Level 3 EV Charger KW: Maximize Your Electric Vehicle Charging Speed
Level 3 EV chargers, also known as DC Fast Chargers, are the pinnacle of electric vehicle charging technology. With their high power ratings, measured in kilowatts (kW), they enable ultrafast charging, making them ideal for long-distance travel. However, before opting for a Level 3 charger, it’s crucial to consider compatibility and other key factors to ensure it’s the right fit for your EV charging needs.

Understanding Level 3 Charging
Definition and Overview
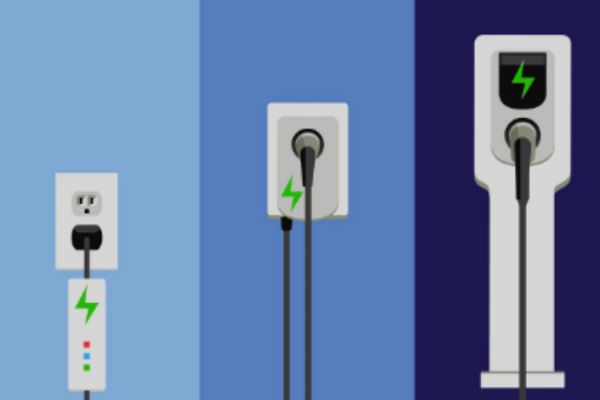
Level 3 charging, also known as DC fast charging or rapid charging, represents the zenith of electric vehicle (EV) charging technology. Unlike Level 1 and Level 2 chargers, which operate on AC power and are primarily suited for overnight charging at home or in workplaces, Level 3 chargers utilize direct current (DC) to deliver a substantial amount of power to the vehicle’s battery in a short span of time. This enables EV drivers to conveniently recharge their vehicles on-the-go, making long-distance travel with electric vehicles a practical reality.
Comparison with Level 1 and Level 2 Charging
In contrast to Level 1 and Level 2 chargers, which typically provide power outputs ranging from 120 volts AC at 1.4 kW to 240 volts AC at 19.2 kW respectively, Level 3 chargers offer significantly higher power levels. While Level 1 and Level 2 charging is ideal for overnight and daily charging needs, Level 3 charging drastically reduces charging times, making it suitable for quick top-ups during long journeys.
Typical kW Range for Level 3 Chargers
Level 3 chargers typically deliver power outputs ranging from 50 kW to 350 kW, with newer installations increasingly pushing towards higher power levels. This immense power output allows EVs to replenish a substantial portion of their battery capacity in a matter of minutes, significantly enhancing the convenience of electric vehicle ownership.

Charging Times and Efficiency
Thanks to their high power output, Level 3 chargers can replenish an EV’s battery much faster than Level 1 or Level 2 chargers. Charging times vary depending on factors such as the vehicle’s battery capacity, state of charge, and the charger’s power output. However, even with larger battery capacities, EVs can achieve significant charge gains in just 30 minutes to an hour, making Level 3 charging ideal for minimizing downtime during long journeys.
Infrastructure Requirements
Installing Level 3 charging infrastructure requires a substantial investment in both hardware and electrical infrastructure. Level 3 chargers rely on high-voltage DC power sources, necessitating robust electrical connections and safety measures to handle the increased power levels safely. Additionally, the deployment of Level 3 chargers often requires strategic planning to ensure accessibility along major transportation routes and in urban areas, thereby fostering widespread adoption of electric vehicles.
Technologies Behind Level 3 Charging

