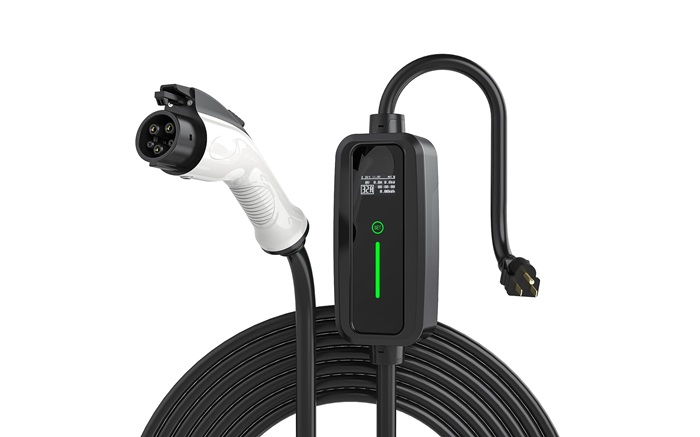
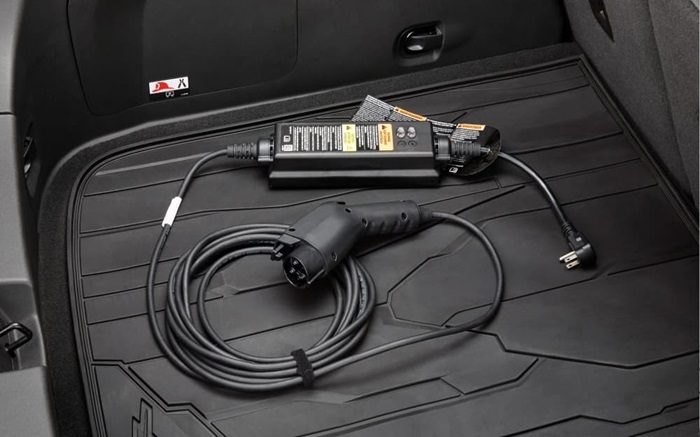
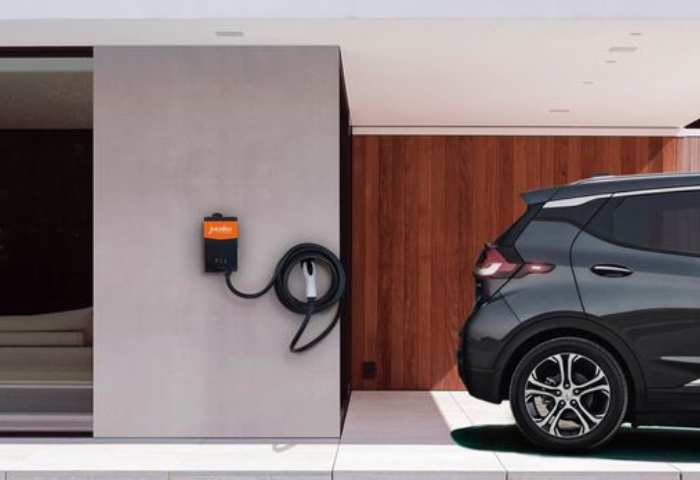
Can I use an extension cord with a level 1 charger?
Level 1 EV chargers are the most basic chargers, designed to plug into a standard 120-volt household outlet. They offer a convenient way to charge your electric vehicle (EV) at home, but questions arise about extending their reach with extension cords. Is this a safe and practical solution?
Let’s delve into the potential risks and explore alternatives.
Safety Concerns of Extension Cords with Level 1 Chargers
Importance of Using Proper Charging Equipment
Using proper charging equipment is essential for the safety, efficiency, and longevity of electric vehicles (EVs) and their charging infrastructure. Here are some key reasons highlighting the importance of using proper charging equipment:
Safety: Proper charging equipment is designed and tested to meet stringent safety standards, ensuring the protection of users, vehicles, and property. This includes features such as overcurrent protection, ground fault protection, and insulation to prevent electric shocks, fires, and other hazards.
Compatibility: Proper charging equipment is compatible with the charging requirements and specifications of electric vehicles. This ensures that the charging process is efficient and reliable, with no risk of damage to the vehicle’s battery or electrical system.
Efficiency: High-quality charging equipment is designed for optimal charging efficiency, minimizing energy losses and charging times. This helps EV owners maximize their driving range and minimize their energy costs by charging their vehicles as quickly and efficiently as possible.
