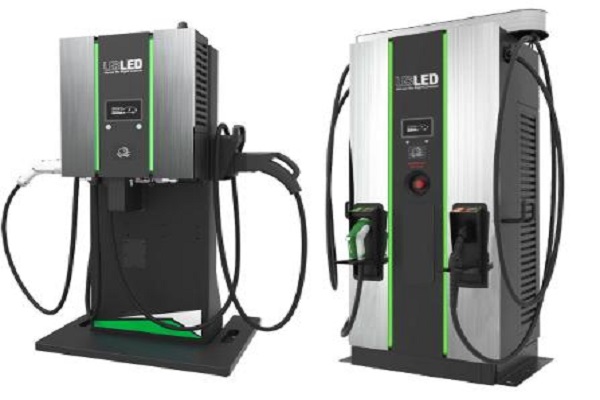
Deciphering Level 3 EV Chargers: A Comprehensive Guide
The electric vehicle revolution is gaining momentum, and charging infrastructure is key. Enter Level 3 EV chargers, also known as DC Fast Chargers, the titans of the charging world. These high-powered stations offer a glimpse into the future, providing ultrafast charging times ideal for long-distance travel. But are Level 3 chargers right for you?
Understanding Level 3 EV Chargers
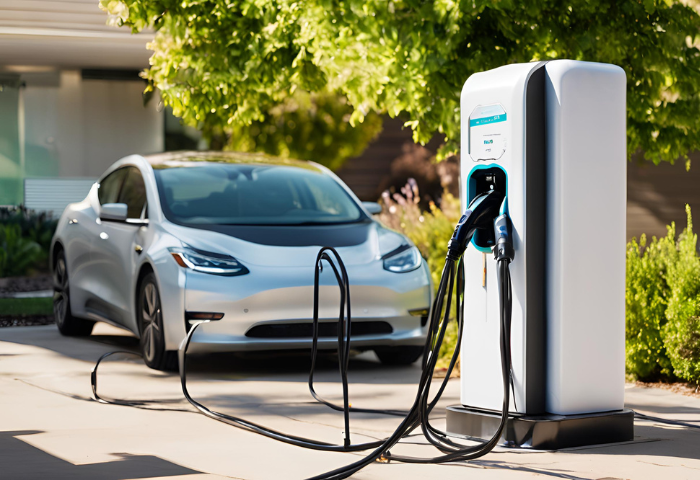
Definition and How It Works
Definition:
Level 3 EV chargers, also known as DC fast chargers, represent a significant advancement in electric vehicle charging technology. Unlike Level 1 and Level 2 chargers, which primarily operate on alternating current (AC) and are typically used for overnight or daily charging, Level 3 chargers utilize direct current (DC) to deliver a substantial amount of power to an electric vehicle’s battery in a relatively short period of time. This enables rapid charging and significantly reduces the time required to replenish the vehicle’s battery, making it ideal for long-distance travel and minimizing charging downtime.
How It Works:
Level 3 EV chargers work by bypassing the onboard AC-to-DC converter found in most electric vehicles. Instead, they directly supply DC power to the vehicle’s battery, allowing for faster and more efficient charging. The charger communicates with the vehicle to negotiate the appropriate charging parameters, such as voltage and current, to ensure safe and optimal charging.
Inside the Level 3 charger, high-powered electronics convert the AC power from the grid into DC power at much higher voltage levels, typically ranging from 200 volts to 1000 volts or more, depending on the charger’s specifications. This high-voltage DC power is then delivered to the vehicle’s battery through specialized connectors and cables designed to handle the high currents and power levels involved in fast charging.
Comparing Level 1, Level 2, and Level 3 Chargers
| Aspect | Level 1 Charger | Level 2 Charger | Level 3 Charger |
| Power Source | Standard 120V AC outlet | 240V AC outlet | High-voltage DC power source |
| Charging Speed | Slow (Typically 2-5 miles of range per hour) | Moderate (Typically 10-30 miles of range per hour) | Rapid (Typically 50-350 miles of range per hour) |
| Typical Power Output | 1.4 kW – 1.9 kW | 3.3 kW – 19.2 kW | 50 kW – 350 kW |
| Ideal Use | Overnight or long-term charging at home or workplace | Daily charging at home or workplace | On-the-go charging for long-distance travel |
| Typical Connector | Standard household outlet or proprietary connector | J1772 connector or proprietary connector | CHAdeMO, CCS, or proprietary connector |
| Compatibility | Compatible with all electric vehicles | Compatible with most electric vehicles | Compatible with select electric vehicles (varies by connector type and manufacturer) |
| Installation Requirements | Standard electrical outlet; minimal installation cost | Dedicated 240V circuit; moderate installation cost | High-voltage DC power source; significant installation cost |
| Infrastructure Needs | Minimal; readily available in most locations | Moderate; increasingly available in public and commercial locations | Advanced; typically found along major transportation routes and in urban areas |
| Typical Application | Personal use; low daily driving needs | Personal and commercial use; moderate daily driving needs | Commercial use; long-distance travel and rapid charging needs |
Charging Time for Different EV Models
| EV Model | Battery Capacity | Level 2 Charging Time (0-100%) |
| Tesla Model S | 75-100 kWh | 8-12 hours |
| Tesla Model 3 | 50-75 kWh | 6-10 hours |
| Nissan Leaf | 40-62 kWh | 6-10 hours |
| Chevrolet Bolt | 60 kWh | 7-11 hours |
| Audi e-tron | 71-95 kWh | 8-12 hours |
| Porsche Taycan | 79.2-93.4 kWh | 9-13 hours |
Common Brands and Models of Level 3 Chargers
| Brand | Model | Maximum Power Output | Connector Types | Features |
| ABB | Terra HP | Up to 350 kW | CCS, CHAdeMO | Modular design, liquid-cooled cables |
| EVgo | EVgo Fast Chargers | Up to 100 kW | CCS, CHAdeMO | Nationwide network, reliable charging |
| ChargePoint | Express Plus | Up to 500 kW | CCS, CHAdeMO | Scalable power output, network integration |
| Tritium | Veefil-PK | Up to 350 kW | CCS, CHAdeMO | Compact design, high-power charging |
| BTC Power | Terra HP | Up to 350 kW | CCS, CHAdeMO | Modular design, high reliability |
| Delta Electronics | DC Wallbox EV Charger | Up to 25 kW | CCS, CHAdeMO | Compact wall-mounted design, versatility |
| Siemens | SICHARGE | Up to 300 kW | CCS, CHAdeMO | Advanced communication capabilities |
Future of Level 3 Charging Technology
| Aspect | Description |
| Increased Power Output | Future Level 3 chargers may support even higher power outputs, enabling faster charging times and reducing overall charging durations. This could involve advancements in power electronics, cooling systems, and grid infrastructure to handle the increased load. |
| Modular Design | Modular design could allow for easier scalability and flexibility in Level 3 charging infrastructure. Charging stations could be easily expanded or upgraded by adding modular units, accommodating future increases in demand and technological advancements without requiring a complete overhaul of the infrastructure. |
| Bidirectional Charging | Bidirectional charging capabilities would enable EV batteries to not only receive power from the grid but also send power back to the grid or support other applications, such as home energy storage or grid stabilization. This could facilitate vehicle-to-grid (V2G) integration, allowing EVs to become part of a dynamic energy ecosystem. |
| Smart Grid Integration | Enhanced integration with smart grid technologies would enable Level 3 chargers to communicate with the grid in real-time, optimizing charging schedules based on grid conditions, energy prices, and user preferences. This could reduce strain on the grid during peak demand periods and promote the use of renewable energy sources for charging. |
| Dynamic Charging | Dynamic charging systems could allow EVs to charge while in motion, eliminating the need for frequent stops and significantly extending driving range. This technology, often referred to as “electric roads” or “inductive charging,” could revolutionize long-distance travel for electric vehicles, making them more competitive with traditional internal combustion engine vehicles. |
| Enhanced User Experience | Future Level 3 chargers may offer improved user interfaces, intuitive payment systems, and enhanced connectivity features, such as smartphone integration and remote monitoring capabilities. This would streamline the charging process, increase user convenience, and provide valuable data insights for operators and stakeholders. |
| Standardization Efforts | Continued efforts to standardize charging protocols, connector types, and communication standards would promote interoperability and compatibility among different EV models and charging networks. This would reduce fragmentation in the EV charging market and enhance the overall user experience, encouraging widespread adoption of electric vehicles. |
Installation Requirements

Electrical Requirements
| Electrical Requirement | Description |
| Power Output | Level 3 EV chargers typically require high-power connections, ranging from 50 kW to over 350 kW, to facilitate fast charging of electric vehicles. |
| Voltage | The voltage requirement for Level 3 chargers varies depending on the charger’s power output and design. Common voltage levels include 200V to 1000V DC, depending on the charger type. |
| Current | Level 3 chargers typically require high-current DC connections, ranging from 100A to 1000A, to deliver the necessary power output for fast charging. |
| Three-Phase Power | Many Level 3 chargers utilize three-phase power connections to efficiently distribute power and minimize grid impact. |
