Juicebox Charger: A Reliable and Feature-Rich EV Charging Solution
The Juicebox Charger is a smart electric vehicle (EV) charging station designed for residential use. It offers a sleek and compact design, along with a variety of features that make it a convenient and efficient charging solution.

Understanding Juicebox Charger
While “juicebox charger” is a term you might encounter casually, it’s not the standard industry term in the world of EV charging. The most common term is EV charger, or EVSE (Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment).
- Definition of JuiceBox Charger:
EMotorWerks is the manufacturer of the JuiceBox brand of electric vehicle charging stations. It is renowned for its svelte form, clever charging capabilities, and adaptability to different EV models. JuiceBox chargers come in a variety of models and configurations to meet the needs of charging in homes, businesses, and public spaces.
- How does a JuiceBox charger work?
JuiceBox chargers work by providing electric power to charge the battery of an electric vehicle. They are typically installed at a fixed location, such as a home, workplace, or public charging station.
When an EV is plugged into a JuiceBox charger, it communicates with the vehicle’s onboard charging system to deliver the appropriate amount of power at the desired charging speed.
Many JuiceBox chargers offer smart charging features, allowing users to monitor and control the charging process remotely via smartphone apps or web interfaces.
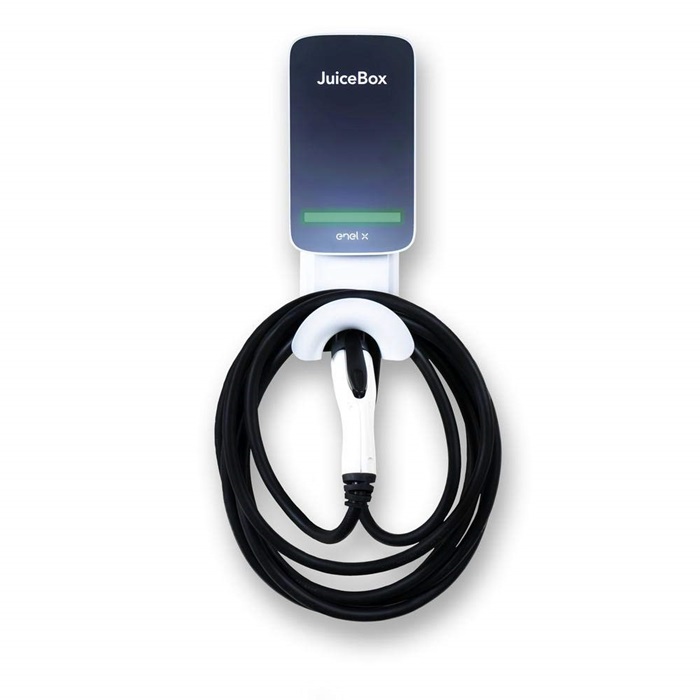

There are two main classifications for EV chargers:
| By Charging Speed | Level 1 Charger (Slow Charging): Plugs into a standard 120-volt household outlet, good for overnight charging but the slowest option. |
| Level 2 Charger (Fast Charging): Uses a 240-volt outlet (like a dryer outlet), significantly faster than Level 1 and common for home and public charging. | |
| Level 3 Charger (DC Fast Charging): Delivers high-voltage DC power directly to the battery, enabling very fast charging (typically for public use on long trips). | |
| By Installation Type | Wall-Mounted Chargers: Compact units permanently mounted on a wall in your garage for convenient home charging (Level 1 or Level 2). |
| Portable Chargers: Can be easily transported and plugged into a standard outlet (Level 1 or Level 2, lower power output than wall-mounted). | |
| Public Chargers: Found in various locations like shopping centers, offering Level 2 or DC Fast Charging options (may require payment or network membership). | |
| Networked Chargers: Connected to a central network for remote monitoring, control, and data collection (often part of public charging stations). |
- Benefits of Using a JuiceBox Charger:
Fast charging speeds: JuiceBox chargers support Level 2 charging, providing faster charging compared to standard Level 1 chargers.
