Tax Credit for EV Chargers: Powering Up with Savings
Governments provide tax credits for EV charger installation as a financial incentive to help with the costs of buying and installing EV charging equipment.
The primary purpose of tax credits for EV charger installation is to accelerate the transition to electric transportation by making EV charging infrastructure more affordable and accessible.
By providing financial incentives, governments aim to reduce barriers to EV adoption, support the growth of the electric vehicle market, and address environmental concerns related to fossil fuel dependency and vehicle emissions.

Understanding Tax Credit for EV Chargers
Governments offer tax credits for electric vehicle (EV) chargers as financial incentives to promote the construction of charging infrastructure. Think of it as a discount: The tax credit acts like a cashback reward for installing an EV charger at your home. The government reimburses you a portion of the cost, making the charger more affordable.
Benefits of Tax Credits for EV Charger Owners
For EV charger owners, tax credits offer significant financial advantages:
- Reduced upfront cost: The credit lowers the effective price of the charger and installation, making it a more attractive investment.
- Faster payback period: By reducing the initial cost, the charger pays for itself sooner through electricity savings compared to gas-powered vehicles.
- Environmental benefits: Increased EV adoption due to tax credits translates to reduced greenhouse gas emissions and improved air quality.
- Long-Term Savings: Investing in EV charging infrastructure can lead to long-term savings for EV owners by reducing fuel costs, maintenance expenses, and reliance on traditional vehicles.

State vs. Federal Tax Credit Differences
Federal Tax Credits: The federal government offers tax credits for EV charger installation as part of broader efforts to support the adoption of electric vehicles. Federal tax credits have varied over time but typically provide a percentage of the total installation costs, up to a maximum limit per charging station. These credits are available nationwide and apply to both residential and commercial installations.
State Tax Credits: Many states offer their own incentives and tax credits for EV charger installation, which may complement or supplement federal incentives. State-level programs can vary significantly in terms of eligibility criteria, credit amounts, and application processes.
Some states offer tax credits, rebates, grants, or other financial incentives to encourage the deployment of EV charging infrastructure within their jurisdictions.
State-level incentives may target specific types of EV charging stations, such as public fast chargers or workplace chargers, and may prioritize installations in underserved or disadvantaged communities.
By combining federal and state credits, EV charger installation can maximize the benefits of these incentives, accelerating the transition to cleaner transportation.
Qualifying for the EV Charger Tax Credit
Eligibility criteria for claiming tax credits for EV chargers may vary depending on the specific tax credit program, but here are some general considerations:
1. Requirements for Claiming Tax Credit:
- To claim the tax credit for EV charger installation, taxpayers typically need to meet certain criteria set by the government offering the credit.
- This may include installing eligible EV charging equipment, such as Level 2 chargers or DC fast chargers, and ensuring compliance with any applicable regulations or standards.
- Taxpayers must also incur eligible expenses related to the purchase and installation of the charging equipment, which may include equipment costs, installation labor, and necessary electrical work or infrastructure upgrades.