| Grid Connection | Level 3 chargers require robust grid connections capable of handling high power loads and complying with local electrical regulations and standards. |
| Transformer | Some Level 3 charging installations may require transformers to step up or step down voltage levels to match the charger’s specifications and grid conditions. |
| Grid Stability | Ensuring grid stability is essential for Level 3 charging installations, requiring coordination with utility providers and adherence to grid connection standards. |
| Cooling System | High-power Level 3 chargers often incorporate sophisticated cooling systems to dissipate heat generated during charging and maintain optimal performance and reliability. |
| Safety Systems | Level 3 chargers must incorporate comprehensive safety systems, including overcurrent protection, ground fault detection, and emergency shut-off mechanisms. |
| Communication Interfaces | Communication interfaces such as Ethernet, Modbus, or CAN bus may be required for data exchange between the charger, electric vehicle, and external management systems. |
Site Preparation and Space Considerations
| Aspect | Description |
| Location Selection | Choose a location with good visibility, accessibility, and proximity to major roads or highways to attract EV drivers. Consider nearby amenities such as restrooms, shops, or restaurants for user convenience. |
| Space Allocation | Allocate sufficient space for the charger(s), associated equipment (such as transformers, switchgear, and cooling systems), and clearances for safe operation, maintenance, and user access. |
| Parking Layout | Designate parking spaces specifically for EV charging, ensuring proper alignment, accessibility, and signage to guide users to the charging stations. Consider the layout’s scalability to accommodate future expansion. |
| Electrical Infrastructure Assessment | Conduct a thorough assessment of the site’s electrical infrastructure to determine compatibility with Level 3 chargers. Ensure adequate electrical capacity, voltage levels, and grid connection capabilities to support the charging stations. |
| Utility Coordination | Coordinate with local utility providers to assess grid capacity, obtain necessary permits, and ensure compliance with electrical regulations and standards. Work with utilities to facilitate grid connection and upgrades if needed. |
| Environmental Considerations | Evaluate environmental factors such as sun exposure, wind, and drainage to minimize the impact on charging infrastructure and ensure optimal performance and longevity. Consider landscaping or shelters to provide protection from the elements. |
| Permitting and Zoning | Obtain necessary permits and approvals from local authorities and adhere to zoning regulations governing EV charger installations. Ensure compliance with building codes, environmental regulations, and ADA accessibility requirements. |
| Safety and Security | Implement safety measures such as bollards, barriers, and lighting to protect charging equipment and ensure user safety. Consider security features such as surveillance cameras and access controls to deter vandalism and theft. |
| Accessibility | Design charging stations and parking spaces to comply with accessibility standards, providing features such as designated accessible parking, signage, and pathways for individuals with disabilities. |
Permits and Local Regulations
| Aspect | Description |
| Permitting Process | Understand the permitting process for EV charger installations in your locality. This may involve obtaining permits from municipal, county, or state authorities, depending on jurisdictional requirements. |
| Zoning Regulations | Familiarize yourself with zoning regulations governing the installation of EV charging infrastructure. Ensure compliance with setback requirements, land use restrictions, and zoning designations for the chosen site. |
| Electrical Codes | Adhere to electrical codes and standards specified by national or regional authorities, such as the National Electrical Code (NEC) in the United States or equivalent regulations in other countries. |
| Building Codes | Comply with building codes applicable to construction, renovation, or modification of structures housing EV charging equipment. This includes considerations for structural integrity, fire safety, and accessibility. |
| Environmental Regulations | Assess environmental regulations governing land use, construction, and potential environmental impacts associated with EV charger installations. Obtain necessary permits for environmental compliance. |
| Historic Preservation | If the installation site is in a historic district or near historically significant structures, consult with historic preservation authorities to ensure compliance with preservation regulations. |
| ADA Accessibility | Ensure that EV charging stations and associated facilities comply with accessibility requirements outlined in the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) or equivalent accessibility standards in other regions. |
| Utility Coordination | Coordinate with utility providers to obtain approvals for grid connection, metering, and any necessary infrastructure upgrades. Ensure compliance with utility regulations and requirements for EV charging. |
| Community Engagement | Engage with local communities, stakeholders, and residents to address concerns, gather feedback, and build support for EV charger installations. Address any public concerns or opposition through transparent communication and collaboration. |
Accessibility Standards
Accessible Parking Spaces: ADA regulations require accessible parking spaces to be provided near Level 3 charger installations. These spaces must have adequate width to accommodate wheelchair-accessible vehicles and include adjacent access aisles to facilitate wheelchair transfers.
Accessible Pathways: Accessible pathways leading to Level 3 charger installations must be provided to enable individuals with disabilities to reach the charging station safely and independently. Pathways should be wide, smooth, and free of obstacles, with minimal changes in elevation and suitable for wheelchair access.
Vertical Clearance: Level 3 charger installations should provide sufficient vertical clearance to accommodate individuals using mobility aids such as wheelchairs or scooters. Overhead structures, signs, and equipment should be positioned to ensure adequate clearance and avoid obstruction.
Signage and Wayfinding: Clear and accessible signage is essential to guiding individuals with disabilities to Level 3 charger installations. Signage should include International Symbol of Accessibility (ISA) symbols, tactile elements, and Braille signage to effectively convey information to individuals with visual or cognitive impairments.
Reach Ranges: Controls and equipment associated with Level 3 charger installations should be positioned within accessible reach ranges to ensure usability by individuals with disabilities. This includes positioning charging connectors, payment terminals, and instructional signage at heights and locations that can be easily accessed from a seated or standing position.
Tactile Indicators: Tactile indicators such as detectable warning surfaces and tactile paving should be provided at Level 3 charger installations to alert individuals with visual impairments to changes in path direction, hazards, or proximity to charging equipment.
Color Contrast: Color contrast is important for individuals with low vision or color vision deficiencies to identify and distinguish elements of Level 3 charger installations. Ensure sufficient contrast between background and foreground colors for signage, markings, and visual cues.
Accessible Features: Level 3 charger installations may incorporate additional accessible features to enhance usability for individuals with disabilities, such as audio feedback, large-print instructions, and remote monitoring capabilities.