Smart charging features: Many JuiceBox chargers offer smart features such as scheduling, energy monitoring, and remote control via smartphone apps.
Compatibility: JuiceBox chargers are compatible with a wide range of electric vehicle models and can be installed in various locations.
Energy efficiency: JuiceBox chargers are designed to be energy-efficient, helping users minimize electricity costs and reduce their environmental footprint.
- Comparison of EV Chargers:
| Feature | Charging Speed | Installation | Ideal Use |
| Level 1 Charger | Slowest | None (plugs into the outlet) | Overnight charging |
| Level 2 Charger | Faster | Requires an electrician (240V outlet) | Home & Public Charging |
| DC Fast Charger | Fastest | Not applicable (public stations) | Long trips, quick top-ups |
| Wall-Mounted Charger | Varies (Level 1 or 2) | Permanent installation | Home charging |
| Portable Charger | Slower than Wall-Mounted | Easy to transport | Backup, occasional charging |
| Public Charger | Varies (Level 2 or DC Fast) | Public locations | Public charging on the go |
| Networked Charger | Varies (Level 2 or DC Fast) | Requires a network connection | Provides remote features, data collection |
Juicebox Chargers: A Closer Look
As discussed earlier, “juicebox charger” isn’t the standard term in EV charging. Let’s analyze these aspects of JuiceBox chargers through the lens of frame semantics.
- Components of an EV Charger:
Input Connector: Plugs into the electrical grid (standard outlet for Level 1 or high-voltage connection for DC Fast Charging).
Converter: Converts AC (alternating current) electricity from the grid to DC (direct current) for your EV battery.
Control Unit: regulates the flow of electricity, monitors charging status, and ensures safety features like surge protection and temperature control.
Output Connector: Connects to the charging port on your electric vehicle.
Cable (optional): connects the charger to the vehicle (more common for portable chargers).
- Charging Speed of an EV Charger:
In the frame of “Charging Speed,” the focus is on the rate at which a JuiceBox charger can replenish the battery of an electric vehicle. This frame encompasses parameters like power output (measured in kilowatts), which determines how quickly the charger can deliver energy to the vehicle.
EV charger speeds vary depending on the type.
- Level 1 Charger (Slow): Adds about 3-5 miles of range per hour.
- Level 2 Charger (Fast): Adds 25–50 miles of range per hour.
- DC Fast Charger (Ultra-Fast): Provides up to 80% charge in 20–30 minutes.
Additionally, factors such as the vehicle’s battery capacity and charging protocol compatibility also influence the effective charging speed.
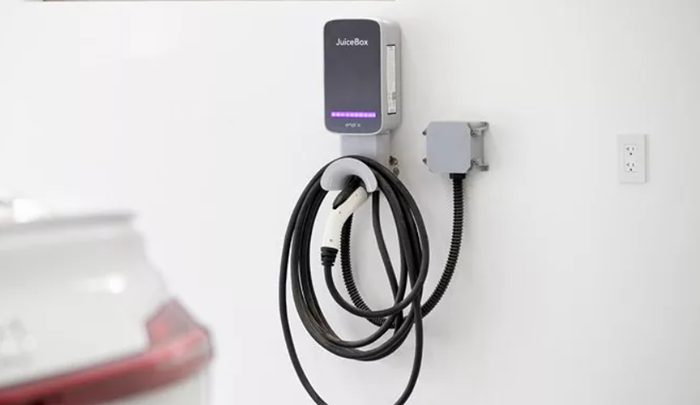

- Compatibility with Different Devices:
Most EV chargers use universal standards for connector types to ensure compatibility with a wide range of electric vehicles.
J1772 (North America): Standard connector for Level 1 and Level 2 AC charging in North America.
CCS (Combined Charging System): Combines J1772 for AC and a DC fast charging port in one connector, becoming increasingly popular globally.
