Level 1 EV Charging Power: A Slow and Steady Approach
Level 1 EV charging, also known as “trickle charging,” utilizes a standard 120-volt household outlet. It delivers the slowest charging rate, typically adding around 3-5 miles of range per hour.
While it is convenient for overnight charging at home, Level 1 is not suitable for long-distance travel due to its extended charging times.
This method is best suited for topping off the battery or for situations where faster charging options are unavailable.

Understanding Level 1 EV Charging: The Ultimate Guide
As electric vehicles (EVs) continue to gain popularity, understanding the fundamentals of EV charging becomes increasingly important. Level 1 EV charging serves as the entry point into the world of electric vehicle ownership. This comprehensive guide aims to unravel the intricacies of Level 1 EV charging, from its basics to its power capabilities and differences from Level 2 charging.
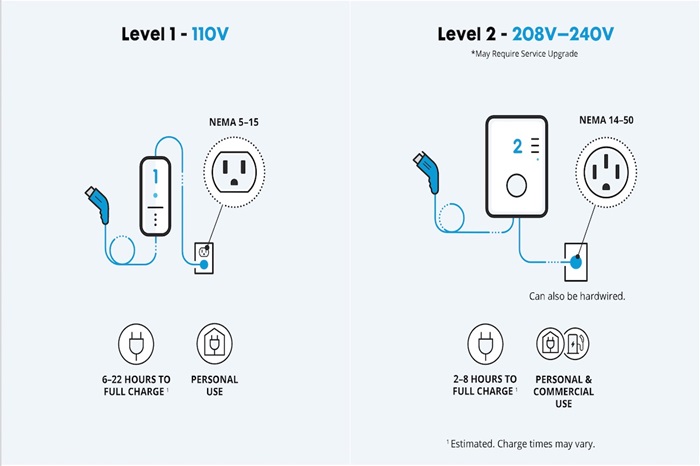
Level 1 EV charging, often referred to as “trickle charging,” utilizes a standard 120-volt household outlet. While convenient and readily accessible, it delivers the lowest power output among EV charging options. This translates to longer charging times, typically adding around 3-5 miles of range per hour.
Level 1 chargers can be easily plugged into existing household outlets without the need for specialized equipment or infrastructure. Due to its slower charging rate, Level 1 charging is best suited for overnight charging or scenarios where rapid charging is not required.
While not ideal for daily commutes or long-distance travel, Level 1 charging proves valuable for residential use, workplace charging, and scenarios where vehicles have extended periods of downtime, such as overnight parking. Understanding Level 1 charging’s capabilities and limitations is crucial for maximizing your electric vehicle experience.