Safety and Compliance Standards
| Standard | Description |
| UL 2202 | Covers safety requirements for charging systems for use with electric vehicles, including protection against electric shock, fire hazards, mechanical hazards, etc. |
| ISO 15118 | Specifies communication protocols between electric vehicles and charging infrastructure for authentication, authorization, and billing. |
| IEC 61851 | a series of standards covering charging infrastructure for electric vehicles, including safety aspects, communication protocols, and performance requirements. |
| NEC (National Electrical Code) | Provides regulations for the installation of electrical equipment, including EV charging stations, ensuring compliance with local electrical codes. |
| CE Marking | Demonstrates compliance with European safety, health, and environmental protection legislation, ensuring the charger meets relevant EU directives. |
| CHADEMO / CCS | Communication and charging protocols ensure interoperability and compatibility with electric vehicles from various manufacturers. |
| IEEE 1547 | Guidelines for the interconnection and interoperability of distributed energy resources, including EV chargers, with the electric power system. |
| NFPA 70 (National Electrical Code) | Provides additional guidelines specific to EV charging installations, ensuring compliance with electrical standards in the United States. |
| IEC 62196 | Specifies dimensions and requirements for plugs, socket-outlets, vehicle connectors, and vehicle inlets for conductive charging of electric vehicles. |
| NEMA Standards | Publishes standards related to electrical equipment, including EV charging stations, ensuring safety, compatibility, and performance. |

Upfront Installation Costs
Charger Equipment Cost: The cost of the Level 3 charger itself is a significant component of upfront installation costs. Level 3 chargers are typically more expensive than Level 1 or Level 2 chargers due to their higher power output and advanced features. Prices can range from tens of thousands to hundreds of thousands of dollars, depending on the manufacturer, model, and specifications of the charger.
Site Preparation: Site preparation costs include expenses related to preparing the installation site for the Level 3 charger, such as excavation, grading, concrete work, and landscaping. Factors such as site accessibility, terrain, and existing infrastructure can influence site preparation costs.
Electrical Infrastructure Upgrades: Installing Level 3 chargers may require upgrades to the existing electrical infrastructure to accommodate the charger’s high-power requirements. This can include upgrading electrical panels, wiring, transformers, and other components to handle the increased load. Electrical infrastructure upgrades can represent a significant portion of upfront installation costs, particularly for installations in remote or underserved areas with limited electrical capacity.
Permitting and Regulatory Fees: Obtaining permits and complying with regulatory requirements for Level 3 charger installations may incur fees and expenses. Permitting fees vary depending on the jurisdiction and the complexity of the installation and may include building permits, electrical permits, zoning approvals, and environmental permits.
Labor Costs: Labor costs for installing Level 3 chargers include expenses for hiring qualified electricians, contractors, and installation crews to perform the installation work. Labor costs can vary depending on factors such as labor rates, project duration, and the complexity of the installation.
Networking and Communication Infrastructure: Level 3 chargers may require networking and communication infrastructure to enable remote monitoring, billing, and software updates. Costs associated with networking equipment, communication devices, and software integration should be considered as part of upfront installation costs.
Accessibility and ADA Compliance: Ensuring accessibility and ADA compliance for Level 3 charger installations may require additional expenses for features such as accessible parking spaces, signage, and pathways. These costs should be factored into the overall installation budget to ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
Miscellaneous Expenses: Miscellaneous expenses such as equipment transportation, insurance, site security, and contingency funds should also be considered when estimating upfront installation costs for Level 3 chargers.
Government Incentives and Rebates
| Type of Incentive | Description | Eligibility | Example Programs |
| Federal Tax Credits | Tax credits provided by the U.S. federal government for the installation of electric vehicle charging infrastructure, including Level 3 chargers. | Businesses, municipalities, and nonprofits | Alternative Fuel Infrastructure Tax Credit |
| State and Local Incentives | Incentives, grants, and rebates offered by states and local governments to support the deployment of electric vehicle charging infrastructure. | Businesses, municipalities, and nonprofits | California Electric Vehicle Infrastructure Project, New York Charge- Ready NY, Texas Emissions Reduction Plan |
| Utility Programs | Incentives and rebates offered by electric utilities to support the installation of electric vehicle charging infrastructure, including Level 3 chargers. | Businesses, municipalities, and nonprofits | Southern California Edison Charge Ready Program, Pacific Gas and Electric EV Charge Network |
| Environmental Programs | Funding opportunities and support provided by environmental programs and initiatives to promote the deployment of electric vehicle charging infrastructure. | Businesses, municipalities, nonprofits | Clean Cities Coalition Programs, Volkswagen Electrify America Program |
| Federal Grant Programs | Grant programs administered by federal agencies to support electric vehicle charging infrastructure projects, including Level 3 chargers. | Businesses, municipalities, nonprofits | U.S. Department of Transportation FAST Act, DOE Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy |
| Public-Private Partnerships | Collaborative efforts between government agencies, private companies, and other stakehwillolders to support the deployment of electric vehicle charging infrastructure. | Businesses, municipalities, and nonprofits | Electrify America, EVgo’s partnership with GM and Nissan |
| Workplace Charging Incentive Programs | Incentive programs specifically for workplace charging infrastructure, including Level 3 chargers, to encourage employers to install charging stations. | Employers, businesses, and municipalities | California Electric Vehicle Charging Incentive Programs, Massachusetts MOR-EV Program |
| Public Charging Incentive Programs | Incentive programs for public charging infrastructure, including Level 3 chargers, to support the deployment of charging stations in public locations. | Businesses, municipalities, and nonprofits | California Electric Vehicle Charging Incentive Programs, New Jersey It Pay$ to Plug In Program |
Operational and Maintenance Costs
| Cost Category | Description |
| Electricity Costs | Expenses related to the consumption of electricity during charging sessions, including utility rates, demand charges, and time-of-use pricing structures. |
| Network Connectivity Fees | Fees for network connectivity services used for remote monitoring, software updates, and payment processing, including subscription fees and data usage charges. |
| Maintenance and Repairs | Costs for routine maintenance, repairs, and troubleshooting to keep charging equipment in proper working condition, including inspections, cleaning, and component replacements. |
| Software Updates and Upgrades | Costs for purchasing, installing, and implementing software updates and upgrades to address bugs, vulnerabilities, and add new features to charging equipment. |
| Monitoring and Management | Expenses related to monitoring charging station performance, collecting usage data, and managing operational aspects of charging infrastructure. |
| Customer Support and Service | Costs associated with providing customer support and service to users, including personnel, software, and infrastructure for assisting with inquiries and technical support. |
| Insurance and Liability Coverage | Expenses for insurance policies to protect against risks, liabilities, and unforeseen events associated with operating charging infrastructure. |
| Regulatory Compliance and Permitting | Costs for maintaining compliance with regulations, standards, and permitting requirements for charging infrastructure, including permit fees and compliance assessments. |
Return on Investment Analysis
Identify Investment Costs: Start by identifying all upfront investment costs associated with the installation of Level 3 chargers. This includes costs such as equipment purchase, site preparation, electrical infrastructure upgrades, permitting fees, and other related expenses.
Estimate Operational Costs: Estimate ongoing operational costs incurred to operate and maintain Level 3 chargers over their lifespan. This includes expenses such as electricity costs, network connectivity fees, maintenance and repairs, software updates, monitoring and management, customer support, insurance, and regulatory compliance.
Forecast Revenue Streams: Forecast revenue streams generated from Level 3 charger operations, including income from charging fees, membership subscriptions, network service fees, and other revenue sources. Consider factors such as charging session rates, utilization rates, peak demand periods, and potential growth in electric vehicle adoption.