Longevity: Using proper charging equipment helps prolong the lifespan of electric vehicle batteries and charging infrastructure. It reduces wear and tear on the battery cells, minimizes heat buildup during charging, and prevents overcharging or undercharging, all of which can contribute to battery degradation over time.
Warranty Compliance: Many electric vehicle manufacturers require the use of approved charging equipment to maintain the warranty coverage of the vehicle. Using unauthorized or incompatible charging equipment may void the warranty and leave the owner liable for any damages or repairs.
Reliability: Proper charging equipment is designed for reliability and durability, with quality components and construction that can withstand daily use and harsh environmental conditions. This ensures that EV owners can depend on their charging infrastructure to deliver consistent and dependable performance over time.
Future-Proofing: Investing in proper charging equipment ensures compatibility with future advancements in electric vehicle technology and charging standards. This allows EV owners to adapt to changes in the industry and take advantage of new features and capabilities as they become available.
Risks of Using an Extension Cord with a Level 1 Charger
Using an extension cord with a Level 1 charger for electric vehicles (EVs) introduces several risks and safety concerns that can compromise the charging process and pose hazards to users, vehicles, and property. Here are some of the key risks associated with using an extension cord:
Voltage Drop and Power Loss: Extension cords can introduce additional resistance and voltage drop, especially if they are of inadequate gauge or length. This can result in power loss and slower charging speeds, as well as reduced efficiency and increased energy consumption.
Overheating and Fire Hazards: Extension cords that are not designed for high-power applications or are damaged or overloaded can overheat, leading to fire hazards. The increased resistance in the extension cord can cause it to heat up, potentially melting the insulation or causing a short circuit, resulting in a fire.
Electrical Overload: Using an extension cord with a Level 1 charger may exceed the cord’s rated capacity, leading to electrical overload. This can cause the extension cord to overheat and potentially melt or catch fire, as well as damage the charger or the electrical outlet.
Compatibility Issues: Extension cords may not be compatible with the plug type or configuration of the Level 1 charger, leading to poor connections, intermittent charging, or electrical faults. Improper connections can increase the risk of electrical arcing, which can cause sparks, damage equipment, and pose a fire hazard.
Trip and Fall Hazards: Extension cords can create trip and fall hazards, especially if they are not properly secured or routed. This is particularly problematic in outdoor or high-traffic areas where the cords may be exposed to foot traffic, vehicles, or environmental hazards.
Voiding Warranties: Some EV manufacturers explicitly prohibit the use of extension cords with their charging equipment, and doing so may void the warranty coverage of the vehicle or charger. Using unauthorized accessories or modifications can leave the owner liable for any damages or repairs resulting from their use.
Alternatives to Extension Cords

Recommended Methods for Charging an Electric Vehicle
For charging an electric vehicle (EV), it’s essential to use safe and efficient methods to ensure optimal performance and longevity of the vehicle and charging infrastructure. Here are the recommended methods for charging an EV:
Level 1 Charging (Home Charging)
Level 1 charging is the simplest and most convenient method for charging an EV at home.
Plug the EV charger into a standard 120-volt household outlet using the provided charging cable.
Level 1 chargers are ideal for overnight charging or when the vehicle is parked for an extended period, such as at home or work.
Level 2 Charging (Home, Workplace, and Public Charging)
Level 2 chargers operate at higher voltages (typically 240 volts) and provide faster charging speeds compared to Level 1 chargers.
Install a Level 2 charging station at home or the workplace to charge your EV more quickly and efficiently.
Level 2 chargers are also available at public charging stations, making them suitable for longer trips or when higher charging speeds are needed.
DC Fast Charging (Public Charging)
DC fast chargers provide the fastest charging speeds available for EVs and are commonly found at public charging stations along highways and travel routes.
These chargers deliver direct current (DC) power to the EV’s battery, bypassing the onboard charger and enabling rapid charging.
DC fast chargers are ideal for long-distance travel or when you need to quickly top up your battery during a trip.
Tesla Superchargers (Tesla Vehicles Only):
Tesla’s proprietary Supercharger network is designed specifically for Tesla vehicles and provides high-speed charging at strategically located stations.
Superchargers deliver DC power directly to the Tesla EV’s battery, allowing for rapid charging speeds and long-distance travel.
Smart Charging and Energy Management
Take advantage of the smart charging features available with some EV charging stations, such as scheduling charging sessions during off-peak hours or optimizing charging based on energy rates.
Monitor your EV’s charging status and energy consumption using mobile apps or vehicle dashboards to ensure efficient charging and manage costs.