Comparing EV Charging Levels: From Level 1 to Level 3
Understanding the differences and benefits of various EV charging levels is essential for EV owners to make informed decisions regarding their charging infrastructure. Whether it’s the convenience of Level 1 charging, the efficiency of Level 2 charging, or the rapid charging capabilities of Level 3 stations, each charging level offers unique advantages to meet the diverse needs of electric vehicle drivers.
| Compare | Level 1 Charging | Level 2 Charging | Level 3 Charging |
| Evaluation | The Slow and Steady Charger | The Workhorse Charger | The Supercharger |
| Think of it as | Plugging in your phone charger at home. | Filling up your car at a gas station, but with electricity! | The “gas station pitstop” for electric vehicles. |
| Power | Utilizes a standard 120V AC household outlet, providing 1.3-2.4 kW. | Uses a 240V AC outlet, delivering 6.2-19.2 kW of power (significantly higher than Level 1). | Utilizes DC (Direct Current) fast charging technology with voltages exceeding 400V and power reaching up to 100+ kW. |
| Charging Speed | Adds only 3-5 miles of range per hour, meaning a full charge can take up to 40 hours! | Offers a substantial jump, adding 25-50 miles of range per hour, making overnight charging or daily top-ups practical. | The king of speed, providing enough juice for long trips in a fraction of the time. You can expect to gain 70-200 miles of range within 30 minutes! |
| Upsides | Convenient and accessible, it’s perfect for topping off your battery overnight at home. No additional equipment is needed (the charger typically comes with your EV). | Significantly faster charging than Level 1. It is found at public charging stations and workplaces, making it a convenient option for daily use. | Perfect for long journeys when you need a quick and significant battery boost. |
| Downsides | Extremely slow charging times. Not ideal for everyday charging unless you have ample time. | Requires the installation of a 240V outlet, which might incur some cost. Not as widely available as Level 1 outlets. | The fastest charging option, is also the least common. May have availability limitations compared to Level 1 & 2. Potential for slightly higher charging costs compared to other levels. |
By exploring the features, speeds, and advancements of Level 1, Level 2, and Level 3 charging, EV enthusiasts can optimize their charging experiences and contribute to the widespread adoption of electric vehicles.
Benefits and Limitations of Level 1 Charging
Level 1 charging, despite being the slowest option, offers some undeniable advantages for home EV charging. Let’s delve into the benefits and limitations to see if it aligns with your needs.
Benefits of Level 1 Charging:
- Simple and Accessible: The biggest perk? Plug-and-play simplicity. No special installation is required. Just use a standard household outlet, making it perfect for topping off your battery overnight at home.
- Cost-Effective: This is the most budget-friendly option. You don’t need any additional equipment beyond the charging cable that typically comes with your EV.
- Easy to Use: Forget complicated settings or unfamiliar stations. Level 1 charging is as straightforward as plugging in your phone charger.
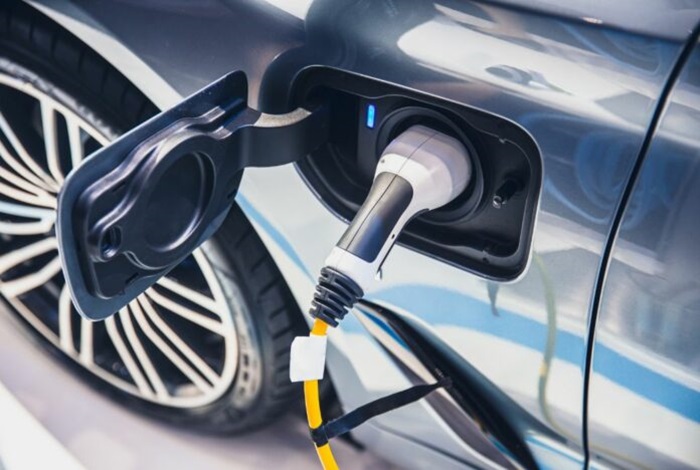

Limitations of Level 1 Charging:
- Slow and Steady Wins the Race (Eventually): Here’s the trade-off for simplicity: Charging speeds are around 3-5 miles per hour, meaning a full charge can take a very long time (think up to 40 hours for a depleted battery). This might not be practical for everyday needs, especially if you have a long commute.
- Limited Range Recovery: Need a quick boost before a trip? Level 1 might not be the answer. It’s not ideal for situations where you need a significant range to increase rapidly.
- Outlet Circuit Considerations: While convenient, using a dedicated outlet for charging is recommended. This helps avoid overloading your home’s electrical circuit, which could lead to safety hazards or tripping breakers.
Level 1 charging, when used properly, shouldn’t negatively impact your battery life. However, frequent charging cycles, regardless of the charging level, can contribute to battery degradation over time. Therefore, it’s essential for EV owners to follow manufacturer recommendations and best practices for charging to optimize battery health and longevity.
Charging Considerations for Level 1 EV Owners:
- Driving Habits: If you have a short daily commute and charge overnight, Level 1 might be sufficient to keep you going.
- Access to Faster Charging: Plan on taking longer trips or need a quicker top-up occasionally? Consider having access to Level 2 charging stations for those situations.
- Home Electrical System: Ensure your home’s electrical system can handle the additional load of Level 1 charging, especially if using a standard outlet. Consulting a qualified electrician can provide peace of mind.
Optimizing Charging with Level 1 Chargers at Home
Level 1 charging, while slow, can be a reliable way to keep your EV topped off at home. Here are some tips to optimize your charging experience:.

- Planning and Scheduling:
Night Owl Charging: Take advantage of off-peak electricity rates if available in your area. Schedule charging to begin at night, when electricity costs are typically lower.
Know Your Range: Plan your charging sessions based on your daily or weekly driving needs. If you only have a short commute, a few hours of overnight charging with Level 1 might be sufficient.
Track Your Battery: Monitor your battery level and plan charging accordingly. Avoid letting your battery completely drain before plugging in, as this can be stressful on the battery over time.
- Maximizing Efficiency:
The Right Outlet: Use a dedicated outlet for charging whenever possible. This reduces the risk of overloading circuits and ensures optimal charging performance.
Weather Matters: Extreme temperatures (hot or cold) can impact charging efficiency. If possible, park your car in a climate-controlled garage while charging.
Lighten the load: Turn off unnecessary electronics in your car while charging to minimize power draw.
- Safety First:
Inspect Your Charger: Regularly inspect your charging cable for any signs of damage or wear. Don’t use a faulty charger.
Extension Cord Caution: Avoid using long extension cords for charging. They can cause voltage drops and potential safety hazards.
Know Your Limits: Consult your car’s owner’s manual for specific charging recommendations and safety precautions.
- Beyond Level 1:
Consider Level 2: If Level 1 charging doesn’t meet your needs due to longer charging times, explore the possibility of installing a Level 2 charger at home. This can significantly reduce charging times and offer greater flexibility.
Public Charging Options: For longer trips or situations where a quick top-up is needed, familiarize yourself with public charging station locations and their charging speeds (Level 2 or 3).
By following these tips, you can optimize your Level 1 charging experience and ensure a smooth, efficient, and safe home charging routine for your electric vehicle.
Potential Impacts of Level 1 Charging on the Electric Vehicle Market
Level 1 charging, despite its slow speed, can have some interesting positive impacts on the EV market:

- Lower Barrier to Entry: The fact that Level 1 charging utilizes standard household outlets eliminates the need for expensive installation of charging infrastructure. This can make EVs more accessible to a wider range of consumers, especially those who live in apartments or areas with limited access to public charging stations.
- Reduced Cost of Ownership: Since Level 1 charging requires no additional equipment beyond the cable that typically comes with the car, it’s the most cost-effective charging option. This can be a significant advantage for budget-minded consumers, considering the initial cost of EVs.
- Increased Home Charging Convenience: The simplicity of plugging into a standard outlet makes Level 1 charging incredibly convenient for home charging. This can encourage more frequent charging and potentially reduce “range anxiety” for some EV owners.
However, there are also some limitations to consider:
- Limited Range Recovery: The slow charging speed of Level 1 can be a major drawback for some consumers. It might not be suitable for those who need to recharge quickly or drive long distances frequently. This could limit the overall appeal of EVs for certain segments of the market.
- Potential Strain on the Electrical Grid: Widespread adoption of EVs relying solely on Level 1 charging could put a strain on the electricity grid during peak charging times, especially in areas with limited power generation capacity. Upgrading the grid infrastructure might be necessary to accommodate a large number of EVs using Level 1 charging regularly.
- Limited Appeal for Long-Distance Drivers: For those who frequently take long trips, the slow charging speeds of Level 1 make it impractical. This could discourage potential EV buyers who rely on their vehicles for long journeys.
Overall Impact:
Level 1 charging can be a positive force in the EV market by making EVs more accessible and affordable for a wider range of consumers. However, its limitations in terms of speed and potential strain on the grid need to be addressed.
The future of Level 1 charging might lie in its role as a complementary charging solution alongside faster Level 2 and DC fast charging options. This would allow consumers to take advantage of the convenience and affordability of Level 1 charging at home while having access to faster charging options for longer trips or situations requiring a quick top-up.
Additional Points to Consider:
- Government incentives promoting home charging infrastructure, including Level 2 charger installations, could help mitigate the limitations of Level 1 charging.
- Technological advancements in battery technology could potentially reduce charging times for Level 1, making it a more viable option for a larger portion of the EV market.
- Public education about responsible charging habits and off-peak charging can help minimize the potential strain on the electricity grid from widespread EV adoption.
By considering both the benefits and limitations of Level 1 charging and exploring ways to address its limitations, it can play a valuable role in the continued growth and adoption of electric vehicles.
Level Up Your Charging Game: Benefits of Level 2 Charging for Electric Vehicles
For electric vehicle (EV) owners, Level 2 charging offers a significant upgrade over standard Level 1 charging. With faster charging times, increased convenience, and long-term cost savings, Level 2 charging provides a clear advantage for daily driving and extended travel.
This technology delivers a substantial boost in charging speed, typically reducing charging times from hours to mere minutes. This translates to less time spent waiting and more time enjoying the benefits of your EV.
Moreover, Level 2 charging offers greater flexibility, allowing for convenient charging at home, workplaces, and public charging stations. This eliminates range anxiety and ensures that your EV is always ready for the road.
In addition to convenience, Level 2 charging can lead to significant cost savings. By utilizing off-peak electricity rates and avoiding the need for frequent public charging, EV owners can substantially reduce their energy expenses.
Overall, Level 2 charging represents a significant leap forward for EV ownership. With its faster charging times, increased convenience, and long-term cost savings, it empowers EV owners to fully embrace the electric driving experience.

Henry Michael is a leading expert in EV charging station research, specializing in innovative solutions for electric vehicle infrastructure. With a passion for sustainability and technological advancement, he is dedicated to advancing the accessibility and efficiency of EV charging worldwide.