Calculate Net Present Value (NPV): Calculate the net present value of the investment by discounting future cash flows (revenue minus expenses) back to their present value using an appropriate discount rate. NPV analysis helps assess the profitability of the investment by accounting for the time value of money and considering the opportunity cost of capital.
Determine Payback Period: Determine the payback period, which is the time it takes for the investment to recoup its initial costs through generated revenue. A shorter payback period indicates a quicker return on investment and higher profitability.
Evaluate Return on Investment (ROI): Calculate the return on investment ratio by dividing the net profit (revenue minus expenses) by the total investment cost and expressing the result as a percentage. A higher ROI indicates a more favorable investment opportunity with greater potential for profitability.
Consider Sensitivity Analysis: Conduct sensitivity analysis to assess the impact of changes in key variables, such as charging fees, electricity prices, utilization rates, and discount rates, on the investment’s financial performance. Sensitivity analysis helps identify potential risks and uncertainties and evaluate the robustness of the investment under different scenarios.
Compare Alternative Scenarios: Compare the ROI, NPV, payback period, and other financial metrics of Level 3 charger installations with alternative investment options or scenarios, such as different charging models, equipment configurations, or site locations. This helps prioritize investments and identify the most cost-effective and profitable opportunities.
Evaluate Non-Financial Benefits: Consider non-financial benefits and factors such as environmental impact, social value, brand reputation, and community benefits associated with Level 3 charger installations. While these benefits may not directly contribute to financial returns, they can enhance the overall value proposition and justify investment decisions from a broader perspective.
Financing Options for Businesses and Municipalities
Grants and Incentives: Government agencies, utility companies, and non-profit organizations often offer grants and incentives to support EV charging infrastructure development. These funds can help offset the upfront costs of purchasing and installing Level 3 chargers.
Rebates: Some regions provide rebates or financial incentives for businesses and municipalities that install EV chargers. These rebates can cover a portion of the installation costs, making it more affordable to implement charging infrastructure.
Tax Credits: Businesses and municipalities may be eligible for tax credits for EV charging infrastructure investments. Federal, state, or local tax credits can help reduce the overall cost of installing Level 3 chargers and provide financial relief.
Low-Interest Loans: Financial institutions, government agencies, and utility companies may offer low-interest loans or financing programs specifically for EV charging infrastructure projects. These loans can provide access to capital at favorable terms, making it easier to finance charging installations.
Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs): Collaborating with private sector partners can help spread the financial burden of EV charging infrastructure projects. Public-private partnerships can involve joint investments, revenue-sharing agreements, or other arrangements to fund and operate charging stations.
Leasing and Financing Plans: Equipment leasing or financing arrangements allow businesses and municipalities to spread the cost of EV charging infrastructure over time. Leasing agreements may include maintenance and service provisions, simplifying the ownership and operation of charging stations.
Energy Service Agreements (ESAs): Energy service agreements allow businesses and municipalities to procure EV charging infrastructure as a service, paying for usage or performance rather than upfront capital costs. ESAs can provide flexibility and cost certainty for charging infrastructure deployments.
Crowdfunding and Community Financing: Crowdfunding platforms and community financing initiatives enable businesses and municipalities to raise funds from local residents, businesses, or EV enthusiasts to support charging infrastructure projects. These grassroots efforts can supplement other financing sources and build community support for EV adoption.
Utility Programs: Some utility companies offer special programs or incentives for businesses and municipalities to install EV charging infrastructure. These programs may include grants, rebates, or discounted electricity rates for charging state risks
Choosing a Location

Traffic and Accessibility for EV Drivers
| Factor | Description |
| Traffic Volume | Assess the average traffic volume and vehicle flow at potential Level 3 charger locations to ensure adequate demand for charging services. |
| Proximity to Highways | Consider the proximity of Level 3 chargers to major highways and arterial roads to cater to long-distance travelers and commuters in need of fast charging options. |
| Accessibility | Evaluate the accessibility of Level 3 charger locations, considering factors such as ease of access from main roads, availability of parking, and proximity to amenities and services. |
| Signage and Wayfinding | Ensure clear signage and wayfinding information to guide EV drivers to Level 3 charger locations, including directional signs, symbols, and digital navigation instructions. |
| Visibility | Ensure high visibility of Level 3 chargers from main roads and nearby intersections to attract attention and facilitate easy identification by EV drivers. |
| Safety and Security | Prioritize Level 3 charger locations in safe and well-lit areas with adequate security measures to enhance user safety and prevent vandalism or theft. |
| Amenities | Consider the availability of amenities and facilities near Level 3 charger locations, such as restrooms, food establishments, and shopping centers, to enhance user convenience. |
| Accessibility Standards | Ensure compliance with accessibility standards and regulations to accommodate individuals with disabilities, including accessible parking spaces and pathways. |
| Real-Time Availability | Implement real-time availability monitoring and reservation systems to provide EV drivers with up-to-date information on charger availability and reduce wait times. |
| Integration with Navigation Systems | Integrate Level 3 charger locations with popular navigation systems and EV charging apps to facilitate route planning and seamless navigation for EV drivers. |
Proximity to Electrical Infrastructure
| Factor | Description |
| Distance to Electrical Grid | Assess the distance of potential Level 3 charger locations from the nearest electrical grid infrastructure to determine the feasibility of connecting to the grid and the potential costs associated with electrical infrastructure upgrades. |
| Availability of Three-Phase Power | Ensure the availability of three-phase power supply at Level 3 charger locations, as most Level 3 chargers require three-phase electricity for operation. Evaluate the capacity and reliability of the three-phase power supply to meet the high-power demands of Level 3 charging equipment. |
| Electrical Capacity | Evaluate the electrical capacity of the existing infrastructure to support Level 3 chargers, considering factors such as load capacity, voltage levels, and transformer capacity. Determine if upgrades or reinforcements to the electrical system are necessary to accommodate the additional load from charging equipment. |
| Distribution Equipment | Identify the distribution equipment, such as transformers, switchgear, and distribution lines, required to connect Level 3 chargers to the electrical grid. Assess the condition, capacity, and compatibility of distribution equipment to ensure reliable and safe operation of charging infrastructure. |
| Grid Stability | Consider the stability and reliability of the electrical grid in the area surrounding Level 3 charger locations. Evaluate factors such as voltage stability, frequency regulation, and grid congestion to mitigate risks of power fluctuations or outages that could impact charging operations. |
| Backup Power Options | Explore backup power options, such as battery storage systems or backup generators, to provide redundancy and ensure continuity of charging services during grid outages or emergencies. Evaluate the feasibility and cost-effectiveness of implementing backup power solutions based on site-specific requirements. |