Tesla Supercharger: Tesla uses a proprietary connector for its Supercharger network, but adapters are available for Teslas to use J1772 and CHAdeMO connectors.
CHAdeMO (Asia & Europe): Common DC fast charging connector type in Asia and Europe, less common in North America.
- Portability and Design of EV Chargers:
Wall-Mounted Chargers: Compact units permanently installed on a wall in your garage for home charging (Level 1 or Level 2).
Portable Chargers: Can be easily transported and plugged into a standard outlet (Level 1 or Level 2, typically lower power output than wall-mounted).
- Safety Features of EV Chargers:
EV chargers incorporate essential safety features to protect your vehicle and electrical system:
- Surge Protection: Guards against sudden voltage spikes.
- Grounding: Ensures proper grounding to prevent electrical leaks.
- Temperature Monitoring: Detects overheating and shuts down the charger if necessary.
- GFCI (Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter): In some chargers, it cuts off power in case of a ground fault.
- Communication Protocols: Modern chargers may use communication protocols to ensure safe and compatible charging between the charger and your vehicle.
Decoding the Lingo of Juicebox Charger
Let’s delve into the lexical semantics of JuiceBox chargers by exploring associated terminology, common brands, charging capacity, voltage and current output, and user interface indicators.

- Terminology Associated with JuiceBox Chargers:
Charging station: a common term for the physical unit where the JuiceBox charger is installed.
EVSE (Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment): refers to the entire charging system, including the JuiceBox charger, cables, and connectors.
Connector types: terms like J1772 (standard connector for North America), Type 2 (common in Europe), and Tesla’s proprietary connector.
- Common Brands of JuiceBox Chargers:
eMotorWerks is the manufacturer of JuiceBox chargers, offering various models for residential, commercial, and public use.
Enel X: Known for their JuiceBox chargers, Enel X acquired eMotorWerks, expanding their portfolio in the EV charging sector.
- Charging Capacity of JuiceBox Chargers:
JuiceBox chargers typically come in various power ratings, ranging from 16 amps (3.8 kW) to 80 amps (19.2 kW) for residential models and even higher for commercial or public-use models.
Charging capacity may also refer to the maximum energy (in kilowatt-hours) that can be delivered to the vehicle’s battery during a charging session.
- Voltage and current output of JuiceBox chargers:
JuiceBox chargers primarily operate at standard household voltages (120V or 240V AC) but can support higher voltages for faster charging.
Current output varies depending on the model and power rating, typically ranging from 12 amps to 80 amps for Level 2 charging.
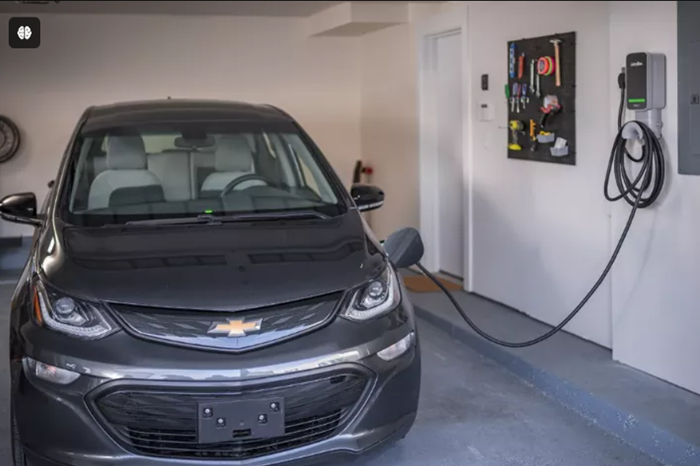

- User Interface and Indicators on JuiceBox Chargers:
LCD Display: Some JuiceBox models feature a built-in display for showing charging status, power output, and error messages.
LED Indicators: Used to indicate charging status (e.g., charging, standby, fault), connectivity, and power output levels.
Buttons or Touchscreen: Interfaces for user interaction, allowing users to start/stop charging, adjust settings, and access advanced features.