2. Residential vs. Commercial Eligibility:
- Tax credits for EV charger installation may be available for both residential and commercial installations.
- Residential eligibility typically applies to homeowners or residential property owners who install EV charging equipment at their primary residence.
- Commercial eligibility applies to businesses, organizations, or property owners who install EV charging equipment at commercial or non-residential properties, such as workplaces, retail locations, or public parking facilities.
3. Income Limitations for Tax Credit Eligibility:
- Some tax credit programs may have income limitations or phase-out thresholds that affect eligibility for claiming the credit.
- Income limitations may be based on the taxpayer’s adjusted gross income (AGI) or other income-related criteria.
- Taxpayers with higher incomes may be subject to reduced or phased-out credits, while lower-income individuals or households may qualify for the full credit amount.
- It’s important for taxpayers to review the specific eligibility requirements and income limitations of the tax credit program they are applying for to determine their eligibility and potential credit amount.
Overall, eligibility criteria for claiming tax credits for EV chargers can vary depending on factors such as the type of charging equipment installed, the property type (residential or commercial), and any income limitations or phase-out thresholds specified by the government offering the credit. Taxpayers should carefully review the requirements of the applicable tax credit program and consult with tax professionals for guidance on claiming the credit effectively.
Types of EV Chargers
Each type of EV charger offers different charging speeds and capabilities, catering to the diverse needs of electric vehicle owners. The choice of charger depends on factors such as charging time requirements, available infrastructure, and personal preferences.
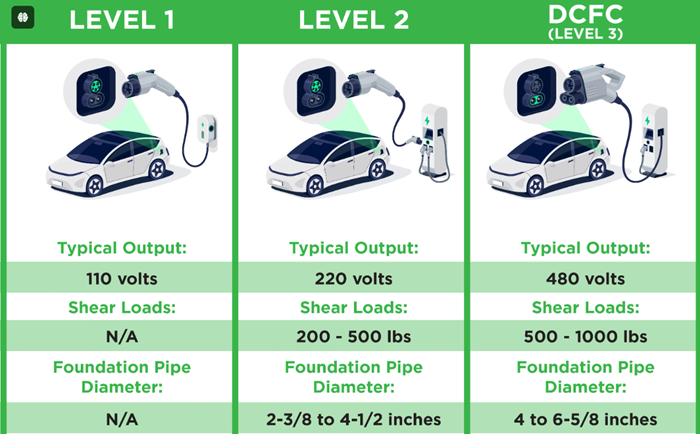
1. Level 1 Chargers:
- Level 1 chargers are the most basic type of EV charger and typically come standard with electric vehicles.
- These chargers use a standard 120-volt AC household outlet.
- They provide the slowest charging rate, typically adding around 2 to 5 miles of range per hour of charging.
- Level 1 chargers are convenient for overnight charging at home or at locations where faster charging is not required.
2. Level 2 Chargers:
- Level 2 chargers are more powerful than Level 1 chargers and are commonly found in public charging stations and installed at homes or businesses.
- They use a 240-volt AC power source, similar to what is used for large household appliances like electric dryers or stoves.
- Level 2 chargers provide a faster charging rate compared to Level 1 chargers, typically adding around 10 to 25 miles of range per hour of charging.
- These chargers are suitable for overnight charging at home, workplace charging, or for longer stops at public charging stations.
3. DC Fast Chargers (Direct Current Fast Chargers):
- DC fast chargers are the fastest type of EV chargers available, capable of providing high-power charging directly to the vehicle’s battery.
- They use direct current (DC) power and bypass the vehicle’s onboard charger, allowing for much faster charging speeds.
- DC fast chargers are commonly found along highways, in urban areas, and at commercial charging stations.
- These chargers can add significant range to an electric vehicle in a short amount of time, making them ideal for long-distance travel or quick stops.
4. Home Charging Stations:
- Home charging stations, also known as home EVSE (Electric Vehicle Service Equipment), are Level 2 chargers specifically designed for residential use.
- They are installed at a homeowner’s residence and provide convenient charging for electric vehicles parked at home.
- Home charging stations typically offer faster charging rates than Level 1 chargers, allowing EV owners to recharge their vehicles more quickly overnight.
- These chargers can be mounted on a wall or installed on a dedicated charging pedestal, depending on the homeowner’s preferences and requirements.
Installation Process
When considering the installation of an EV charger and potentially qualifying for tax credits, it’s crucial to navigate the process carefully. Here’s a breakdown of the key steps:

1. Permitting Requirements
- Check local regulations and permitting requirements for EV charger installations. Permitting processes can vary depending on your location and jurisdiction.
- Obtain any necessary permits before proceeding with the installation to ensure compliance with local building codes and regulations.
- Some jurisdictions may offer expedited permitting processes or incentives for EV charger installations to streamline the process and encourage adoption.
2. Choosing the Right Location for Charger Installation:
- Select an appropriate location for the EV charger installation based on factors such as accessibility, visibility, and proximity to electrical infrastructure.
- Consider factors like parking space availability, convenience for EV owners, and the potential future expansion of charging infrastructure.
- Evaluate the electrical capacity of the chosen location to ensure it can support the charging equipment and any necessary upgrades.
3. Hiring a qualified electrician:
- Hire a licensed and experienced electrician to perform the installation of the EV charger.
- Ensure that the electrician is familiar with EV charger installations and follows manufacturer specifications and guidelines.
- The electrician should assess the existing electrical infrastructure, perform any necessary upgrades or modifications, and install the charging equipment safely and correctly.
4. Ensuring Code Compliance:
- Ensure that the EV charger installation complies with relevant building codes, electrical codes, and safety standards.
- Electric vehicle charging installations are subject to specific code requirements to ensure safety and proper operation.
- The electrician should be knowledgeable about local code requirements and ensure that the installation meets or exceeds these standards.
By following these steps and working with qualified professionals, you can ensure a smooth and compliant EV charger installation process. Meeting permitting requirements, choosing the right location, hiring a qualified electrician, and ensuring code compliance are essential aspects of installing EV chargers and potentially qualifying for tax credits or incentives.
Be sure to keep documentation of the installation process and any associated expenses, as these may be necessary when claiming tax credits or incentives.
Calculating Tax Credit
Calculating the tax credit for EV charger installation involves understanding the criteria used to determine the credit amount, as well as the factors that can influence this calculation. Here’s a breakdown:

Understanding the Tax Credit Amount:
- The tax credit amount for EV charger installation is typically calculated as a percentage of the eligible expenses incurred during the installation process.
- The percentage and maximum credit amount vary depending on the specific tax credit program, which can be at the federal, state, or local level.
- The eligible expenses may include the cost of purchasing and installing the EV charging equipment, as well as any associated electrical work or infrastructure upgrades required for the installation.
Factors Affecting Tax Credit Calculation:
- Percentage of Credit: The tax credit percentage determines how much of the eligible expenses can be claimed as a credit. This percentage can range from a fixed amount to a percentage of the total expenses, up to a maximum limit.
- Maximum Credit Amount: Tax credit programs often have a maximum credit amount that can be claimed per charging station or per installation. This limit caps the total credit amount that can be claimed, regardless of the actual expenses incurred.
- Eligible Expenses: Only certain expenses related to EV charger installation may qualify for the tax credit. Eligible expenses typically include the cost of the charging equipment and installation labor, but may exclude other expenses such as maintenance or operational costs.
- Program Requirements: Tax credit programs may have specific requirements or eligibility criteria that must be met in order to qualify for the credit. These requirements can vary depending on the program and may include factors such as the type of charging equipment installed, the location of the installation, or the intended use of the charging station.
Examples of Tax Credit Calculation:
- Federal Tax Credit: For example, the federal government may offer a tax credit of up to 30% of the total cost of EV charger installation, up to a maximum credit amount of $1,000 per residential charging station and $30,000 per commercial charging station.
- State Tax Credit: Alternatively, a state-level tax credit program may offer a tax credit of 50% of the eligible expenses incurred during EV charger installation, up to a maximum credit amount of $5,000 per charging station.
- Total Expense: If the total expenses for installing a commercial charging station amount to $50,000, the federal tax credit would be $15,000 (30% of $50,000), while the state tax credit would be $25,000 (50% of $50,000). However, the federal credit would be capped at $30,000 for commercial stations.
These examples illustrate how tax credits for EV charger installation can vary based on factors such as the percentage of the credit, maximum credit amount, and eligible expenses.
It’s important to carefully review the specific tax credit program requirements and consult with tax professionals to accurately calculate and claim the tax credit for EV charger installation.
Claiming Tax Credit
Claiming the tax credit for EV charger installation involves gathering the necessary documentation, understanding how to include the credit on your tax return, and avoiding common mistakes. Here’s a guide:

Documentation Needed for Filing:
- Receipts and Invoices: Keep copies of receipts and invoices for all expenses related to EV charger installation, including the cost of purchasing the charging equipment and any installation labor or materials.
- Permits and Approvals: Documentation of any permits obtained and approvals received during the installation process.
- Manufacturer Specifications: Specifications and documentation provided by the manufacturer of the EV charging equipment, including information on the model, capacity, and compliance with relevant standards.
- Contractor Information: Information about the licensed electrician or contractor who performed the installation, including their contact information and license number.
- Proof of Payment: Bank statements or other proof of payment showing that the expenses for EV charger installation were paid.
How to Claim the Tax Credit on Your Tax Return:
- Complete IRS Form 8911: Use IRS Form 8911, “Alternative Fuel Vehicle Refueling Property Credit,” to claim the tax credit for EV charger installation.
- Provide the required information: Fill out the form with the required information, including details about the installed charging equipment, total eligible expenses, and other relevant information.
- Attach Form to Tax Return: Include Form 8911 with your federal income tax return when filing for the year in which the EV charger was installed.
- Review Instructions: Review the instructions provided with Form 8911 to ensure that you accurately complete the form and meet all requirements for claiming the tax credit.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Claiming the Tax Credit:
- Failure to Keep Records: Make sure to retain all necessary documentation related to EV charger installation, as you will need this information when claiming the tax credit.
- Incorrect Calculation: Double-check your calculations to ensure that you accurately determine the eligible expenses and the corresponding tax credit amount.
- Missing Deadlines: Be aware of any deadlines for claiming the tax credit and file your tax return on time to avoid missing out on the credit.
- Not Following Instructions: Carefully follow the instructions provided with Form 8911 to ensure that you complete the form correctly and include all required information.
- Claiming Ineligible Expenses: Only certain expenses related to EV charger installation qualify for the tax credit, so be sure to exclude any ineligible expenses from your claim.

By gathering the necessary documentation, understanding how to claim the tax credit on your tax return, and avoiding common mistakes, you can effectively claim the tax credit for EV charger installation and potentially reduce your tax liability. If you have any questions or concerns about claiming the tax credit, consider consulting with a tax professional for guidance.
Incentives and Rebates
In addition to tax credits, there are various other incentives, rebates, and savings programs available to encourage the installation of EV chargers and support electric vehicle ownership.
- Federal tax credit:The Inflation Reduction Act, passed in August 2022, allows homeowners to claim a tax credit of 30% of the cost of purchasing and installing a qualified EV charger, up to a maximum credit of $1,000. This credit is available for chargers installed between December 31, 2023, and December 31, 2032.
- Rebates from utilities: Many utilities offer rebates to their customers who purchase and install EV chargers at home. These rebates can vary in amount, but they can significantly reduce the cost of a charger.
- State and local incentives: Some states and localities also offer incentives for EV charger installation. These incentives can take the form of tax credits, rebates, or grants.
- Savings from time-of-use rates: Many utilities offer time-of-use (TOU) rates, which charge different rates for electricity depending on the time of day. By charging your EV at night, when rates are typically lower, you can save money on your electricity bill.
- EV-Specific Tariffs: Some utility companies offer special electricity tariffs tailored to electric vehicle owners. These tariffs may include discounted rates for EV charging or other incentives to encourage off-peak charging and support the integration of electric vehicles into the grid.
- Demand Response Programs: Utility companies may also offer demand response programs that provide incentives for EV owners to temporarily reduce or shift their electricity consumption during periods of high demand on the grid. By participating in demand response events, EV owners can earn credits or other rewards from their utility company.
In addition to the incentives listed above, there are a number of other benefits to owning an EV charger at home. For example, having a charger at home means that you can always be sure that your EV is charged and ready to go. It can also save you time and money compared to relying on public charging stations.
EV Chargers and Impact on Environment
The adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) and the installation of EV chargers have significant positive impacts on the environment, contributing to efforts to reduce carbon emissions, promote clean energy initiatives, and improve air quality.