| Electrical Code Compliance | Ensure compliance with electrical codes, standards, and regulations when connecting Level 3 chargers to the electrical infrastructure. Adhere to safety guidelines and requirements specified by national, regional, and local authorities to minimize risks and ensure safe operation of charging equipment. |
| Coordination with Utility | Coordinate with electric utility providers to assess the feasibility of connecting Level 3 chargers to the electrical grid. Collaborate with utility representatives to evaluate technical requirements, obtain permits, and coordinate grid interconnection processes to ensure seamless integration with the electrical infrastructure. |
| Future Expansion Potential | Consider the future expansion potential of electrical infrastructure to accommodate additional Level 3 chargers and increased charging demand. Evaluate scalability and flexibility to support future growth and expansion of charging infrastructure based on evolving market trends and user demand. |
Visibility and Signage
| Factor | Description |
| Placement | Strategically place Level 3 chargers in highly visible locations, such as near entrances, main thoroughfares, or parking lot entrances, to maximize visibility and attract attention from EV drivers. |
| Clear Signage | Install clear and prominent signage indicating the presence of Level 3 chargers, including directional signs, informational signage, and symbols, to guide EV drivers to charging locations efficiently. |
| Iconography | Use universally recognizable icons and symbols to denote charging stations, such as the “EV charging” symbol or the international standard for electric vehicle charging station signage (ISO 7000). |
| Illumination | Ensure signage and charging stations are well-illuminated, particularly in low-light conditions or during nighttime hours, to enhance visibility and facilitate easy identification by EV drivers. |
| Branding and Messaging | Incorporate branding elements and messaging on signage to promote awareness of charging infrastructure, highlight sponsorships or partnerships, and convey information about charging services and amenities. |
| Consistency | Maintain consistency in signage design, placement, and messaging across different charging locations to facilitate familiarity and ease of navigation for EV drivers, regardless of location or operator. |
| Digital Navigation Tools | Integrate Level 3 charger locations with digital navigation tools, such as GPS systems, mobile apps, and mapping platforms, to provide real-time directions and navigation assistance to EV drivers seeking charging stations. |
| On-Site Information | Provide on-site information, such as charging rates, availability, and operational hours, on signage or display panels near Level 3 chargers to keep EV drivers informed and help them make informed decisions about charging. |
| Accessibility | Ensure signage and charging infrastructure comply with accessibility standards and regulations, including requirements for accessible parking spaces, signage height, and readability for individuals with disabilities. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Adhere to regulatory requirements and standards for signage, including local zoning regulations, building codes, and signage ordinances, to ensure compliance and avoid potential fines or penalties. |
Impact on Local Grid and Energy Demand
| Factor | Description |
| Peak Demand | Evaluate the potential impact of Level 3 chargers on peak electricity demand, particularly during periods of high charging activity or simultaneous charging sessions. Assess the capacity of the local grid to meet peak demand and mitigate risks of grid overloads or voltage fluctuations. |
| Load Management | Implement load management strategies to optimize the distribution of charging loads and minimize peak demand on the grid. Utilize smart charging technologies, demand response programs, and time-of-use pricing incentives to encourage off-peak charging and balance electricity demand across different times of the day. |
| Grid Upgrades | Assess the need for grid upgrades or reinforcements to accommodate additional load from Level 3 chargers. Identify areas with inadequate grid capacity and prioritize investments in infrastructure upgrades to support charging infrastructure deployment and meet future demand growth. |
| Distributed Energy Resources | Explore opportunities for integrating distributed energy resources, such as solar PV systems, energy storage, and demand-side management solutions, to support Level 3 charger deployment and mitigate grid impacts. Coordinate with local utilities and stakeholders to leverage distributed energy resources effectively. |
| Grid Stability | Monitor grid stability and reliability to ensure that the integration of Level 3 chargers does not compromise grid performance or reliability. Implement measures to enhance voltage regulation, frequency control, and grid resilience to manage the impact of charging infrastructure on grid operations. |
| Energy Demand Forecasting | Utilize energy demand forecasting models and tools to project future electricity demand from Level 3 chargers and assess the capacity requirements of the local grid. Incorporate factors such as EV adoption rates, charging behaviors, and infrastructure expansion plans into demand projections. |
| Grid Interconnection Standards | Adhere to grid interconnection standards and regulations specified by utility providers and regulatory authorities when connecting Level 3 chargers to the electrical grid. Ensure compliance with safety, reliability, and technical requirements to facilitate seamless integration with the local grid infrastructure. |
| Demand-side Side programs | Participate in demand-side management programs offered by electric utilities to optimize charging schedules, reduce peak demand, and enhance grid stability. Leverage incentives, rebates, and tariff structures to incentivize EV drivers to participate in demand response initiatives and support grid reliability. |
| Infrastructure Planning | Collaborate with utilities, grid operators, and regulatory agencies to develop long-term infrastructure planning strategies that account for the impact of electric vehicle charging infrastructure on the local grid. Coordinate charging infrastructure deployment with grid modernization efforts and infrastructure investments. |
Zoning and Local Approval
| Factor | Description |
| Zoning Regulations | Familiarize with local zoning regulations, ordinances, and land use policies that govern the installation and operation of Level 3 chargers. Determine permitted land use categories, zoning districts, and applicable zoning codes for charging infrastructure. |
| Permitting Requirements | Identify permitting requirements for Level 3 charger installations, including building permits, electrical permits, environmental permits, and any other permits required by local authorities or regulatory agencies. Ensure compliance with permit application processes and timelines. |
| Land Use Compatibility | Assess the compatibility of Level 3 charger installations with existing land uses and development plans in the area. Consider factors such as land zoning, property setbacks, land use designations, and compatibility with adjacent land uses. |
| Environmental Impact Assessment | Conduct environmental impact assessments, if required, to evaluate potential environmental impacts of Level 3 charger installations. Assess impacts on air quality, noise levels, water resources, wildlife habitats, and other environmental factors. |
| Public Consultation | Engage in public consultation and community outreach initiatives to inform stakeholders, address concerns, and gather feedback on proposed Level 3 charger installations. Hold public meetings, workshops, or informational sessions to facilitate dialogue and participation. |
| Aesthetic Considerations | Consider aesthetic considerations and design guidelines for Level 3 charger installations to ensure compatibility with surrounding architecture, landscapes, and visual character of the area. Incorporate architectural features, landscaping, or screening measures as needed. |
| Historic Preservation | Evaluate potential impacts on historic preservation areas or cultural heritage sites near proposed Level 3 charger locations. Ensure compliance with historic preservation regulations and coordinate with local historic preservation authorities as necessary. |
| ADA Compliance | Ensure compliance with accessibility standards outlined in the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) for Level 3 charger installations. Provide accessible parking spaces, pathways, signage, and amenities to accommodate individuals with disabilities. |