Wi-Fi Connectivity: Enables remote monitoring and control via smartphone apps or web interfaces, providing real-time updates and alerts.
Studies and expert opinions on Juicebox Charger
Let’s explore topical authority related to JuiceBox chargers across expert reviews, user ratings and feedback, industry standards, technological innovations, and popular use cases:
- Expert Reviews on JuiceBox Chargers:
While “juicebox charger” isn’t the standard term, there are many resources for expert reviews on EV chargers:
- Consumer Reports
- Electric Vehicle Charging Directory
- US Department of Energy
- Websites of Major EV Charger Brands:
These resources provide in-depth reviews considering factors like charging speed, features, ease of use, compatibility, warranty, and customer service.
- User Ratings and Feedback on JuiceBox Chargers:
Platforms like Amazon, Home Depot, and eMotorWerks’ own website host user reviews and ratings for JuiceBox chargers, offering insights into real-world experiences.
Forums and online communities such as Reddit’s r/electricvehicles or EV enthusiast groups on Facebook often discuss personal experiences and recommendations regarding JuiceBox chargers.

- Industry Standards for JuiceBox Chargers:
JuiceBox chargers adhere to industry standards such as SAE J1772 for connector compatibility and communication protocols.
Other relevant standards may include UL (Underwriters Laboratories) certifications for safety, OCPP (Open Charge Point Protocol) for interoperability, and NEC (National Electrical Code) compliance for installation requirements.
- Innovations in JuiceBox Charger Technology:
Innovations in JuiceBox chargers may include advanced smart charging features like load balancing, dynamic pricing integration, and vehicle-to-grid (V2G) capabilities.
Improvements in hardware design, such as compact form factors, enhanced durability, and increased power output, contribute to the evolving landscape of JuiceBox charger technology.
- Popular use cases for JuiceBox chargers:
Residential Charging: JuiceBox chargers are commonly installed at homes for convenient overnight charging of electric vehicles.
Workplace Charging: Employers provide JuiceBox chargers to support employees who drive electric vehicles, promoting sustainability and employee satisfaction.
Public Charging: JuiceBox chargers are installed at public locations like shopping centers, parking garages, and hotels to serve the needs of electric vehicle owners on the go.
Market Trends
- Demand for JuiceBox Chargers:
The demand for JuiceBox chargers is experiencing steady growth, driven by the increasing adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) worldwide.
Factors such as government incentives, environmental awareness, and improvements in EV technology contribute to the rising demand for home and public charging solutions.
- Price Ranges of JuiceBox Chargers:
JuiceBox chargers come in a range of price points depending on factors such as power output, smart features, and installation requirements.
Residential JuiceBox chargers typically range from $400 to $1,000, while commercial or high-power models may cost upwards of $1,000 to $2,000 or more.

- Market Share of Different JuiceBox Charger Brands:
eMotorWerks, the manufacturer of JuiceBox chargers, holds a significant market share in the EV charging sector.
Other notable brands in the market include ChargePoint, Tesla, Siemens, and Schneider Electric, among others.
- Emerging Technologies in JuiceBox Chargers:
Smart Charging: JuiceBox chargers are integrating advanced smart features like Wi-Fi connectivity, smartphone app control, energy monitoring, and scheduling capabilities.
Bidirectional Charging (V2G): Some JuiceBox chargers are exploring bidirectional charging capabilities, allowing EVs to serve as energy storage devices and feed power back to the grid during peak demand periods.
- Future Prospects for the JuiceBox Charger Market:
The future of the JuiceBox charger market looks promising, with continued growth expected as the electric vehicle market expands.
Innovations in technology, such as faster charging speeds, enhanced interoperability, and an improved user experience, will drive further adoption of JuiceBox chargers.
Market expansion into new regions, along with partnerships with automakers, utilities, and infrastructure providers, will play a crucial role in shaping the future landscape of the JuiceBox charger market.
Maintenance and Care
Following the instructions below will help ensure the longevity and proper operation of your juice box charger and the responsible disposal of your old device.

