Level 3 EV Charger Wiring: Essential Tips and Instructions
Level 3 EV charger wiring, also referred to as DC fast charging, prioritizes speed. Nevertheless, this rapid charging capability entails substantial electrical demands. Below, we’ll outline the crucial electrical considerations you must account for when installing a Level 3 EV charging system.

Power Supply Needs
- High Voltage: Level 3 chargers require a high voltage source, typically 480 volts (three-phase) or even 1000 volts. This is significantly higher than the 240 volts used for Level 2 chargers, and far exceeds the standard 120-volt household outlet.
- Existing Infrastructure: Many commercial buildings may not have the existing electrical infrastructure to support Level 3 charging. Upgrading to a higher voltage service may be necessary.
Grid Impact and Management
- High Power Draw: Level 3 chargers pull a significant amount of power from the grid. This can strain the local grid, especially if multiple chargers are used simultaneously.
- Demand Management: Strategies like load management may be required to ensure the grid can handle the increased demand without overloading.
Transformer and Substation Requirements
- Transformer Capacity: Depending on the existing electrical service, upgrades to transformers or even the substation that supplies power may be needed to handle the additional load from Level 3 chargers.
Upgrading Infrastructure
- Cost Considerations: Upgrading the electrical infrastructure to support Level 3 charging can be expensive. These costs need to be factored into the overall investment decision.
Additional Resources
For a deeper dive into specific aspects, you can search for:
- Level 2 Versus Level 3 EV Chargers [Search for level 2 vs level 3 ev charger]
- Switching & Protection for Level 3 DC Fast Chargers [Search for switching and protection for level 3 dc fast chargers]
Level 3 EV Charger Wiring Basics
Level 3 EV charger wiring involves high voltage and significant power compared to residential electrical systems. Due to the complexity and safety risks, professional installation by a qualified electrician is crucial. Here’s a look at some key aspects to understand:
Types of Cables and Connectors
- Level 3 chargers use high-voltage direct current (DC) cables with large diameters to handle the high current flow. Specific cable types and connectors will depend on the charger model and local regulations.
- Common connector standards include: CCS Combo (Combo Charging System) and CHAdeMO.
Wire Gauge and Length Considerations
- Thick gauge wires are needed to minimize resistance and prevent overheating. The specific wire gauge will depend on the charger’s power output and cable length.
- Keeping cable length as short as possible is recommended to reduce voltage drop and improve efficiency.
Conduit and Protective Components
- Conduits made of rigid metal are typically used to protect the cables from physical damage and environmental factors.
- Additional protective components like fuses, circuit breakers, and surge protectors are essential to ensure safety and prevent damage from overload or faults.
Grounding and Safety Standards
- Proper grounding is critical to prevent electrical shock and ensure safe operation. Grounding systems must comply with relevant safety standards like the National Electrical Code (NEC) in the United States.
- Qualified electricians are familiar with these standards and can ensure a safe installation.
Installation Best Practices
- Clear labeling of cables and components is crucial for future maintenance and troubleshooting.
- Maintaining proper clearances around high-voltage cables is essential for safety.
- Following manufacturer’s instructions for the specific charger model is important.
Energy Management for Level 3 Charging Stations: Load Balancing and Grid Integration
The high power demands of Level 3 chargers can strain the local electricity grid, especially if multiple chargers are operating simultaneously. To address this challenge, energy management strategies are crucial for Level 3 charging stations. Here’s a closer look at two key approaches:
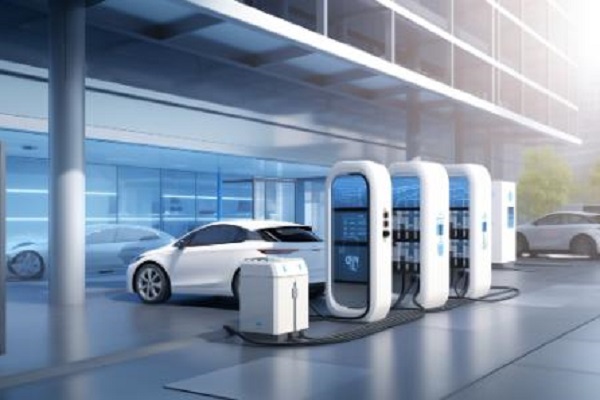

Load Balancing
- Distributing Power Efficiently: Load balancing ensures that available power is distributed efficiently among multiple charging vehicles. This prevents overloading the grid connection and potential disruptions.
- Technologies for Load Balancing: Several technologies can be employed for load balancing. These include:
- Smart Chargers: These chargers can communicate with each other and a central management system to dynamically adjust power output based on the number of vehicles charging and their battery status.
- Power Sharing Systems: These systems allow multiple chargers to share a single power connection, intelligently allocating power based on real-time needs.
Grid Integration
- Optimizing Grid Impact: Strategies for grid integration aim to minimize the impact of Level 3 chargers on the grid and optimize energy usage.
- Potential Approaches:
- Time-of-Day Charging: Encouraging charging during off-peak hours when grid demand is lower can significantly reduce strain.
- Demand Response Programs: Participating in utility-offered demand response programs can allow charging stations to adjust power usage in response to grid conditions.
- Renewable Energy Integration: Integrating renewable energy sources like solar panels into the charging station can help offset the reliance on the traditional grid.
Benefits of Effective Energy Management
- Reduced Grid Strain: By implementing effective energy management strategies, Level 3 charging stations can minimize their impact on the grid, facilitating wider adoption of electric vehicles.
- Cost Savings: Load balancing and grid integration can help charging station operators optimize energy usage and potentially reduce electricity costs.
- Improved Sustainability: Utilizing renewable energy sources and optimizing grid usage contributes to a more sustainable electric vehicle charging infrastructure.

Further Exploration
You can search for the following to learn more about specific technologies:
- Smart Charging for Electric Vehicles
- Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) Technology

Henry Michael is a leading expert in EV charging station research, specializing in innovative solutions for electric vehicle infrastructure. With a passion for sustainability and technological advancement, he is dedicated to advancing the accessibility and efficiency of EV charging worldwide.