DC Fast Charging Principles
Level 3 charging relies on direct current (DC) fast charging principles to deliver high-power electricity directly to the vehicle’s battery. Unlike Level 1 and Level 2 chargers, which convert alternating current (AC) to DC within the vehicle’s onboard charger, Level 3 chargers bypass this step, supplying DC power directly to the battery. This streamlined approach allows for faster charging rates, making Level 3 chargers essential for long-distance travel and minimizing charging times.
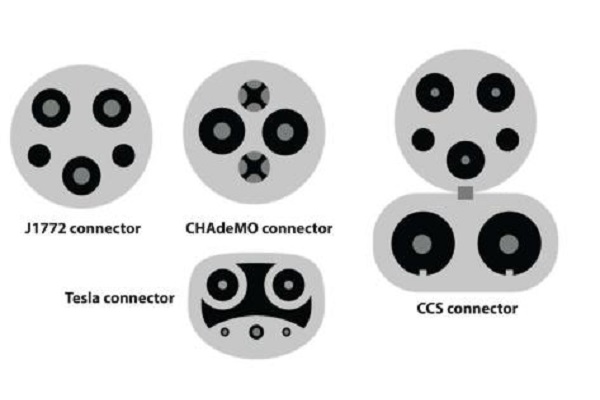
Connector Types (CHAdeMO, CCS, Tesla Supercharger)
Several connector types are used for Level 3 charging, each associated with different electric vehicle manufacturers or standards:
- CHAdeMO: Developed by Japanese companies, CHAdeMO is a DC fast charging standard commonly used by Nissan and other Japanese automakers. It features a unique connector design and protocol for delivering high-power DC charging.
- CCS (Combined Charging System): Embraced by European and American automakers, CCS combines AC and DC charging into a single connector. This versatile approach supports both Level 2 AC charging and Level 3 DC fast charging, making it a prevalent standard in many regions.
- Tesla Supercharger: Tesla’s proprietary fast charging network utilizes a unique connector designed specifically for Tesla vehicles. While initially exclusive to Tesla, adapters are available to enable compatibility with CHAdeMO and CCS connectors at certain Supercharger stations.
Power Conversion Technologies
Level 3 chargers employ sophisticated power conversion technologies to efficiently convert AC grid power into high-voltage DC suitable for rapid charging. These technologies include high-powered rectifiers and inverters capable of handling the immense power levels required for Level 3 charging while minimizing energy losses and maximizing charging efficiency.
Cooling Systems for High-Power Charging
Given the substantial power output and energy transfer involved in Level 3 charging, cooling systems are crucial to maintain optimal operating temperatures and prevent overheating. Liquid cooling systems, often integrated into the charging infrastructure and connectors, dissipate excess heat generated during the charging process, ensuring safe and reliable operation even under high-power charging conditions.
Safety Features and Standards
Level 3 charging systems adhere to stringent safety standards and incorporate various features to protect both the vehicle and charging infrastructure. These include overcurrent protection, ground fault detection, temperature monitoring, and communication protocols between the charger and vehicle to regulate charging parameters and prevent potential hazards such as overcharging or overheating. Compliance with industry standards such as ISO 15118 and IEC 61851 ensures interoperability and safety across different charging networks and vehicle platforms.
EV Models and Level 3 Charging Compatibility

EVs with Built-In Fast Charging Capability
Numerous electric vehicle (EV) models come equipped with built-in fast charging capability, enabling them to utilize Level 3 charging infrastructure for rapid replenishment of their battery packs. Manufacturers recognize the importance of fast charging for long-distance travel and have integrated this feature into many modern EVs. Some notable examples include:
- Tesla Model S, Model 3, Model X, and Model Y: Tesla vehicles are equipped with the proprietary Supercharger network, providing high-speed charging capabilities using Tesla’s unique connector design.
- Nissan Leaf: The Nissan Leaf is compatible with CHAdeMO DC fast chargers, allowing for rapid charging at Level 3 charging stations.
- Audi e-tron: Audi’s e-tron SUV supports fast charging via CCS connectors, enabling quick charging sessions at Level 3 charging stations.
- Porsche Taycan: Porsche’s first all-electric vehicle, the Taycan, features high-power charging capabilities utilizing CCS connectors, allowing for fast charging on compatible Level 3 chargers.
Maximum Charging Rates by EV Model
Certainly! Here’s a table showcasing maximum charging rates for various electric vehicle (EV) models:
| EV Model | Maximum Charging Rate (kW) |
| Tesla Model S | Up to 250 kW (Supercharger V3) |
| Tesla Model 3 | Up to 250 kW (Supercharger V3) |
| Tesla Model X | Up to 250 kW (Supercharger V3) |
| Tesla Model Y | Up to 250 kW (Supercharger V3) |
| Nissan Leaf | Up to 50 kW (CHAdeMO) |
| Audi e-tron | Up to 150 kW (CCS) |
| Porsche Taycan | Up to 270 kW (CCS) |
Please note that these are approximate maximum charging rates and may vary depending on factors such as battery condition, state of charge, and specific charging infrastructure. Always refer to the manufacturer’s specifications for the most accurate charging rate information.
Adapters and Retrofitting for Older Models
For older EV models or those without built-in support for Level 3 charging, adapters or retrofitting solutions may provide compatibility with certain fast charging standards. For example:
- Tesla vehicles can use CHAdeMO or CCS adapters to connect to non-Tesla DC fast chargers.
- Some aftermarket solutions exist to retrofit older EV models with compatible fast charging hardware, although the feasibility and effectiveness of these solutions may vary depending on the vehicle’s design and electrical system.
Future EV Models and Expected Charging Capabilities
As electric vehicle technology continues to evolve, future EV models are expected to offer even faster charging capabilities and broader compatibility with Level 3 charging infrastructure. Manufacturers are investing heavily in research and development to improve battery technology, charging efficiency, and power electronics, paving the way for:
- Increased charging rates, potentially exceeding 350 kW.
- Enhanced interoperability with multiple fast charging standards.
- Integration of advanced thermal management systems to optimize charging performance and battery longevity.