Battery Health and Maintenance
Follow recommended battery maintenance practices, such as avoiding frequent deep discharges, minimizing exposure to extreme temperatures, and maintaining appropriate state of charge (SoC) levels.
Avoid prolonged periods of high or low SoC, as this can accelerate battery degradation and reduce overall battery life.
Exploring Portable Level 1 Chargers
Exploring portable Level 1 chargers opens up opportunities for electric vehicle (EV) owners to conveniently charge their vehicles wherever there’s a standard 120-volt household outlet available. Portable Level 1 chargers offer flexibility and convenience, making them ideal for EV owners who frequently travel or need to charge their vehicles at various locations. Here are some key points to consider when exploring portable Level 1 chargers:
Compatibility: Ensure that the portable Level 1 charger is compatible with your EV model. Most Level 1 chargers use a standard J1772 connector, which is compatible with the majority of EVs and plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs). However, it’s always advisable to double-check compatibility with your specific vehicle.
Charging Power: Portable Level 1 chargers typically operate at standard 120-volt outlets and provide charging power ranging from approximately 1.2 kW to 1.9 kW. While they offer slower charging speeds compared to higher-level chargers, they are suitable for overnight charging or topping up the battery during short stops.
Portability: Look for a portable Level 1 charger that is lightweight, compact, and easy to transport. Consider features such as foldable handles, retractable cables, or storage bags for convenient portability. Portable chargers are ideal for EV owners who frequently travel or need to charge their vehicles on the go.
Durability: Choose a portable Level 1 charger that is durable and built to withstand various environmental conditions. Look for features such as weatherproofing, robust construction, and high-quality materials that ensure longevity and reliability, especially if you plan to use the charger outdoors.
Safety Features: Ensure that the portable Level 1 charger has built-in safety features to protect against overcharging, overheating, short circuits, and other potential hazards. Look for certifications such as UL certification, which indicates that the charger meets safety standards.
User-Friendly Features: Look for user-friendly features such as LED indicators, intuitive controls, and easy-to-read displays that make it simple to monitor charging status and operation. Some chargers may also offer additional features like adjustable charging current or programmable timers.
Cable Length: Consider the length of the charging cable, as it can affect convenience and accessibility when charging your EV. Opt for a charger with a longer cable length if you need flexibility in reaching the charging port of your vehicle.
Warranty and Customer Support: Choose a portable Level 1 charger from a reputable manufacturer that offers a warranty and reliable customer support. A warranty provides peace of mind and protection against any potential defects or issues with the charger.
Level 2 Chargers as a Safe Alternative
Level 2 chargers offer a safe and efficient alternative to Level 1 chargers for electric vehicle (EV) owners looking for faster charging speeds and greater convenience. Here are some reasons why Level 2 chargers are considered a safe alternative:
Faster Charging Speeds: Level 2 chargers operate at higher voltages (typically 240 volts) and provide faster charging speeds compared to Level 1 chargers. This means that EV owners can charge their vehicles more quickly, reducing the time required to top up the battery.
Built-in Safety Features: Level 2 chargers are equipped with built-in safety features to protect against overcharging, overheating, short circuits, and other potential hazards. These safety features help ensure that the charging process is safe and reliable, providing peace of mind for EV owners.
Professional Installation: Level 2 chargers typically require professional installation by a qualified electrician, ensuring that the charger is properly installed and meets all safety standards and regulations. Professional installation reduces the risk of installation errors and ensures that the charger operates safely and efficiently.
Compatibility with EVs: Level 2 chargers are compatible with a wide range of electric vehicles (EVs) and plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs) that use a standard J1772 connector. This compatibility ensures that EV owners can use the charger with their vehicle without any compatibility issues or concerns.
Weatherproof and Durable Construction: Many Level 2 chargers are designed for outdoor use and feature weatherproof and durable construction to withstand various environmental conditions. This ensures that the charger remains safe and operational, even when exposed to rain, snow, or extreme temperatures.
Smart Charging Features: Some Level 2 chargers offer smart charging features, such as scheduling charging sessions, monitoring energy consumption, and adjusting charging rates based on utility rates or grid demand. These features help optimize charging efficiency and maximize safety while minimizing energy costs.
Level 2 chargers are typically covered by a warranty and provide dependable customer support from the manufacturer. A warranty provides protection against any potential defects or issues with the charger, while customer support ensures that EV owners have access to assistance and guidance when needed.
Understanding Level 1 Chargers (Optional)

What is a Level 1 charger and how does it work?
