 chargers (6.2–19.2 kW), translating to fewer kWh consumed per charging session.
- Slower charging translates to spread-out energy use: While you’ll use less power per hour, Level 1 charging takes longer to fully charge your battery. This can be advantageous if you have time-of-use electricity plans where rates are cheaper during off-peak hours. You can schedule charging for these times to minimize costs.
- The cost ultimately depends on your electricity rate: Multiply the kWh used (from your calculation in the previous section) by your electricity rate per kWh to determine the charging cost.
Here are some additional factors to consider:
- Charging frequency: The more frequently you charge, the bigger the impact on your bill.
- Efficiency losses: A small amount of energy is lost during charging regardless of the charger type. However, losses might be slightly higher with Level 1 due to longer charging times.
Overall, Level 1 charging offers a more cost-effective way to charge your EV compared to Level 2, especially if you can take advantage of off-peak electricity rates.
However, keep in mind the trade-off for charging speed. If you need more flexibility or have a longer commute, a Level 2 charger installation at home might be a better option, despite the potentially higher electricity cost.

Henry Michael is a leading expert in EV charging station research, specializing in innovative solutions for electric vehicle infrastructure. With a passion for sustainability and technological advancement, he is dedicated to advancing the accessibility and efficiency of EV charging worldwide.