Market Trends and Future Prospects
Growth of EV Adoption
The adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) continues to surge globally, driven by factors such as environmental concerns, government incentives, and advancements in EV technology. Market trends indicate a steady increase in EV sales, with electric vehicles gaining significant market share in various regions. Countries like China, Europe, and the United States lead the way in EV adoption, with automakers introducing an ever-expanding lineup of electric models to meet growing consumer demand.
Expansion of Charging Infrastructure
To support the burgeoning EV market, significant investments are being made in expanding charging infrastructure worldwide. Governments, private companies, and utilities are collaborating to deploy more charging stations, including Level 3 fast chargers along highways and in urban areas. Initiatives such as the European Union’s Green Deal and the US’ infrastructure bills allocate funding for EV charging infrastructure development, aiming to ensure widespread access to charging facilities and alleviate range anxiety among EV drivers.
Technological Advances in Battery and Charging
Continuous innovation in battery technology and charging systems is driving improvements in EV performance, range, and charging speed. Lithium-ion battery advancements, such as higher energy density and faster charging capabilities, enable longer driving ranges and reduced charging times for EVs. Additionally, developments in charging infrastructure, including higher-power Level 3 chargers and bidirectional charging capabilities, enhance the convenience and versatility of electric vehicles, fostering greater adoption among consumers.