| Traffic and Parking | Assess the impact of Level 3 charger installations on traffic patterns, parking availability, and circulation within the vicinity. Consider measures to mitigate traffic congestion, optimize parking layout, and ensure safe and efficient access to charging stations. |
| Community Benefits | Identify potential community benefits associated with Level 3 charger installations, such as improved air quality, reduced greenhouse gas emissions, economic development, and enhanced public infrastructure. Highlight community benefits in project proposals and outreach efforts. |
Installation Process
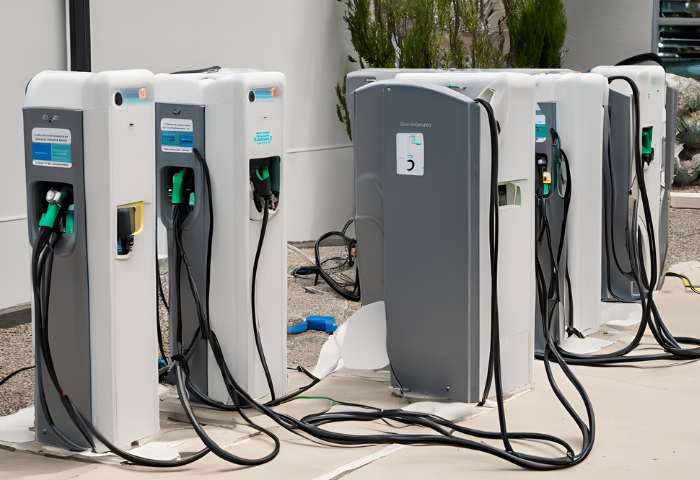

Selecting a Qualified Installer
| Factor | Description |
| Experience and Expertise | Evaluate the installer’s experience and expertise in installing Level 3 chargers and other electric vehicle charging infrastructure. Look for installers with a proven track record and experience working with similar projects and equipment. |
| Certification and Credentials | Check the installer’s certifications, credentials, and licenses to ensure they meet industry standards and regulatory requirements for electrical work and charging infrastructure installation. Look for certifications from recognized organizations or manufacturers. |
| Manufacturer Partnerships | Consider installers with partnerships or certifications from Level 3 charger manufacturers. Installer partnerships with manufacturers may indicate specialized training, technical support, and access to quality equipment and parts for installations. |
| References and Portfolio | Request references, testimonials, and examples of past projects from the installer. Review their portfolio to assess the quality of their workmanship, adherence to timelines, and customer satisfaction. Contact references to inquire about their experience with the installer. |
| Compliance with Standards | Ensure the installer complies with relevant standards, codes, and regulations governing electrical installations, safety, and accessibility. Verify that the installer follows industry best practices and adheres to local building codes and regulations. |
| Warranty and Support | Inquire about the warranty coverage and support services offered by the installer. Ensure that the installer provides warranty coverage for equipment and workmanship and offers responsive support for troubleshooting, maintenance, and repairs. |
| Cost and Pricing | Compare cost estimates and pricing proposals from multiple installers. Evaluate the scope of work, materials, labor costs, and any additional fees or charges included in the pricing. Consider the overall value, not just the upfront cost, when selecting an installer. |
| Communication and Collaboration | Assess the installer’s communication skills and ability to collaborate effectively with stakeholders. Choose an installer who communicates clearly, listens to your needs, and provides timely updates throughout the installation process. |
| Safety Practices | Prioritize installers with a strong commitment to safety practices and protocols. Ensure that the installer follows safety guidelines, uses appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), and conducts installations in compliance with safety regulations. |
| Project Management | Evaluate the installer’s project management capabilities and ability to coordinate with other stakeholders, such as electric utilities, permitting agencies, and property owners. Choose an installer who can effectively manage the installation process from start to finish. |
Timeline From Planning to Operation
| Stage | Description | Duration |
| Needs Assessment | Conduct a needs assessment to identify locations with high demand for Level 3 chargers. | 1-2 weeks |
| Site Selection | Identify potential sites for Level 3 charger installations based on needs assessment and criteria. | 2-4 weeks |
| Feasibility Study | Conduct a feasibility study to evaluate site suitability, electrical infrastructure, and costs. | 4-6 weeks |
| Permitting and Approvals | Obtain necessary permits and approvals from local authorities, utilities, and property owners. | 4–12 weeks (varies) |
| Installer Selection | Select a qualified installer based on experience, expertise, certifications, and references. | 2-4 weeks |
| Equipment Procurement | Purchase Level 3 charging equipment and associated hardware, accessories, and software. | 4-8 weeks (lead time) |
| Electrical Infrastructure Upgrades | Upgrade electrical infrastructure to support Level 3 chargers, if necessary. | 4-8 weeks (varies) |
| Installation | Install Level 3 chargers, including electrical connections, mounting hardware, and signage. | 2-4 weeks (per site) |
| Testing and Commissioning | Conduct testing and commissioning of charging equipment to ensure proper functionality and safety. | 1-2 weeks (per site) |
| Network Integration | Integrate Level 3 chargers into charging network platforms, software systems, and payment systems. | 2-4 weeks (per site) |
| Training and Education | Provide training and education to staff, operators, and users on how to use and maintain charging equipment. | 1-2 weeks (varies) |
| Soft Opening and Marketing | Conduct a soft opening to introduce Level 3 chargers to the public and begin marketing and promotion efforts. | 2-4 weeks (varies) |
| Full Operation | Transition Level 3 chargers to full operation, including regular monitoring, maintenance, and user support. | Ongoing |
Installation Best Practices
Site Selection: Choose locations with high visibility, accessibility, and adequate electrical infrastructure to support Level 3 chargers. Consider factors such as traffic flow, parking availability, proximity to highways, and amenities.
Electrical Assessment: Conduct a thorough assessment of the existing electrical infrastructure to ensure it can accommodate the power demands of Level 3 chargers. Upgrade electrical systems as needed to meet voltage and capacity requirements.
Compliance with Regulations: Adhere to local building codes, zoning regulations, and permitting requirements when installing Level 3 chargers. Obtain necessary permits and approvals from local authorities and utilities.
Safety Precautions: Follow safety guidelines and protocols during installation to prevent electrical hazards, fires, and accidents. Use proper personal protective equipment (PPE) and follow manufacturer recommendations for equipment installation.
Installer Qualifications: Hire qualified installers with experience and expertise in installing Level 3 chargers. Ensure installers have the necessary certifications, licenses, and training to perform electrical work safely and effectively.
Proper Equipment Installation: Install Level 3 charging equipment according to manufacturer specifications and industry standards. Follow installation guidelines for mounting, wiring, grounding, and connecting charging stations to the electrical grid.
Quality Assurance: Conduct quality assurance checks and inspections throughout the installation process to ensure workmanship and equipment quality. Verify connections, test functionality, and address any issues promptly to prevent future problems.
Accessibility and ADA Compliance: Design charging stations and surrounding infrastructure to comply with accessibility standards outlined in the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA). Provide accessible parking spaces, pathways, signage, and amenities for individuals with disabilities.
Network Integration: Integrate Level 3 chargers into charging network platforms, software systems, and payment systems for seamless operation and management. Ensure compatibility with existing infrastructure and user interfaces.
Training and Education: Provide training and education to staff, operators, and users on how to use and maintain Level 3 chargers safely and effectively. Offer instructional materials, user manuals, and support resources to enhance user experience and satisfaction.
Regular Maintenance: Establish a maintenance schedule and protocol for routine inspections, cleaning, and servicing of Level 3 chargers. Monitor equipment performance, address issues promptly, and conduct preventive maintenance to minimize downtime and ensure optimal operation.
Emergency Response Plan: Develop an emergency response plan outlining procedures for handling emergencies, such as equipment malfunctions, power outages, or safety incidents. Train staff on emergency protocols and provide contact information for reporting issues and seeking assistance.