1. Cleaning and upkeep:
- Regularly wipe down the exterior of the juicebox charger with a damp cloth to remove any dust or dirt.
- Use a soft brush or compressed air to clean out any debris from the charging ports.
- Avoid using harsh chemicals or abrasive materials that could damage the charger.
2. Storage Recommendations:
- Store the juicebox charger in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and moisture.
- Avoid storing the charger in extreme temperatures or humid environments.
- Keep the charger in its original packaging or in a protective case when not in use to prevent damage.
3. Troubleshooting Common Issues:
- If the charger is not charging properly, check the power source and ensure it is working.
- Inspect the charging cable for any signs of damage or fraying.
- Try using the charger with different devices to determine if the issue is with the charger or the device.
- Reset the charger by unplugging it from the power source for a few minutes, then plugging it back in.
4. Warranty and Customer Support:
- Refer to the warranty information provided with the juicebox charger for details on coverage and duration.
- Contact the manufacturer’s customer support for assistance with warranty claims, troubleshooting, or any other issues.
- Keep proof of purchase and warranty documentation in a safe place for future reference.
5. Recycling and Disposal:
- When disposing of old juicebox chargers, check local regulations for electronic waste recycling options.
- Many electronics retailers and recycling centers accept old chargers for proper disposal and recycling.
- Remove any batteries or other components that may require separate disposal, following applicable guidelines.
Accessories and Add-ons
When selecting accessories and add-ons for your juicebox charger, prioritize compatibility, quality, and convenience to enhance your charging experience while maintaining the safety and efficiency of your devices.
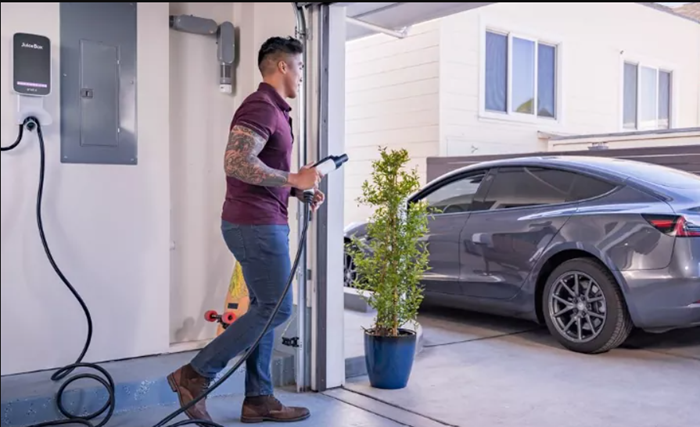

- Cables and Connectors for EV Chargers (not Juicebox Chargers)
EV chargers typically come with cables pre-attached for the intended charging level (Level 1 or Level 2). However, there might be situations where you need additional cables or connectors:
Replacement Cables: If your original cable gets damaged, you can purchase a replacement from the charger manufacturer or a compatible third-party vendor.
Adapter Cables: In rare cases, you might need an adapter cable if you’re using a public charging station with a connector type different from your car’s charging port (for example, an adapter from Tesla’s proprietary connector to a J1772 connector).
- Protective Cases for EV Chargers (Portable Chargers)
Carrying Cases: Portable EV charger carrying cases offer protection from scratches, bumps, and dust during storage or transportation.
Weatherproof Enclosures (Optional): While most portable chargers are designed for outdoor use, a weatherproof enclosure can provide additional protection from harsh weather conditions if needed.
- Car Adapters for Juicebox Chargers (Not Applicable)
Car adapters are typically needed to convert a cigarette lighter socket in a gasoline-powered car to a USB port for charging mobile devices. EV chargers are designed to directly charge electric vehicles, not other devices.
- Wireless Charging Options for Juicebox Chargers (Not Applicable)
Juicebox chargers, or more accurately, EV chargers, are for the wired charging of electric vehicles. Wireless charging for EVs is still under development but not commercially available yet. It might become an option in the future, but currently, wired charging is the standard.