Investment and Funding Trends
Investment in the electric vehicle sector remains robust, with venture capital firms, automakers, and tech companies pouring billions of dollars into EV startups, battery manufacturers, and charging infrastructure projects. Governments are also offering incentives and grants to stimulate investment in EV-related industries, such as battery manufacturing and electric vehicle production facilities. This influx of capital accelerates technological innovation, drives down costs, and fuels the expansion of the electric vehicle ecosystem.
Predictions for Future Charging Speeds and Technologies
The future of EV charging holds promises of even faster charging speeds and groundbreaking technologies. Forecasts suggest that charging speeds could surpass 500 kW, enabling ultra-fast charging sessions that rival the time it takes to refuel a gasoline vehicle. Advancements in solid-state batteries, wireless charging, and vehicle-to-grid (V2G) integration are expected to revolutionize the EV charging experience, offering greater convenience, efficiency, and grid flexibility. Furthermore, standardization efforts and interoperability between different charging networks and protocols will streamline EV charging operations, making it easier for consumers to adopt electric vehicles as their primary mode of transportation.
Safety and Security Considerations
Electrical Safety Standards
Ensuring electrical safety is paramount in the design and operation of electric vehicle (EV) charging infrastructure. Compliance with established electrical safety standards, such as NEC (National Electrical Code) in the United States and IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) standards internationally, is essential. These standards outline requirements for electrical equipment, wiring, grounding, and installation practices to mitigate risks of electric shock, fire, and other hazards associated with charging equipment.
Data Security for Connected Chargers
As EV charging infrastructure becomes increasingly interconnected and data-driven, safeguarding data security is critical. Connected chargers may collect and transmit sensitive information, including user data, charging session details, and payment information. Implementing robust cybersecurity measures, such as encryption, authentication protocols, and secure data transmission protocols, helps protect against unauthorized access, data breaches, and cyber attacks targeting charging networks.
Physical Security of Charging Stations
Ensuring the physical security of charging stations is essential to prevent vandalism, theft, and tampering. Installing chargers in well-lit areas, employing surveillance cameras, and implementing physical barriers or access controls help deter unauthorized access and enhance the security of charging infrastructure. Additionally, tamper-resistant hardware and anti-theft features can safeguard equipment and prevent damage or disruption to charging operations.
Emergency Response Protocols
Developing comprehensive emergency response protocols is vital to address potential safety incidents or emergencies involving EV charging infrastructure. Training personnel on proper emergency procedures, including shutdown protocols, evacuation plans, and coordination with emergency responders, ensures a timely and effective response to incidents such as electrical faults, fires, or accidents at charging stations. Clear signage and emergency contact information should also be prominently displayed to assist users in reporting emergencies and seeking assistance when needed.
Accessibility and ADA Compliance
Ensuring accessibility and compliance with the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) is essential to promote inclusivity and accommodate users with disabilities at charging stations. Designating accessible parking spaces with appropriate signage and providing features such as wheelchair-accessible pathways, tactile indicators, and height-adjustable charging equipment facilitate access for individuals with mobility impairments. Furthermore, ensuring that charging stations are located in accessible locations and equipped with user-friendly interfaces enhances the overall accessibility of EV charging infrastructure for all users.
Case Studies and Real-World Applications
Successful Implementations of Level 3 Charging Stations
One notable example of successful Level 3 charging station implementation is Tesla’s Supercharger network. With thousands of stations globally, Tesla has created a robust infrastructure that enables long-distance travel for its electric vehicles. These stations are strategically located along highways and in urban areas, providing convenient access to high-speed charging for Tesla owners.
Impact on Local and National Grids
The deployment of Level 3 charging stations has implications for local and national grids. While high-power charging can strain local distribution networks, proper planning and grid integration strategies can mitigate these challenges. Additionally, smart charging technologies and demand response programs help optimize charging schedules and balance grid load, minimizing the impact of EV charging on electricity infrastructure.
User Adoption Stories and Feedback
User adoption stories and feedback provide valuable insights into the effectiveness and usability of Level 3 charging infrastructure. Many EV drivers appreciate the convenience and reliability of Level 3 charging, especially during long-distance trips. Positive experiences with fast charging networks contribute to increased confidence in electric vehicles and encourage further adoption among consumers.
Innovations in Level 3 Charging Technology
Innovations in Level 3 charging technology continue to enhance the efficiency and capabilities of fast charging infrastructure. For example, advancements in liquid-cooled cables and connectors improve charging reliability and reduce heat-related wear and tear. Moreover, bidirectional charging capabilities enable vehicle-to-grid (V2G) integration, allowing EVs to serve as grid storage resources during peak demand periods.
Partnerships and Collaborations in the EV Charging Sector
Partnerships and collaborations play a crucial role in advancing EV charging infrastructure. For instance, automakers, utilities, and charging network operators collaborate to expand charging networks, develop interoperable standards, and deploy innovative charging solutions. These partnerships facilitate the integration of EV charging into existing infrastructure and accelerate the transition to electric mobility.
Looking ahead, the future of Level 3 EV charging holds promises of even faster charging speeds, enhanced interoperability, and innovative technologies such as bidirectional charging and vehicle-to-grid integration. Continued investment, collaboration, and technological innovation will further accelerate the transition to electric mobility, shaping a sustainable transportation future powered by high-power, rapid charging solutions.

Henry Michael is a leading expert in EV charging station research, specializing in innovative solutions for electric vehicle infrastructure. With a passion for sustainability and technological advancement, he is dedicated to advancing the accessibility and efficiency of EV charging worldwide.