Troubleshooting Common Installation Issues
| Common Installation Issue | Troubleshooting Steps |
| Electrical Connection Problems | – Verify that electrical connections are secure, properly terminated, and free from corrosion.- Check wiring connections, terminals, and junction boxes for signs of damage or loose connections. Test voltage and continuity to ensure electrical integrity. |
| Power Supply Issues | – That the power supply meets the voltage and current requirements specified by the charger manufacturer. – Check for voltage drops, circuit overloads, or phase imbalances in the electrical system. – Consider upgrading electrical infrastructure if necessary. |
| Grounding Problems | – Ensure grounding connections are installed correctly and comply with electrical codes and regulations. – Test grounding continuity and resistance to verify proper grounding. Address any issues with ground connections promptly to prevent electrical hazards. |
| Equipment Compatibility | – Verify that charging equipment is compatible with the electrical system’s voltage, phase, and capacity. – Check for compatibility issues with communication protocols, connectors, and software interfaces. – Ensure equipment firmware and software are up-to-date. |
| Communication Errors | – Verify network connectivity and communication pathways between charging equipment, backend systems, and user interfaces. – Check network settings, IP configurations, and firewall settings for compatibility and accessibility. – Ensure communication protocols and interfaces are configured correctly. |
| Environmental Factors | – Inspect charging equipment for signs of environmental damage, corrosion, or contamination.- Install weatherproof enclosures, protective covers, or environmental controls to shield equipment from adverse conditions. – Monitor environmental conditions and implement mitigation measures as needed. |
| User Interface Errors | – Test user interfaces, touchscreens, or keypads for responsiveness and accuracy. – Check for software glitches, firmware bugs, or configuration errors affecting user interaction. – Provide user training and support resources to address interface issues. |
| Safety System Faults | – Test safety systems, sensors, and protective devices for proper operation and responsiveness. – Verify that safety mechanisms are not being triggered by false alarms or environmental conditions. – Address any safety system faults promptly to ensure safe charging operations. |
| Network Congestion or Interference | – Monitor network performance and bandwidth usage to identify congestion or interference issues. – Optimize network settings, protocols, or configurations to improve data transmission reliability and speed. – Consider upgrading network infrastructure if needed. |
| Equipment Malfunctions | – Conduct diagnostic tests, firmware updates, or component replacements as needed to address equipment malfunctions. – Follow manufacturer guidelines and warranty procedures for troubleshooting and resolving equipment issues. – Document equipment malfunctions and resolution steps for future reference. |
Post-installation Inspection and Testing
| Inspection and Testing Component | Description |
| Visual Inspection | Inspect physical condition, mounting, electrical connections, signage, and accessibility features. |
| Electrical Testing | Verify wiring, grounding, voltage levels, GFCIs, protective devices, and insulation resistance. |
| Functionality Testing | Test charging equipment for communication, authentication, charging protocols, and session performance. |
| Safety Checks | Test safety features, emergency shutdown mechanisms, thermal protections, and temperature management. |
| Network Integration | Test network connectivity, data transmission, remote monitoring, diagnostics, and interoperability. |
| Compliance Verification | Confirm compliance with regulatory standards, codes, ADA requirements, and local zoning regulations. |
| Documentation and Reporting | Document inspection findings, test results, generate reports, and maintain records for future reference. |
| User Training and Education | Provide user training, demonstrate charging procedures, safety protocols, and distribute instructional materials. |
| Follow-Up Maintenance | Schedule follow-up maintenance, address identified issues, and monitor equipment performance and user feedback. |
Operational Management
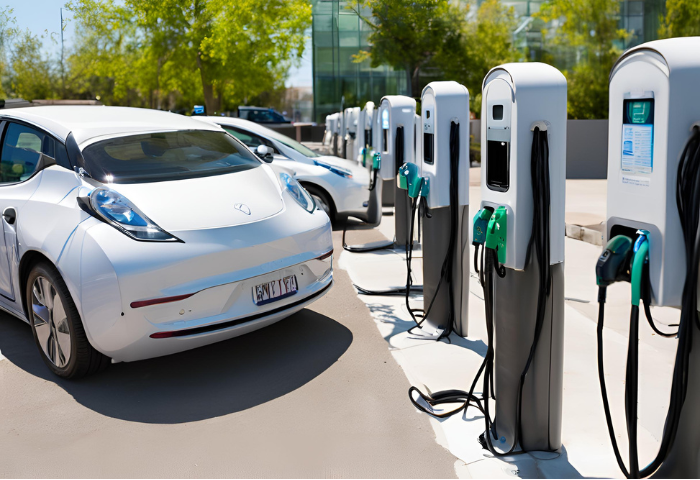

Software for Charger Management and Payment Processing
| Software Feature | Description |
| Charger Management | Comprehensive management of charging stations, including monitoring, scheduling, maintenance, and firmware updates. |
| Payment Processing | Support for various payment methods, such as credit/debit cards, mobile payments, RFID cards, subscriptions, and loyalty programs. |
| Billing and Invoicing | Automated billing, invoicing, and revenue tracking for charging sessions, subscriptions, and membership plans. |
| User Authentication | Secure user authentication methods, include account creation, login credentials, PIN codes, QR codes, and RFID/NFC card authentication. |
| Reservation System | Reservation system for users to book charging sessions in advance, manage reservations, and receive notifications. |
| Real-Time Monitoring | Real-time monitoring of charging station status, availability, usage data, energy consumption, and performance metrics. |
| Remote Diagnostics | Remote diagnostics and troubleshooting capabilities to identify and resolve issues without on-site intervention. |
| Network Integration | Integration with charging networks, roaming platforms, and third-party services for seamless interoperability and roaming agreements. |
| Reporting and Analytics | Comprehensive reporting and analytics tools to track usage trends, revenue generation, energy consumption, and performance metrics. |
| Mobile App Integration | Mobile app integration allows users to locate, navigate, reserve, and pay for charging sessions, as well as access account information and charging history. |
| Customer Support | Customer support features, include helpdesk ticketing systems, chat support, knowledge base, and FAQs for user assistance and issue resolution. |
| Scalability and Flexibility | Scalable and flexible software architecture to accommodate future growth, additional features, and integration with emerging technologies. |
| Customization Options | Customization options for branding, user interface design, pricing structures, and billing configurations to meet specific business requirements. |
| Compliance and Security | Compliance with data protection regulations (e.g., GDPR), security standards (e.g., PCI DSS), and interoperability protocols (e.g., OCPP) for secure and reliable operation. |
Customer Service for EV Drivers
Accessible Support Channels:
Offer multiple channels for EV drivers to reach customer support, including phone, email, chat, and in-person assistance.
Provide clear instructions on how to access customer support through mobile apps, signage, and website portals.
Responsive Assistance:
Respond promptly to inquiries, requests for assistance, and technical issues reported by EV drivers.
Establish service level agreements (SLAs) for response times and ensure timely resolution of customer queries and concerns.
User-Friendly Interfaces:
Design intuitive user interfaces for mobile apps, kiosks, and online portals to facilitate easy navigation and access to support resources.
Provide step-by-step guidance on how to use charging stations, initiate charging sessions, and troubleshoot common issues.
24/7 Availability:
Offer round-the-clock customer support services to accommodate EV drivers charging at any time of the day or night.
Partner with third-party call centers or support teams to extend coverage and ensure availability during peak hours.
Technical Assistance:
Provide technical assistance and troubleshooting support for EV drivers encountering charging-related issues, such as connectivity problems, payment processing errors, or equipment malfunctions.
Train customer support staff to diagnose and resolve technical issues efficiently and effectively.
Educational Resources:
Develop educational materials, FAQs, tutorials, and user guides to educate EV drivers about charging procedures, best practices, and safety tips.
Offer training sessions or webinars for new EV owners to learn about charging infrastructure and EV operation.
Community Engagement:
Foster a sense of community among EV drivers by organizing events, meetups, and online forums for sharing experiences, tips, and feedback.
Encourage EV drivers to provide input on charging infrastructure improvements and service enhancements.
Feedback Mechanisms:
Solicit feedback from EV drivers through surveys, satisfaction ratings, and suggestion forms to gather insights into their charging experiences.
Use feedback to identify areas for improvement, prioritize service enhancements, and address customer concerns proactively.
Issue Resolution Process:
Establish a structured process for handling customer complaints, escalations, and service disruptions.
Implement procedures for tracking and documenting customer issues, escalating unresolved issues to higher tiers of support, and providing timely updates to customers.
Continuous Improvement:
Regularly review customer feedback, performance metrics, and service quality indicators to identify opportunities for service improvement.
Invest in staff training, technology upgrades, and process optimizations to enhance the overall customer service experience.