- Multi-Device Charging Stations Compatible with Juicebox Chargers (Limited Compatibility)
While juicebox chargers (EV chargers) are designed for electric vehicle charging, some home charging stations offer additional functionalities:
- Multi-Port Charging Stations: Some wall-mounted Level 2 charger models might have additional USB ports for charging smartphones, tablets, or other devices simultaneously while your car is plugged in.
- Smart Charging Stations: These integrate with smart home systems and might allow you to manage charging schedules or monitor energy consumption for both your EV and other devices plugged into the station (depending on the specific model’s features).
Environmental Impact
By considering the energy efficiency, materials used, carbon footprint, recycling programs, and sustainability initiatives associated with juicebox chargers, consumers can make more environmentally conscious choices when selecting and using these devices.
- Energy Efficiency:
Juicebox chargers often prioritize energy efficiency, with features like auto-shutdown when devices are fully charged and low standby power consumption.
Look for Energy Star-certified chargers or those with other energy efficiency certifications to ensure minimal energy consumption during charging.
- Materials used in manufacturing:
Many juicebox chargers are made from durable and recyclable materials such as ABS plastic, aluminum, and recyclable metals.
Some manufacturers prioritize the use of eco-friendly materials and avoid hazardous substances like lead and mercury in their chargers.
- Carbon Footprint:
The carbon footprint of using juicebox chargers depends on factors like the energy source used for charging (e.g., renewable vs. non-renewable), charger efficiency, and charging frequency.
Using renewable energy sources for charging and opting for energy-efficient chargers can help reduce the carbon footprint associated with charging devices.
- Recycling Programs:
Many electronics manufacturers offer recycling programs for their products, including juicebox chargers.
Check with the manufacturer or local electronic waste recycling centers to learn about recycling options for your old juicebox chargers.
Some retailers may also offer trade-in or recycling programs for old electronics when purchasing new chargers.
- Sustainability Initiatives:
The juicebox charger industry is increasingly focusing on sustainability initiatives to reduce environmental impact.
This may include efforts to minimize packaging waste, increase product durability and longevity, and use eco-friendly materials in manufacturing.
Some companies may also participate in carbon offset programs or invest in renewable energy projects to mitigate environmental impacts.
User Experience
Considering factors such as ease of use, charging speed, design preferences, user recommendations, and customization options can help users find the most suitable juicebox charger for their needs and preferences.
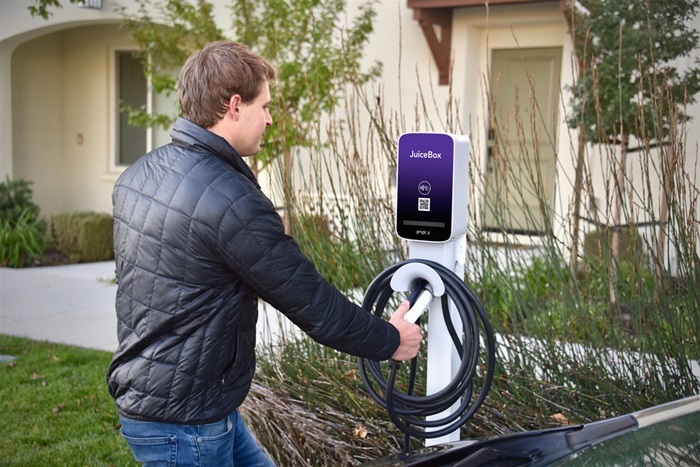

- Ease of Use:
Juicebox chargers are designed to be user-friendly, with intuitive interfaces and simple plug-and-play functionality.
Look for chargers with features like LED indicators to signal charging status and easy-to-access ports for convenient device connection.
- Charging Speed and Efficiency:
Charging speed and efficiency can vary depending on factors like the charger’s output power, device compatibility, and charging protocols supported.
High-speed charging technologies like Quick Charge and Power Delivery can significantly reduce charging times for compatible devices.