A Level 1 charger is the most basic type of electric vehicle (EV) charging equipment, designed for residential charging using a standard 120-volt household outlet. Here’s how a Level 1 charger works:
Charging Power: Level 1 chargers typically operate at 120 volts AC (alternating current) and provide charging power ranging from around 1.2 kW to 1.9 kW. This charging power is lower compared to higher-level chargers like Level 2 or DC fast chargers, resulting in slower charging speeds.
Charging Cable: A Level 1 charger comes with a charging cable that is equipped with a standard connector on one end for plugging into the EV’s charging port and a plug on the other end for connecting to a standard 120-volt household outlet. The length of the charging cable may vary depending on the charger model.
Standard Outlet: Level 1 chargers are designed to be plugged into a standard NEMA 5-15 outlet, which is the same type of outlet used for common household appliances like lamps or computers. This makes Level 1 chargers convenient to use at home without requiring any special installation or electrical work.
Charging Process: When plugged into a standard household outlet, the Level 1 charger converts the AC power from the outlet into DC (direct current) power suitable for charging the EV’s battery. The charger communicates with the EV to initiate the charging process and monitor the charging status.
Charging Time: Due to the lower charging power of Level 1 chargers, the charging time for an EV can vary significantly depending on factors such as the battery capacity, state of charge, and efficiency of the charging process. It can take anywhere from several hours to overnight to fully charge an EV using a Level 1 charger.
Safety Features: Level 1 chargers are equipped with built-in safety features to protect against overcharging, overheating, short circuits, and other potential hazards. These safety features help ensure that the charging process is safe and reliable for both the EV and the charging equipment.
Pros and Cons of Using a Level 1 Charger
Using a Level 1 charger for electric vehicle (EV) charging offers several advantages and disadvantages. Let’s explore the pros and cons:
Pros of Using a Level 1 Charger
Convenience: Level 1 chargers can be plugged into any standard 120-volt household outlet, making them incredibly convenient for residential use. There’s no need for special installation or electrical work, and you can charge your EV wherever there’s an available outlet, whether it’s in your garage, driveway, or parking space.
Cost-effective: Level 1 chargers are typically the most affordable option for EV charging, both in terms of equipment cost and installation. Since they use existing household outlets, there’s no need for expensive infrastructure upgrades or additional electrical work.
Universal Compatibility: Level 1 chargers are compatible with all electric vehicles (EVs) and plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs) that use a standard J1772 connector. This universal compatibility means you can use the same charger for different EV models, making it convenient if you have multiple EVs or plan to switch vehicles in the future.
Suitability for Overnight Charging: Level 1 chargers are best suited for overnight charging, particularly for EV owners with short daily commutes. While they may not offer the fastest charging speeds, they provide ample time to recharge your EV overnight, ensuring it’s ready to go in the morning. This is especially beneficial if you have access to lower electricity rates during off-peak hours.
Low Energy Costs: Level 1 chargers typically draw less power compared to higher-level chargers, resulting in lower energy costs for charging your EV. Since they use standard household outlets, they operate at a lower voltage and amperage, which can help reduce electricity consumption and minimize utility bills.
Cons of Using a Level 1 Charger
Slow Charging Speeds: Level 1 chargers provide slower charging speeds compared to higher-level chargers like Level 2 or DC fast chargers. This means it takes longer to fully charge your EV using a Level 1 charger, which may not be suitable for EV owners with longer daily commutes or frequent long-distance travel.
Limited Range Extension: Due to the slower charging speeds of Level 1 chargers, they may not be sufficient for extending the range of your EV during shorter charging sessions, such as during work breaks or shopping trips. EV owners may need to plan their charging sessions carefully to ensure the vehicle has enough charge for their needs.
Dependence on Standard Outlets: Level 1 chargers rely on standard 120-volt household outlets for charging, which may not be available in all locations or may be limited in availability in some situations. This can restrict charging options for EV owners who need to charge their vehicles away from home or in areas with limited access to charging infrastructure.
Inconvenient for Travel: While Level 1 chargers are convenient for residential use, they may not be practical for charging during travel or road trips, where faster charging speeds are often preferred. EV owners may need to rely on higher-level chargers or public charging stations for faster charging when away from home.
Charging Your EV Safely and Efficiently

Installation and Maintenance of EV Charging Infrastructure (Optional)
Installation and maintenance of electric vehicle (EV) charging infrastructure are critical aspects of ensuring reliable and efficient charging for EV owners. Here’s a brief overview of these processes:
Installation of EV Charging Infrastructure (Optional)
Site Assessment: Before installation, conduct a thorough site assessment to determine the optimal location for the charging equipment. Consider factors such as proximity to electrical service, accessibility, parking layout, and future expansion needs.