Regular Maintenance and Upkeep
| Maintenance Component | Description |
| Scheduled Inspections | Conduct visual inspections of physical components, electrical connections, signage, and environmental conditions. |
| Preventive Maintenance | Implement a schedule for cleaning, lubrication, calibration, and component replacement based on manufacturer recommendations. |
| Electrical Testing | Perform regular electrical testing to ensure proper wiring, grounding, voltage levels, and insulation resistance. |
| Software Updates | Stay up-to-date with software updates, firmware upgrades, and security patches provided by the charger manufacturer. |
| Battery Health Monitoring | Monitor battery health, charging cycles, state of charge, temperature, and voltage levels to optimize performance and prolong battery life. |
| Cooling System Maintenance | Maintain cooling systems, fans, and ventilation mechanisms to prevent overheating during high-power charging. |
| Network Connectivity | Monitor network connectivity and communication pathways between charging equipment, backend systems, and user interfaces. |
| Emergency Preparedness | Develop an emergency response plan outlining procedures for handling equipment malfunctions, power outages, or safety incidents. |
| Documentation and Recordkeeping | Maintain comprehensive records of maintenance activities, inspections, repairs, and service history for each charging station. |
| User Feedback and Monitoring | Solicit feedback from EV drivers, monitor user complaints, and service requests to identify recurring issues and prioritize maintenance efforts. |
| Vendor Support and Partnerships | Establish partnerships with equipment vendors and service providers to access technical support, spare parts, and specialized expertise. |
Upgrading and Adding More Chargers
| Task | Description |
| Needs Assessment | Conduct assessments to identify high-demand areas, expansion opportunities, and optimal charger placement. |
| Capacity Planning | Evaluate current capacity, utilization rates, and peak demand to determine the required number of additional chargers. |
| Infrastructure Assessment | Assess the existing electrical infrastructure, grid capacity, and site suitability for accommodating more chargers. |
| Equipment Selection | Choose Level 3 charging equipment based on compatibility, charging speed, connector types, and network integration. |
| Permitting and Approvals | Obtain necessary permits and approvals from local authorities, utilities, and regulatory agencies for new installations. |
| Installation and Integration | Install new chargers and integrate them into existing infrastructure, network systems, and backend platforms. |
| Network Expansion | Expand charging network coverage by adding new locations, creating charging corridors, and strategically placing chargers. |
| User Education and Promotion | Educate EV drivers about the availability of new chargers, benefits of Level 3 charging, and expanded charging options. |
| Monitoring and Optimization | Monitor performance, usage patterns, and customer feedback to optimize charger placement, pricing strategies, and operations. |
| Maintenance and Support | Establish maintenance protocols, service agreements, and support channels to ensure ongoing reliability and customer satisfaction. |
Managing Demand and Energy Consumption
| Strategy | Description |
| Load Management | Implement strategies to distribute charging demand evenly throughout the day, such as smart scheduling algorithms and off-peak incentives. |
| Peak Load Shaving | Reduce the impact of charging on peak demand periods by prioritizing charging during off-peak hours and using demand response programs. |
| Dynamic Pricing | Adjust charging rates based on real-time grid conditions and electricity supply/demand fluctuations, encouraging charging during periods of low demand. |
| Grid Integration and Flexibility | Integrate charging infrastructure with grid management systems, energy storage, and renewable energy sources to enhance flexibility and support grid balancing initiatives. |
| Charging Infrastructure Optimization | Optimize charger placement, capacity, and distribution to minimize grid impacts and maximize utilization, using predictive analytics and machine learning algorithms. |
| User Engagement and Education | Educate EV drivers about energy conservation practices, dynamic pricing, and incentives for load management, and provide real-time feedback and incentives to encourage sustainable charging behavior. |
| Regulatory Compliance and Standards | Ensure compliance with regulatory requirements, industry standards, and grid codes related to demand management and energy consumption, collaborating with utilities and regulatory agencies to develop best practices for promoting grid stability. |
Technical Specifications of Level 3 Chargers
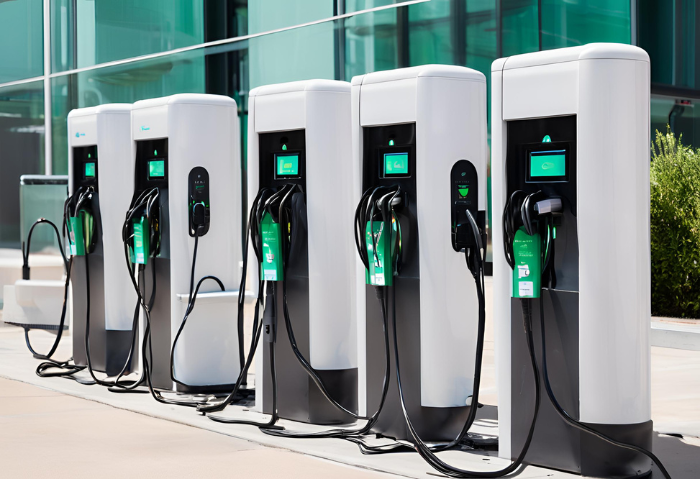

Power Output and Charging Speeds
| Power Output (kW) | Charging Speed | Example |
| 50 kW | Medium/fast charging | Nissan Leaf, Chevrolet Bolt |
| 100 kW | Fast charging | Audi e-Tron, Jaguar I-PACE |
| 150 kW | Ultra-fast charging | Porsche Taycan, Tesla Model 3, Hyundai Ioniq 5 |
| 200+ kW | Ultra-rapid charging | Tesla Model S Plaid, Lucid Air, Rivian R1T/R1S |
Connector Types and Compatibility
| Connector Type | Description | Compatibility |
| CHAdeMO | Japanese and some European automakers are the main users of this CHAdeMO Association-developed technology. | Compatible with CHAdeMO-enabled EVs, such as Nissan LEAF, Mitsubishi i-MiEV, and Kia Soul EV. |
| CCS (Combo) | SAE International developed the Combined Charging System, which combines AC and DC charging into one plug. | Compatible with CCS-enabled EVs, including many European and American models like Audi e-Tron, BMW i3, and Chevrolet Bolt. |
| Tesla Supercharger | Tesla vehicles are the main users of its proprietary fast-charging system. | Compatible with Tesla vehicles using a Tesla-specific connector. Other EVs require an adapter. |
Network Connectivity Requirements
| Connectivity Requirement | Description |
| Internet Connection | Required for remote monitoring, management, and software updates of charging stations. |
| Cellular or Wi-Fi | Options for internet connectivity, with cellular being more common due to its wider coverage and reliability. |
| Ethernet | Wired Ethernet connection for faster and more reliable data transmission, often used for backhaul connectivity. |
| VPN (Virtual Private Network) | Secure network tunneling technology for remote access, data encryption, and protection against cybersecurity threats. |
| OCPP (Open Charge Point Protocol) | Standardized communication protocol for interoperability between charging stations and network management systems. |
Standards and Protocols for Communication
| Standard/Protocol | Description |
| OCPP (Open Charge Point Protocol) | Open standard for communication between charging stations and central management systems, enabling interoperability and remote management. |
| ISO 15118 | is the communication protocol for Plug and Charge functionality, allowing EVs to authenticate and authorize charging sessions without additional user input. |
| CCS (Combined Charging System) | Communication protocol for CCS charging connectors, integrating AC and DC charging, and supporting bidirectional communication between vehicles and chargers. |
| CHAdeMO | Communication protocol for CHAdeMO charging connectors, enabling high-power DC fast charging, primarily used by Japanese and some European automakers. |
By understanding Level 3 EV chargers and their kW ratings, you can make informed decisions about your EV charging needs. With faster charging times and a growing infrastructure, Level 3 chargers are poised to play a vital role in the future of electric mobility, paving the way for a cleaner and more sustainable transportation landscape.

Henry Michael is a leading expert in EV charging station research, specializing in innovative solutions for electric vehicle infrastructure. With a passion for sustainability and technological advancement, he is dedicated to advancing the accessibility and efficiency of EV charging worldwide.