Users should consider their device’s charging requirements and choose a juicebox charger with appropriate output power and compatibility.
- Ergonomics and Design Preferences:
Ergonomics play a crucial role in user comfort and satisfaction with juicebox chargers.
Consider factors such as size, shape, and weight when selecting a charger, especially for portable use.
Design preferences may vary among users, with options ranging from sleek and minimalist designs to rugged and durable constructions.
- User Recommendations:
User recommendations for the best juicebox chargers often consider factors like charging speed, reliability, durability, and value for money.
Online reviews and forums can provide valuable insights from real users about their experiences with different chargers.
Users frequently recommend well-known brands and models with consistently positive reviews and ratings.
- Customization Options:
Some juicebox chargers offer customization options to cater to individual preferences and needs.
This may include features like interchangeable faceplates, customizable LED lighting, or optional accessories for added functionality.
Users interested in customization should look for chargers that offer compatible accessories or aftermarket customization options.
Safety and Regulations
- Overheating Protection:
Juicebox chargers often incorporate built-in mechanisms for overheating protection to prevent damage to the charger and connected devices.
These protections may include temperature sensors, thermal cutoff switches, and circuitry to regulate heat dissipation during charging.
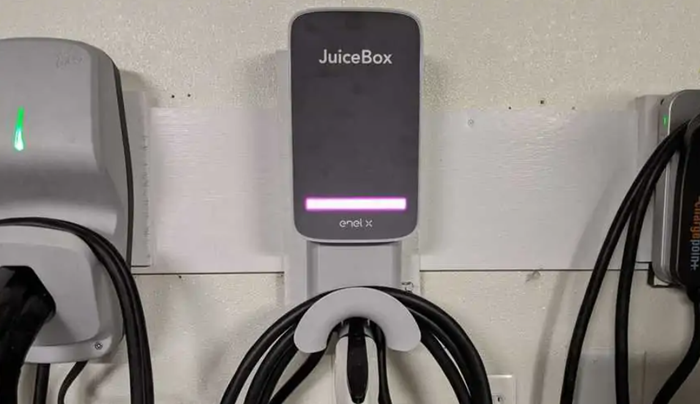

- Compliance with Safety Standards:
Manufacturers of juicebox chargers typically adhere to established safety standards for electronic devices, such as those set by organizations like UL (Underwriters Laboratories), CE (Conformité Européenne), and the FCC (Federal Communications Commission).
Compliance with these standards ensures that chargers meet minimum safety requirements for electrical, electromagnetic, and mechanical hazards.
- Regulatory Certifications:
Look for regulatory certifications and markings on juicebox chargers, such as the UL mark, CE mark, or FCC ID.
These certifications indicate that the charger has undergone testing and meets the safety and regulatory requirements in the regions where it is sold.
- Best Practices for Safe Use:
Follow the manufacturer’s instructions and guidelines for using juicebox chargers, including recommended input and output voltage, current ratings, and compatible devices.
Avoid using damaged or frayed charging cables, and ensure proper ventilation around the charger to prevent overheating.
Unplug the charger from the power source when not in use and avoid overcharging devices to prolong battery life and prevent potential safety hazards.
- Tips for Avoiding Counterfeit Chargers:
Purchase juicebox chargers from reputable retailers and authorized distributors to reduce the risk of counterfeit products.
Check for authenticity markers such as holographic labels, serial numbers, and manufacturer branding to verify the legitimacy of the charger.
Be cautious of unusually low prices or suspiciously similar packaging that may indicate counterfeit products.
By prioritizing safety features, complying with regulations and standards, and following best practices for safe use, users can minimize the risk of accidents and ensure the safe and reliable operation of their juicebox chargers.

Henry Michael is a leading expert in EV charging station research, specializing in innovative solutions for electric vehicle infrastructure. With a passion for sustainability and technological advancement, he is dedicated to advancing the accessibility and efficiency of EV charging worldwide.