Electrical Upgrades: Determine if any electrical upgrades are needed to support the charging equipment, such as installing dedicated circuits, upgrading electrical panels, or increasing service capacity. Work with a qualified electrician to ensure that the electrical system meets all safety and code requirements.
Permitting and Approvals: Obtain any necessary permits and approvals from local authorities or building departments before installing the charging equipment. This may include zoning permits, electrical permits, or construction permits, depending on the jurisdiction.
Equipment Selection: Choose the appropriate charging equipment based on factors such as charging speed, power requirements, compatibility with EVs, and budget constraints. Consider options such as Level 2 chargers, DC fast chargers, or Tesla Superchargers, depending on the specific needs of the location and user base.
Installation Process: Install the charging equipment according to the manufacturer’s specifications and best practices. This may involve mounting charging stations on pedestals or walls, routing electrical wiring, connecting to utility power, and testing the system for proper operation.
Testing and Commissioning: Test the installed charging infrastructure to ensure that it meets all safety and performance requirements. Verify proper electrical connections, functionality of charging stations, and compatibility with EVs. Conduct any necessary adjustments or troubleshooting to address any issues that arise during testing.
Maintenance of EV Charging Infrastructure (Optional)
Regular Inspections: Conduct regular inspections of the charging infrastructure to identify any signs of damage, wear, or malfunction. Inspect charging stations, cables, connectors, and electrical components for signs of corrosion, overheating, or physical damage.
Cleaning and Maintenance: Keep the charging equipment clean and well-maintained to ensure optimal performance.
Software Updates: Stay informed about software updates and firmware upgrades for the charging equipment. Install updates as needed to ensure compatibility with EVs, improve performance, and address any security vulnerabilities or software bugs.
Emergency Response: Develop procedures for responding to emergencies or incidents involving the charging infrastructure, such as power outages, equipment failures, or accidents. Ensure that staff are trained on proper emergency protocols and know how to safely shut down or isolate charging equipment if needed.
User Support and Maintenance Reporting: Provide ongoing support to users of the charging infrastructure, including troubleshooting assistance, maintenance reporting, and feedback collection. Establish channels for users to report any issues or concerns with the charging equipment and respond promptly to address them.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Charger
When choosing an electric vehicle (EV) charger, several factors should be considered to ensure that it meets your needs and preferences. Here are some key factors to consider:
Charging Speed: Determine the desired charging speed based on your driving habits and lifestyle. Level 1 chargers offer slower charging speeds, while Level 2 chargers and DC fast chargers provide faster charging options.
Charger Compatibility: Ensure that the charger is compatible with your specific EV model. Look for chargers that support the connector type and charging standards used by your vehicle.
Installation Requirements: Consider the installation requirements of the charger, including electrical capacity, available space, and any necessary permits or approvals. Determine if professional installation is required and factor in installation costs.
Charging Location: Decide where the charger will be installed, such as at home, work, or public charging stations. Choose a charger that is suitable for the intended location and provides convenient access for charging.
Charger Features: Evaluate the features and capabilities of the charger, such as smart charging functionality, Wi-Fi connectivity, mobile app integration, and compatibility with renewable energy sources. Choose a charger with features that meet your preferences and requirements.
Cost: Consider the cost of the charger, including the initial purchase price, installation costs, and any ongoing maintenance or subscription fees. Compare prices from different manufacturers and vendors to find the best value for your budget.
Warranty and Support: Check the warranty coverage and customer support options provided by the charger manufacturer. Choose a charger with a reliable warranty and responsive customer support to ensure assistance and protection against defects or issues.
Scalability and Future-Proofing: Consider the scalability and future-proofing of the charger, especially if you plan to expand your EV fleet or upgrade your charging infrastructure in the future. Choose a charger that can accommodate future needs and advancements in EV technology.
Safety and Compliance: Ensure that the charger meets all safety standards and regulations applicable to EV charging equipment. Look for certifications, such as an UL listing or compliance with industry standards, to ensure safe and reliable operation.
By prioritizing safety and using approved charging equipment, EV owners can ensure a safe and reliable charging experience while minimizing the risk of electrical hazards associated with using extension cords with Level 1 chargers.

Henry Michael is a leading expert in EV charging station research, specializing in innovative solutions for electric vehicle infrastructure. With a passion for sustainability and technological advancement, he is dedicated to advancing the accessibility and efficiency of EV charging worldwide.