1. Reduction of Carbon Emissions:
Compared to conventional internal combustion engine vehicles that rely on fossil fuels, EVs have zero tailpipe emissions, significantly reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Adopting electric vehicles (EVs), which can run on renewable energy sources like solar or wind, helps to lessen the negative effects of carbon emissions on climate change.
2. Contribution to Clean Energy Initiatives:
The increased adoption of EVs creates a demand for clean electricity generation. This incentivizes the development and use of renewable energy sources like wind and solar power, reducing our dependence on fossil fuels, and reinforcing efforts to transition to a cleaner and more sustainable energy future.
3. Effects of EV Adoption on Air Quality:
EV adoption has positive implications for air quality, particularly in urban areas where air pollution from vehicle emissions is a significant concern.
By eliminating tailpipe emissions, EVs help reduce the release of harmful pollutants such as nitrogen oxides (NOx), particulate matter (PM), and volatile organic compounds (VOCs), which contribute to respiratory illnesses, cardiovascular diseases, and environmental degradation.
The installation of EV chargers facilitates the widespread adoption of EVs, encouraging more drivers to transition away from gasoline and diesel-powered vehicles, thereby improving air quality and public health outcomes.
Zooming into the Future: EV Charger Tax Credit Trends
The landscape of EV charger tax incentives is a dynamic one, and we can expect to see some exciting developments in the coming years.

1. Changing Landscape of EV Charger Tax Incentives:
- Program Extensions: The current federal tax credit is set to expire at the end of 2025. Policymakers might consider extending or modifying the program based on its success in promoting EV adoption.
- State Spotlight: Individual states are likely to play a growing role in shaping EV charger incentives. We may see more states offering additional tax credits, rebates, or other programs to further encourage charger installation.
- Targeting Needs: Future incentive programs might become more targeted to address specific needs. For example, there could be increased credits for installing chargers in underserved communities or workplaces.
2. Potential for Increased Tax Credits in the Future:
- Reaching Critical Mass: As EV adoption accelerates, policymakers might offer even higher tax credits to incentivize charger installation in new locations like apartment buildings or public parking spaces. This would help build a robust charging infrastructure to support a growing number of EVs.
- Focus on Equity: There could be a push for programs that make EV ownership more accessible to low- and middle-income households. This might involve higher credits for specific income brackets or incentives for used EV chargers.
3. Advancements in EV Charging Technology:
- Faster Charging, Wider Availability: The future holds promise for faster charging technologies that can significantly reduce charging times. This would address “range anxiety” – a major concern for potential EV owners – and encourage wider EV adoption.
- Smart Charging Integration: EV chargers are likely to become more sophisticated, integrating with smart grid technologies to optimize energy use and potentially offer cost savings to EV owners.
- Public-Private Partnerships: We might see more collaboration between governments, utilities, and private companies to develop and expand public charging infrastructure.
Government Agencies
Here are some reputable sources to bolster your topical authority on EV charger tax credits:

- US Department of Energy Alternative Fuels Data Center: https://afdc.energy.gov/ (This is a comprehensive resource) maintained by the Department of Energy. It provides detailed information on state-by-state EV incentives, including tax credits for charger installation.
- Internal Revenue Service (IRS): https://www.irs.gov/ This is the official website of the IRS. You can find information on the federal tax credit for EV chargers, including eligibility requirements and how to claim the credit on your tax return.
Industry Associations:
- Electric Vehicle Charging Association (EVCA): https://goevca.org/ This association represents companies involved in the EV charging industry. Their website may have resources on the latest trends in EV charger tax credits and policy developments.
News and Research Organizations:
- Green Car Reports: This publication is a well-respected source for news and information on electric vehicles and clean transportation. They frequently cover policy issues related to EV incentives, including tax credits for chargers.
- The Pew Research Center: This non-partisan research organization has conducted surveys on public attitudes towards electric vehicles. Their findings can provide insights into the potential impact of EV charger tax credits.

Henry Michael is a leading expert in EV charging station research, specializing in innovative solutions for electric vehicle infrastructure. With a passion for sustainability and technological advancement, he is dedicated to advancing the accessibility and efficiency of EV charging worldwide.